licenses
sequencelengths 1
3
| version
stringclasses 677
values | tree_hash
stringlengths 40
40
| path
stringclasses 1
value | type
stringclasses 2
values | size
stringlengths 2
8
| text
stringlengths 25
67.1M
| package_name
stringlengths 2
41
| repo
stringlengths 33
86
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 572 | using SimpleSolvers
using Documenter
makedocs(;
modules=[SimpleSolvers],
authors="Michael Kraus",
repo="https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl/blob/{commit}{path}#L{line}",
sitename="SimpleSolvers.jl",
format=Documenter.HTML(;
prettyurls=get(ENV, "CI", "false") == "true",
canonical="https://JuliaGNI.github.io/SimpleSolvers.jl",
assets=String[],
),
pages=[
"Home" => "index.md",
],
)
deploydocs(;
repo = "github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl",
devurl = "latest",
devbranch = "main",
)
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 3724 | module SimpleSolvers
using Distances
using ForwardDiff
using LinearAlgebra
using Printf
import Base.minimum
import Base.Callable
import GeometricBase: AbstractSolver, SolverMethod
import GeometricBase: value
include("utils.jl")
export solve!
export config, result, state, status
export algorithm, objective
export solution, minimizer, minimum
export SolverMethod
export BracketingMethod
export LinearMethod, DirectMethod, IterativeMethod
export NonlinearMethod, PicardMethod, LinesearchMethod
export NewtonMethod, Newton, DFP, BFGS
include("base/methods.jl")
export UnivariateObjective,
TemporaryUnivariateObjective,
MultivariateObjective
export value, value!, value!!,
derivative, derivative!, derivative!!,
gradient, gradient!, gradient!!,
hessian, hessian!, hessian!!,
d_calls, f_calls, g_calls, h_calls
include("base/objectives.jl")
export Options
include("base/options.jl")
export Gradient,
GradientAutodiff,
GradientFiniteDifferences,
GradientFunction
export compute_gradient,
compute_gradient!,
compute_gradient_ad!,
compute_gradient_fd!
export check_gradient,
print_gradient
include("base/gradient.jl")
export Hessian,
HessianAutodiff,
HessianFunction
export compute_hessian,
compute_hessian!,
compute_hessian_ad!
export check_hessian,
print_hessian
include("base/hessian.jl")
export Jacobian,
JacobianAutodiff,
JacobianFiniteDifferences,
JacobianFunction
export compute_jacobian!,
compute_jacobian_ad!,
compute_jacobian_fd!
export check_jacobian,
print_jacobian
include("base/jacobian.jl")
export LinearSolver, LUSolver, LUSolverLAPACK,
factorize!
include("linear/linear_solvers.jl")
include("linear/lu_solver.jl")
include("linear/lu_solver_lapack.jl")
export bracket_minimum
include("bracketing/bracketing.jl")
include("bracketing/bracket_minimum.jl")
export Linesearch, Static
export Backtracking, backtracking,
Bisection, bisection,
Quadratic, quadratic
include("linesearch/linesearch.jl")
include("linesearch/static.jl")
include("linesearch/backtracking.jl")
include("linesearch/bisection.jl")
include("linesearch/quadratic.jl")
export NonlinearSolver, NonlinearSolverException,
AbstractNewtonSolver, NLsolveNewton, NewtonSolver, QuasiNewtonSolver,
residual_initial!, residual_absolute!, residual_relative!,
assess_convergence, assess_convergence!,
print_status, check_solver_status,
get_solver_status, get_solver_status!,
solve!
