license: cc-by-nc-4.0
language:
- en
tags:
- chemistry
nach0
Multimodal Natural and Chemical Languages Foundation Model
📃 Paper • ⏬ Base nach0 • ⏬ Large nach0
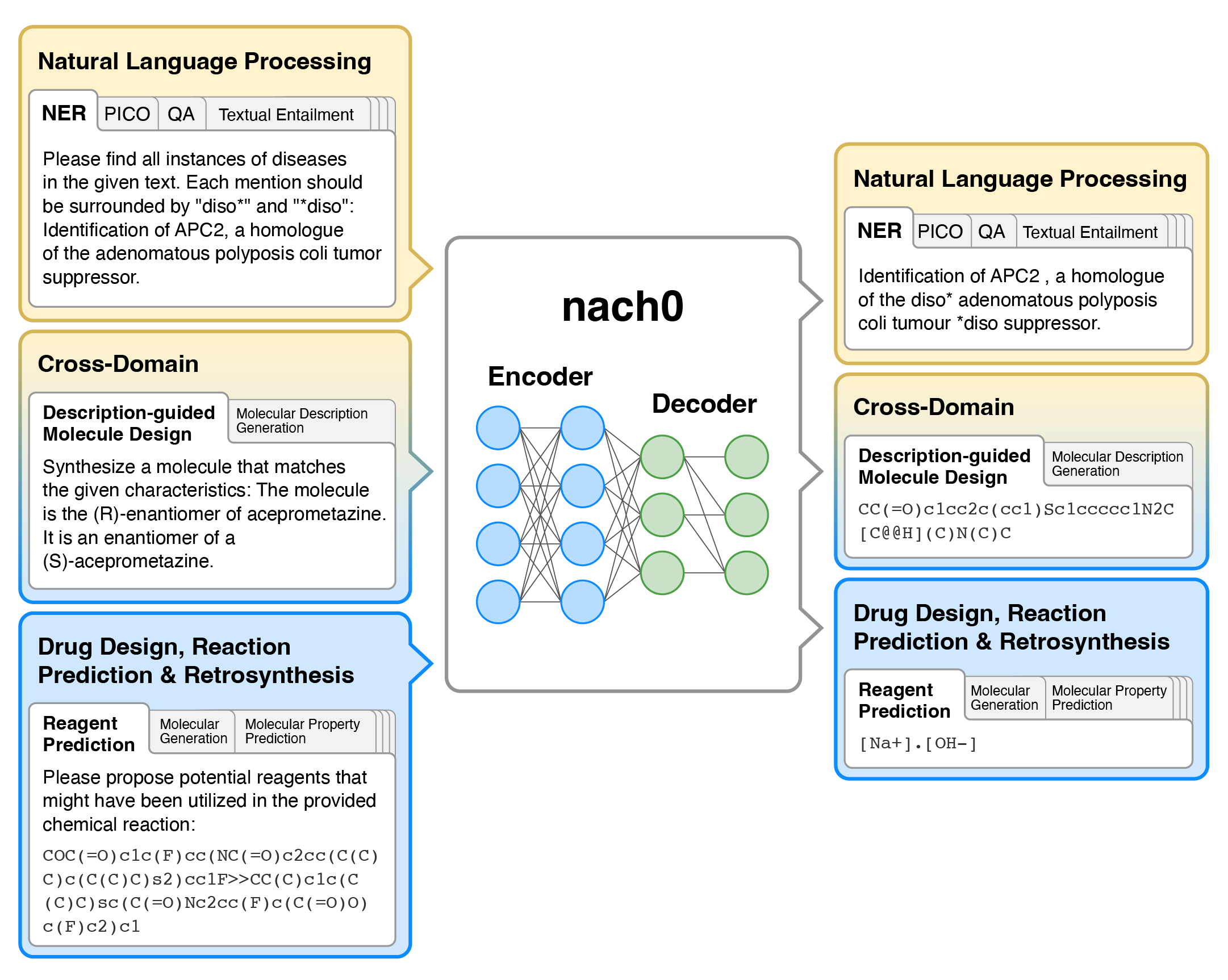
Overview
nach0 is a multi-domain and multi-task encoder-decoder LLM pre-trained on unlabeled text from scientific literature, patents, and molecule strings to incorporate a range of chemical and linguistic knowledge.
We employed instruction tuning, where specific task-related instructions are utilized to fine-tune nach0 for the final set of tasks. To train nach0 effectively, we leverage the NeMo framework, enabling efficient parallel optimization of both base and large model versions.
Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on single-domain and cross-domain tasks. Furthermore, it can generate high-quality outputs in molecular and textual formats, showcasing its effectiveness in multi-domain setups.