include("nonlinear/nonlinear_solver_status.jl")
include("nonlinear/nonlinear_solver.jl")
include("nonlinear/abstract_newton_solver.jl")
include("nonlinear/newton_solver.jl")
include("nonlinear/quasi_newton_solver.jl")
include("nonlinear/nlsolve_newton.jl")
export Optimizer,
OptimizationAlgorithm, isaOptimizationAlgorithm,
NewtonOptimizer,
BFGSOptimizer,
DFPOptimizer,
HessianBFGS,
HessianDFP
include("optimization/optimizer_status.jl")
include("optimization/optimizer_result.jl")
include("optimization/optimizer.jl")
include("optimization/hessian_bfgs.jl")
include("optimization/hessian_dfp.jl")
include("optimization/newton_optimizer.jl")
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1035 |
macro define(name, definition)
quote
macro $(esc(name))()
esc($(Expr(:quote, definition)))
end
end
end
alloc_x(x::Number) = typeof(x)(NaN)
alloc_f(x::Number) = real(typeof(x))(NaN)
alloc_d(x::Number) = typeof(x)(NaN)
alloc_x(x::AbstractArray) = eltype(x)(NaN) .* x
alloc_f(x::AbstractArray) = real(eltype(x))(NaN)
alloc_g(x::AbstractArray) = eltype(x)(NaN) .* x
alloc_h(x::AbstractArray) = eltype(x)(NaN) .* x*x'
alloc_j(x::AbstractArray, f::AbstractArray) = eltype(x)(NaN) .* vec(f) .* vec(x)'
function L2norm(x)
local l2::eltype(x) = 0
for xᵢ in x
l2 += xᵢ^2
end
l2
end
function l2norm(x)
sqrt(L2norm(x))
end
function maxnorm(x)
local r² = zero(eltype(x))
@inbounds for xᵢ in x
r² = max(r², xᵢ^2)
end
sqrt(r²)
end
function outer!(O, x, y)
@assert axes(O,1) == axes(x,1)
@assert axes(O,2) == axes(y,1)
@inbounds @simd for i in axes(O, 1)
for j in axes(O, 2)
O[i,j] = x[i] * y[j]
end
end
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 3340 |
const DEFAULT_GRADIENT_ϵ = 8sqrt(eps())
abstract type Gradient{T} end
compute_gradient!(g::AbstractVector, x::AbstractVector, grad::Gradient) = grad(g,x)
function compute_gradient(x, grad::Gradient)
g = alloc_g(x)
grad(g,x)
return g
end
function check_gradient(g::AbstractVector)
println("norm(Gradient): ", norm(g))
println("minimum(|Gradient|): ", minimum(abs.(g)))
println("maximum(|Gradient|): ", maximum(abs.(g)))
println()
end
function print_gradient(g::AbstractVector)
display(g)
println()
end
struct GradientFunction{T, ∇T} <: Gradient{T}
∇F!::∇T
end
function (grad::GradientFunction{T})(g::AbstractVector{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
grad.∇F!(g, x)
end
struct GradientAutodiff{T, FT, ∇T <: ForwardDiff.GradientConfig} <: Gradient{T}
F::FT
∇config::∇T
function GradientAutodiff(F::FT, x::VT) where {T, FT, VT <: AbstractVector{T}}
∇config = ForwardDiff.GradientConfig(F, x)
new{T, FT, typeof(∇config)}(F, ∇config)
end
end
function GradientAutodiff{T}(F::FT, nx::Int) where {T, FT}
GradientAutodiff(F, zeros(T, nx))
end
function (grad::GradientAutodiff{T})(g::AbstractVector{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
ForwardDiff.gradient!(g, grad.F, x, grad.∇config)
end
function compute_gradient_ad!(g::AbstractVector{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}, F) where {T}
grad = GradientAutodiff{T}(F, length(x))
grad(g,x)
end
struct GradientFiniteDifferences{T, FT} <: Gradient{T}
ϵ::T
F::FT
e::Vector{T}
tx::Vector{T}
end
function GradientFiniteDifferences{T}(F::FT, nx::Int; ϵ=DEFAULT_GRADIENT_ϵ) where {T, FT}
e = zeros(T, nx)
tx = zeros(T, nx)
GradientFiniteDifferences{T,FT}(ϵ, F, e, tx)
end
function (grad::GradientFiniteDifferences{T})(g::AbstractVector{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
local ϵⱼ::T
for j in eachindex(x,g)
ϵⱼ = grad.ϵ * x[j] + grad.ϵ
fill!(grad.e, 0)
grad.e[j] = 1
grad.tx .= x .- ϵⱼ .* grad.e
f1 = grad.F(grad.tx)
grad.tx .= x .+ ϵⱼ .* grad.e
f2 = grad.F(grad.tx)
g[j] = (f2 - f1)/(2ϵⱼ)
end
end
function compute_gradient_fd!(g::AbstractVector{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}, F::FT; kwargs...) where {T, FT}
grad = GradientFiniteDifferences{T}(F, length(x); kwargs...)
grad(g,x)
end
function Gradient{T}(ForG, nx::Int; mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :forward, kwargs...) where {T}
if mode == :autodiff
if diff_type == :forward
Gparams = GradientAutodiff{T}(ForG, nx)
else
Gparams = GradientFiniteDifferences{T}(ForG, nx; kwargs...)
end
else
Gparams = GradientFunction{T, typeof(ForG)}(ForG)
end
return Gparams
end
Gradient{T}(∇F!, F, nx::Int; kwargs...) where {T} = Gradient{T}(∇F!, nx; mode = :user, kwargs...)
Gradient{T}(∇F!::Nothing, F, nx::Int; kwargs...) where {T} = Gradient{T}(F, nx; mode = :autodiff, kwargs...)
Gradient(∇F!, F, x::AbstractVector{T}; kwargs...) where {T} = Gradient{T}(∇F!, F, length(x); kwargs...)
Gradient(F, x::AbstractVector{T}; kwargs...) where {T} = Gradient{T}(F, length(x); kwargs...)
function compute_gradient!(g::AbstractVector{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}, ForG; kwargs...) where {T}
grad = Gradient{T}(ForG, length(x); kwargs...)
grad(g,x)
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 3055 |
abstract type Hessian{T} end
initialize!(::Hessian) = nothing
compute_hessian!(h::AbstractMatrix, x::AbstractVector, hessian::Hessian) = hessian(h,x)
function compute_hessian(x, hessian::Hessian)
h = alloc_h(x)
hessian(h,x)
return h
end
function check_hessian(H::AbstractMatrix)
println("Condition Number of Hessian: ", cond(H))
println("Determinant of Hessian: ", det(H))
println("minimum(|Hessian|): ", minimum(abs.(H)))
println("maximum(|Hessian|): ", maximum(abs.(H)))
println()
end
function print_hessian(H::AbstractMatrix)
display(H)
println()
end
struct HessianFunction{T, HT} <: Hessian{T}
H!::HT
end
HessianFunction(H!::HT, ::AbstractVector{T}) where {T,HT} = HessianFunction{T,HT}(H!)
function (hes::HessianFunction{T})(H::AbstractMatrix{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
hes.H!(H, x)
end
struct HessianAutodiff{T, FT, HT <: AbstractMatrix, CT <: ForwardDiff.HessianConfig} <: Hessian{T}
F::FT
H::HT
Hconfig::CT
function HessianAutodiff{T}(F::FT, H::HT, Hconfig::CT) where {T, FT, HT, CT}
new{T, FT, HT, CT}(F, H, Hconfig)
end
end
function HessianAutodiff(F::Callable, x::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
Hconfig = ForwardDiff.HessianConfig(F, x)
HessianAutodiff{T}(F, alloc_h(x), Hconfig)
end
HessianAutodiff(F::MultivariateObjective, x) = HessianAutodiff(F.F, x)
HessianAutodiff{T}(F, nx::Int) where {T} = HessianAutodiff{T}(F, zeros(T, nx))
function (hes::HessianAutodiff{T})(H::AbstractMatrix{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
ForwardDiff.hessian!(H, hes.F, x, hes.Hconfig)
end
function (hes::HessianAutodiff{T})(x::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
ForwardDiff.hessian!(hes.H, hes.F, x, hes.Hconfig)
end
function compute_hessian_ad!(H::AbstractMatrix{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}, F::FT) where {T, FT}
hes = HessianAutodiff(F, x)
hes(H,x)
end
initialize!(H::HessianAutodiff, x) = H(x)
update!(H::HessianAutodiff, x::AbstractVector) = H(x)
Base.inv(H::HessianAutodiff) = inv(H.H)
Base.:\(H::HessianAutodiff, b) = H.H \ b
LinearAlgebra.ldiv!(x, H::HessianAutodiff, b) = x .= H \ b
# LinearAlgebra.ldiv!(x, H::HessianAD, b) = LinearAlgebra.ldiv!(x, H.H, b)
# TODO: Make this work!
function Hessian(ForH, x::AbstractVector{T}; mode = :autodiff, kwargs...) where {T}
if mode == :autodiff
Hparams = HessianAutodiff(ForH, x)
else
Hparams = HessianFunction(ForH, x)
end
return Hparams
end
Hessian(H!, F, x::AbstractVector; kwargs...) = Hessian(H!, nx; mode = :user, kwargs...)
Hessian(H!::Nothing, F, x::AbstractVector; kwargs...) = Hessian(F, nx; mode = :autodiff, kwargs...)