Tasks
Datasets used for training and evaluation. Colour represents the type of tasks. Yellow and blue datasets are single-domain, typically requiring regression/classification losses or generation in the target domain (natural language or SMILES strings). Gradients from yellow to blue represent cross-domain generation tasks that require natural language input and SMILES output, or vise versa.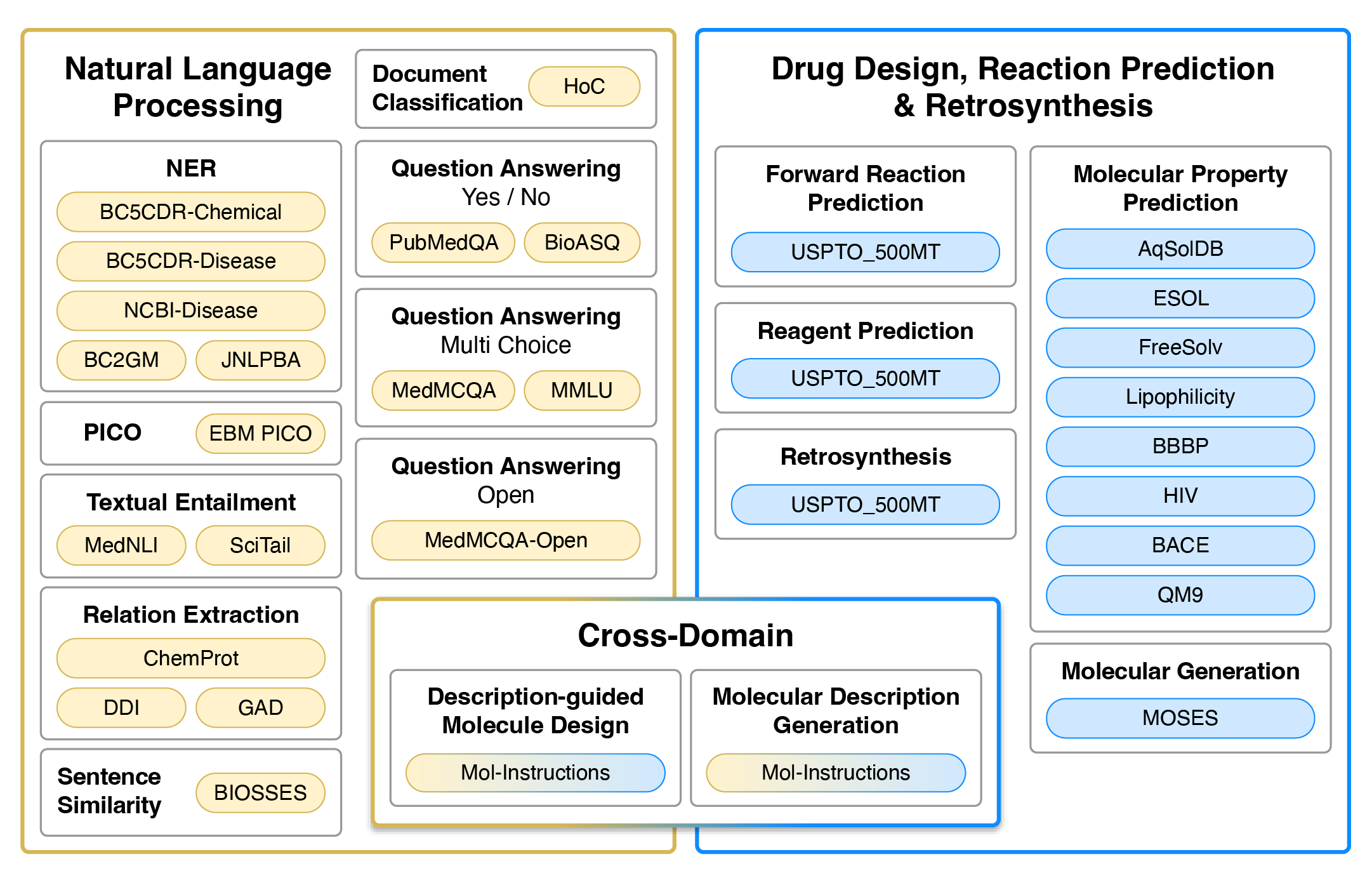
Model Usage Guide
To use model for the inference follow the steps bellow:
- Preprocess the input by replacing the atom tokens with special tokens.
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
import re
from rdkit.Chem import MolFromSmiles
import string
from rdkit import RDLogger
RDLogger.DisableLog('rdApp.*')
atoms_tokens = ['Ag','Al','As','Au','B','Ba','Bi','Br','C','Ca',
'Cd','Cl','Co','Cr','Cs','Cu','F','Fe','Ga','Gd',
'Ge','H','Hg','I','In','K','Li','M','Mg','Mn',
'Mo','N','Na','O','P','Pt','Ru','S','Sb','Sc',
'Se','Si','Sn','V','W','Z','Zn','c','e','n','o','p','s']
atoms_tokens = sorted(atoms_tokens, key=lambda s: len(s), reverse=True)
SMI_REGEX_PATTERN = r"(\[|\]|\(|\)|\.|=|#|-|\+|\\|\/|:|~|@|\?|>>?|\*|\$|\%[0-9]{2}|[0-9]|" + \
'|'.join(atoms_tokens) + ")"
regex = re.compile(SMI_REGEX_PATTERN)
def clean_output_sequence(output_sequence):
return output_sequence.replace('</s>', '').replace('<sm_', '').replace(' sm_', '').replace('>', '').strip()
def add_special_symbols(text):
output = []
for word in text.split():
tokens = [token for token in regex.findall(word)]
if len(tokens) > 4 and (word == ''.join(tokens)) and MolFromSmiles(word):
output.append(''.join(['<sm_'+t+'>' for t in tokens]))
else:
output.append(word)
return ' '.join(output)
PROMPT = """Given the following reactants and reagents, please provide a possible product.
CCN(CC)CC.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C.CN(C)C=O.Cl.NC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1N.O.O=C(O)CCCCCNC(=O)C=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C12.OC1=CC=CC2=C1N=NN2.[Cl-].[Na+]"""
PROMPT = add_special_symbols(PROMPT)
- Load the model checkoint
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained('insilicomedicine/nach0_base')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('insilicomedicine/nach0_base')
- Generate response to prompt and replace special tokens with corresponding atom tokens
input_text_ids = tokenizer(PROMPT, padding="longest", max_length=512, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
generated_text_ids = model.generate(**input_text_ids, do_sample=True, top_k=100, top_p=0.95, max_length=512)
generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_text_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
generated_text = clean_output_sequence(generated_text)
# NC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1NC(=O)CCCCCNC(=O)C=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C12
References
If you use our repository, please cite the following related paper:@inproceedings{....
}