Hessian{T}(ForH, nx::Int; kwargs...) where {T} = Hessian(ForH, zeros(T,nx); kwargs...)
Hessian{T}(H!, F, nx::Int; kwargs...) where {T} = Hessian(H!, nx; kwargs...)
Hessian{T}(H!::Nothing, F, nx::Int; kwargs...) where {T} = Hessian(F, nx; kwargs...)
function compute_hessian!(h::AbstractMatrix, x::AbstractVector, ForH; kwargs...)
hessian = Hessian(ForH, x; kwargs...)
hessian(h,x)
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 3595 |
const DEFAULT_JACOBIAN_ϵ = 8sqrt(eps())
abstract type Jacobian{T} end
compute_jacobian!(j::AbstractMatrix, x::AbstractVector, jacobian::Jacobian) = jacobian(j,x)
function check_jacobian(J::AbstractMatrix)
println("Condition Number of Jacobian: ", cond(J))
println("Determinant of Jacobian: ", det(J))
println("minimum(|Jacobian|): ", minimum(abs.(J)))
println("maximum(|Jacobian|): ", maximum(abs.(J)))
println()
end
function print_jacobian(J::AbstractMatrix)
display(J)
println()
end
struct JacobianFunction{T} <: Jacobian{T}
end
JacobianFunction(::AbstractArray{T}) where {T} = JacobianFunction{T}()
function (::JacobianFunction{T})(j::AbstractMatrix{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}, jac::Callable) where {T}
jac(j, x)
end
struct JacobianAutodiff{T, JT <: ForwardDiff.JacobianConfig, YT <: AbstractVector{T}} <: Jacobian{T}
Jconfig::JT
ty::YT
function JacobianAutodiff{T}(Jconfig::JT, y::YT) where {T, JT, YT}
new{T, JT, YT}(Jconfig, y)
end
end
function JacobianAutodiff(x::AbstractVector{T}, y::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
Jconfig = ForwardDiff.JacobianConfig(nothing, y, x)
JacobianAutodiff{T}(Jconfig, zero(y))
end
function JacobianAutodiff{T}(nx::Int, ny::Int) where {T}
tx = zeros(T, nx)
ty = zeros(T, ny)
JacobianAutodiff(tx, ty)
end
JacobianAutodiff{T}(n) where {T} = JacobianAutodiff{T}(n, n)
function (jac::JacobianAutodiff{T})(J::AbstractMatrix{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}, f::Callable) where {T}
ForwardDiff.jacobian!(J, f, jac.ty, x, jac.Jconfig)
end
struct JacobianFiniteDifferences{T} <: Jacobian{T}
ϵ::T
f1::Vector{T}
f2::Vector{T}
e::Vector{T}
tx::Vector{T}
end
function JacobianFiniteDifferences{T}(nx::Int, ny::Int; ϵ=DEFAULT_JACOBIAN_ϵ) where {T}
f1 = zeros(T, ny)
f2 = zeros(T, ny)
e = zeros(T, nx)
tx = zeros(T, nx)
JacobianFiniteDifferences{T}(ϵ, f1, f2, e, tx)
end
JacobianFiniteDifferences{T}(n; kwargs...) where {T} = JacobianFiniteDifferences{T}(n, n; kwargs...)
function (jac::JacobianFiniteDifferences{T})(J::AbstractMatrix{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}, f::Callable) where {T}
local ϵⱼ::T
for j in eachindex(x)
ϵⱼ = jac.ϵ * x[j] + jac.ϵ
fill!(jac.e, 0)
jac.e[j] = 1
jac.tx .= x .- ϵⱼ .* jac.e
f(jac.f1, jac.tx)
jac.tx .= x .+ ϵⱼ .* jac.e
f(jac.f2, jac.tx)
for i in eachindex(x)
J[i,j] = (jac.f2[i] - jac.f1[i]) / (2ϵⱼ)
end
end
end
function Jacobian{T}(nx::Int, ny::Int; mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :forward, kwargs...) where {T}
if mode == :autodiff
if diff_type == :forward
Jparams = JacobianAutodiff{T}(nx, ny)
else
Jparams = JacobianFiniteDifferences{T}(nx, ny; kwargs...)
end
else
Jparams = JacobianFunction{T}()
end
return Jparams
end
Jacobian{T}(n::Int; kwargs...) where {T} = Jacobian{T}(n, n; kwargs...)
Jacobian{T}(J!::Callable, nx, ny; kwargs...) where {T} = Jacobian{T}(nx, ny; mode = :user, kwargs...)
Jacobian{T}(J!::Union{Nothing,Missing}, nx, ny; kwargs...) where {T} = Jacobian{T}(nx, ny; mode = :autodiff, kwargs...)
Jacobian{T}(J!, n; kwargs...) where {T} = Jacobian{T}(J!, n, n; kwargs...)
function compute_jacobian!(j::AbstractMatrix{T}, x::AbstractVector{T}, ForJ::Callable; kwargs...) where {T}
jacobian = Jacobian{T}(size(j,1), size(j,2); kwargs...)
jacobian(j,x,ForJ)
end
function compute_jacobian!(j::AbstractMatrix, x::AbstractVector, ForJ::Callable, jacobian::Jacobian)
jacobian(j,x,ForJ)
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1134 |
abstract type BracketingMethod <: SolverMethod end
abstract type LinearMethod <: SolverMethod end
abstract type NonlinearMethod <: SolverMethod end
abstract type DirectMethod <: LinearMethod end
abstract type IterativeMethod <: LinearMethod end
abstract type NewtonMethod <: NonlinearMethod end
abstract type PicardMethod <: NonlinearMethod end
abstract type LinesearchMethod <: NonlinearMethod end
struct Newton <: NewtonMethod end
struct DFP <: NewtonMethod end
struct BFGS <: NewtonMethod end
struct Backtracking <: LinesearchMethod end
struct Bisection <: LinesearchMethod end
struct Quadratic <: LinesearchMethod end
struct Static{T} <: LinesearchMethod
alpha::T
Static(alpha::T = 1.0) where {T} = new{T}(alpha)
end
Base.show(io::IO, alg::Newton) = print(io, "Newton")
Base.show(io::IO, alg::DFP) = print(io, "DFP")
Base.show(io::IO, alg::BFGS) = print(io, "BFGS")
Base.show(io::IO, alg::Static) = print(io, "Static")
Base.show(io::IO, alg::Backtracking) = print(io, "Backtracking")
Base.show(io::IO, alg::Bisection) = print(io, "Bisection")
Base.show(io::IO, alg::Quadratic) = print(io, "Quadratic Polynomial")
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 6671 |
abstract type AbstractObjective end
abstract type AbstractUnivariateObjective <: AbstractObjective end
clear!(::Function) = nothing
mutable struct UnivariateObjective{TF, TD, Tf, Td, Tx} <: AbstractUnivariateObjective
F::TF # objective
D::TD # derivative of objective
f::Tf # cache for f output
d::Td # cache for d output
x_f::Tx # x used to evaluate F (stored in f)
x_d::Tx # x used to evaluate D (stored in d)
f_calls::Int
d_calls::Int
end
function UnivariateObjective(F::Callable, D::Callable, x::Number;
f::Real = alloc_f(x),
d::Number = alloc_d(x))
UnivariateObjective(F, D, f, d, alloc_x(x), alloc_x(x), 0, 0)
end
function UnivariateObjective(F::Callable, x::Number; kwargs...)
D = (x) -> ForwardDiff.derivative(F,x)
UnivariateObjective(F, D, x; kwargs...)
end
UnivariateObjective(F::Callable, D::Nothing, x::Number; kwargs...) = UnivariateObjective(F, x; kwargs...)
"""
Evaluates the objective value at `x`.
Returns `f(x)`, but does *not* store the value in `obj.F`
"""
function value(obj::UnivariateObjective, x)
obj.f_calls += 1
return obj.F(x)
end
"Get the most recently evaluated objective value of `obj`."
value(obj::UnivariateObjective) = obj.f
"""
Force (re-)evaluation of the objective value at `x`.
Returns `f(x)` and stores the value in `obj.F`
"""
function value!!(obj::UnivariateObjective, x)
obj.x_f = x
obj.f = obj.F(x)
obj.f_calls += 1
value(obj)
end
"""
Evaluates the objective value at `x`.
Returns `f(x)` and stores the value in `obj.F`
"""
function value!(obj::UnivariateObjective, x)
if x != obj.x_f
value!!(obj, x)
end
value(obj)
end
"""
Evaluates the derivative of the objective at `x`.
Returns `f'(x)`, but does *not* store the derivative in `obj.D`
"""
function derivative(obj::UnivariateObjective, x)
obj.d_calls += 1
return obj.D(x)
end
"Get the most recently evaluated derivative of the objective of `obj`."
derivative(obj::UnivariateObjective) = obj.d
"""
Force (re-)evaluation of the derivative of the objective at `x`.
Returns `f'(x)` and stores the derivative in `obj.D`
"""
function derivative!!(obj::UnivariateObjective, x)
obj.x_d = x
obj.d = obj.D(x)
obj.d_calls += 1
derivative(obj)
end
"""
Evaluates the derivative of the objective at `x`.
Returns `f'(x)` and stores the derivative in `obj.D`
"""
function derivative!(obj::UnivariateObjective, x)
if x != obj.x_d
derivative!!(obj, x)
end
derivative(obj)
end
(obj::UnivariateObjective)(x) = value!(obj, x)
function _clear_f!(obj::UnivariateObjective)
obj.f_calls = 0
obj.f = typeof(obj.f)(NaN)
obj.x_f = typeof(obj.x_f)(NaN)
nothing
end
function _clear_d!(obj::UnivariateObjective)
obj.d_calls = 0
obj.d = eltype(obj.d)(NaN)
obj.x_d = eltype(obj.x_d)(NaN)
nothing
end
function clear!(obj::UnivariateObjective)
_clear_f!(obj)
_clear_d!(obj)
nothing
end
struct TemporaryUnivariateObjective{TF, TD} <: AbstractUnivariateObjective
F::TF # objective
D::TD # derivative of objective
end
TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, d, x) = TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, d)
value(obj::TemporaryUnivariateObjective, x) = obj.F(x)
derivative(obj::TemporaryUnivariateObjective, x) = obj.D(x)
value!(obj::TemporaryUnivariateObjective, x) = value(obj, x)
derivative!(obj::TemporaryUnivariateObjective, x) = derivative(obj, x)
(obj::TemporaryUnivariateObjective)(x) = value(obj, x)
mutable struct MultivariateObjective{TF, TG, Tf, Tg, Tx} <: AbstractObjective
F::TF
G::TG
f::Tf
g::Tg
x_f::Tx
x_g::Tx
f_calls::Int
g_calls::Int
end
function MultivariateObjective(F, G,
x::AbstractArray;
f::Real = alloc_f(x),
g::AbstractArray = alloc_g(x))
MultivariateObjective(F, G, f, g, alloc_x(x), alloc_x(x), 0, 0)
end
function MultivariateObjective(F, x::AbstractArray; kwargs...)
G = GradientAutodiff(F, x)
MultivariateObjective(F, G, x; kwargs...)
end
MultivariateObjective(F, G::Nothing, x::AbstractArray; kwargs...) = MultivariateObjective(F, x; kwargs...)
"""
Evaluates the objective value at `x`.
Returns `f(x)`, but does *not* store the value in `obj.f`
"""
function value(obj::MultivariateObjective, x)
obj.f_calls += 1
return obj.F(x)
end
"Get the most recently evaluated objective value of `obj`."
value(obj::MultivariateObjective) = obj.f
"""
Force (re-)evaluation of the objective at `x`.
Returns `f(x)` and stores the value in `obj.f`
"""
function value!!(obj::MultivariateObjective, x)
copyto!(obj.x_f, x)
obj.f = obj.F(x)
obj.f_calls += 1
value(obj)
end
"""
Evaluates the objective at `x`.
Returns `f(x)` and stores the value in `obj.f`
"""
function value!(obj::MultivariateObjective, x)
if x != obj.x_f
value!!(obj, x)
end
value(obj)
end
"Get the most recently evaluated gradient of `obj`."
gradient(obj::MultivariateObjective) = obj.g
"""
Evaluates the gradient at `x`.
This does *not* update `obj.g` or `obj.x_g`.
"""
function gradient(obj::MultivariateObjective, x)
ḡ = copy(obj.g)
obj.G(ḡ, x)
obj.g_calls += 1
return ḡ
end
"""
Force (re-)evaluation of the gradient at `x`.
Returns ∇f(x) and stores the value in `obj.g`.
"""
function gradient!!(obj::MultivariateObjective, x)
copyto!(obj.x_g, x)
obj.G(obj.g, x)
obj.g_calls += 1
gradient(obj)
end
"""
Evaluates the gradient at `x`.
Returns ∇f(x) and stores the value in `obj.g`.
"""
function gradient!(obj::MultivariateObjective, x)
if x != obj.x_g
gradient!!(obj, x)
end
gradient(obj)
end
(obj::MultivariateObjective)(x) = value!(obj, x)
function _clear_f!(obj::MultivariateObjective)
obj.f_calls = 0
obj.f = typeof(obj.f)(NaN)
obj.x_f .= eltype(obj.x_f)(NaN)
nothing
end
function _clear_g!(obj::MultivariateObjective)
obj.g_calls = 0
obj.g .= eltype(obj.g)(NaN)
obj.x_g .= eltype(obj.x_g)(NaN)
nothing
end
function clear!(obj::MultivariateObjective)
_clear_f!(obj)
_clear_g!(obj)
nothing
end
f_calls(o::AbstractObjective) = error("f_calls is not implemented for $(summary(o)).")
f_calls(o::UnivariateObjective) = o.f_calls
f_calls(o::MultivariateObjective) = o.f_calls
d_calls(o::AbstractObjective) = error("d_calls is not implemented for $(summary(o)).")
d_calls(o::UnivariateObjective) = o.d_calls
g_calls(o::AbstractObjective) = error("g_calls is not implemented for $(summary(o)).")
g_calls(o::MultivariateObjective) = o.g_calls
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 4353 | """
Configurable options with defaults (values 0 and NaN indicate unlimited):
```
x_abstol::Real = -Inf,
x_reltol::Real = 2eps(),
f_abstol::Real = 1e-50,
f_reltol::Real = 2eps(),
f_mindec::Real = 1e-4,
g_restol::Real = sqrt(eps()),
x_abstol_break::Real = Inf,
x_reltol_break::Real = Inf,
f_abstol_break::Real = Inf,
f_reltol_break::Real = Inf,
g_restol_break::Real = Inf,
f_calls_limit::Int = 0,
g_calls_limit::Int = 0,
h_calls_limit::Int = 0,
allow_f_increases::Bool = true,
min_iterations::Int = 0,
max_iterations::Int = 1_000,
warn_iterations::Int = max_iterations,
show_trace::Bool = false,
store_trace::Bool = false,
extended_trace::Bool = false,
show_every::Int = 1,
verbosity::Int = 1
```
"""
struct Options{T}
x_abstol::T
x_reltol::T
x_suctol::T
f_abstol::T
f_reltol::T
f_suctol::T
f_mindec::T
g_restol::T
x_abstol_break::T
x_reltol_break::T
f_abstol_break::T
f_reltol_break::T
g_restol_break::T
f_calls_limit::Int
g_calls_limit::Int
h_calls_limit::Int
allow_f_increases::Bool
min_iterations::Int
max_iterations::Int
warn_iterations::Int
show_trace::Bool
store_trace::Bool
extended_trace::Bool
show_every::Int
verbosity::Int
end
function Options(;
x_tol = nothing,
f_tol = nothing,
g_tol = nothing,
x_abstol::Real = -Inf,
x_reltol::Real = 2eps(),
x_suctol::Real = 2eps(),
f_abstol::Real = 1e-50,
f_reltol::Real = 2eps(),
f_suctol::Real = 2eps(),
f_mindec::Real = 1e-4,
g_restol::Real = sqrt(eps()),
x_abstol_break::Real = Inf,
x_reltol_break::Real = Inf,
f_abstol_break::Real = Inf,
f_reltol_break::Real = Inf,
g_restol_break::Real = Inf,
f_calls_limit::Int = 0,
g_calls_limit::Int = 0,
h_calls_limit::Int = 0,
allow_f_increases::Bool = true,
min_iterations::Int = 0,
max_iterations::Int = 1_000,
warn_iterations::Int = max_iterations,
show_trace::Bool = false,
store_trace::Bool = false,
extended_trace::Bool = false,
show_every::Int = 1,
verbosity::Int = 1)
show_every = show_every > 0 ? show_every : 1
if extended_trace
show_trace = true
end
if !(x_tol === nothing)
x_abstol = x_tol
end
if !(g_tol === nothing)
g_restol = g_tol
end
if !(f_tol === nothing)
f_reltol = f_tol
end
Options(promote(x_abstol, x_reltol, x_suctol, f_abstol, f_reltol, f_suctol, f_mindec, g_restol,
x_abstol_break, x_reltol_break, f_abstol_break, f_reltol_break, g_restol_break)...,
f_calls_limit, g_calls_limit, h_calls_limit, allow_f_increases, min_iterations, max_iterations, warn_iterations,
show_trace, store_trace, extended_trace, show_every, verbosity)
end
function Options(T, options)
floatopts = (
options.x_abstol,
options.x_reltol,
options.x_suctol,
options.f_abstol,
options.f_reltol,
options.f_suctol,
options.f_mindec,
options.g_restol,
options.x_abstol_break,
options.x_reltol_break,
options.f_abstol_break,
options.f_reltol_break,
options.g_restol_break,
)
nonfloats = (
options.f_calls_limit,
options.g_calls_limit,
options.h_calls_limit,
options.allow_f_increases,
options.min_iterations,
options.max_iterations,
options.warn_iterations,
options.show_trace,
options.store_trace,
options.extended_trace,
options.show_every,
options.verbosity,
)
Options(map(x -> convert(T, x), floatopts)..., nonfloats...)
end
function Base.show(io::IO, o::SimpleSolvers.Options)
for k in fieldnames(typeof(o))
v = getfield(o, k)
if v isa Nothing
@printf io "%24s = %s\n" k "nothing"
else
@printf io "%24s = %s\n" k v
end
end
end
x_abstol(o::Options) = o.x_abstol
x_reltol(o::Options) = o.x_reltol
x_suctol(o::Options) = o.x_suctol
f_abstol(o::Options) = o.f_abstol
f_reltol(o::Options) = o.f_reltol
f_suctol(o::Options) = o.f_suctol
f_mindec(o::Options) = o.f_mindec
g_restol(o::Options) = o.g_restol
verbosity(o::Options) = o.verbosity
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 621 |
const DEFAULT_BRACKETING_s = 1E-2
const DEFAULT_BRACKETING_k = 2.0
function bracket_minimum(f, x=0.0; s=DEFAULT_BRACKETING_s, k=DEFAULT_BRACKETING_k, nmax=DEFAULT_BRACKETING_nmax)
a, ya = x, f(x)
b, yb = a + s, f(a + s)
if yb > ya
a, b = b, a
ya, yb = yb, ya
s = -s
end
for _ in 1:nmax
c, yc = b + s, f(b + s)
# println("a=$a, b=$b, c=$c, f(a)=$ya, f(b)=$yb, f(c)=$yc")
if yc > yb
return a < c ? (a,c) : (c,a)
end
a, ya, b, yb = b, yb, c, yc
s *= k
end
error("Unable to bracket f starting at x = $x.")
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 35 |
const DEFAULT_BRACKETING_nmax=100
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 651 |
abstract type LinearSolver{T} <: AbstractSolver end
factorize!(s::LinearSolver) = error("factorize! not implemented for $(typeof(s))")
LinearAlgebra.ldiv!(s::LinearSolver) = error("ldiv! not implemented for $(typeof(s))")
function LinearSolver(x::AbstractVector{T}; linear_solver = :julia) where {T}
n = length(x)
if linear_solver === nothing || linear_solver == :julia
linear_solver = LUSolver{T}(n)
elseif linear_solver == :lapack
linear_solver = LUSolverLAPACK{T}(BlasInt(n))
else
@assert typeof(linear_solver) <: LinearSolver{T}
@assert n == linear_solver.n
end
return linear_solver
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 2238 |
mutable struct LUSolver{T} <: LinearSolver{T}
n::Int
A::Matrix{T}
pivots::Vector{Int}
perms::Vector{Int}
info::Int
end
function LUSolver(A::AbstractMatrix{T}) where {T}
n = checksquare(A)
lu = LUSolver{T}(n, zero(A), zeros(Int, n), zeros(Int, n), 0)
factorize!(lu, A)
end
LUSolver{T}(n::Int) where {T} = LUSolver(zeros(T, n, n))
function factorize!(lu::LUSolver{T}, A::AbstractMatrix{T}, pivot=true) where {T}
copy!(lu.A, A)
@inbounds for i in eachindex(lu.perms)
lu.perms[i] = i
end
@inbounds for k in 1:lu.n
# find index max
kp = k
if pivot
amax = real(zero(T))
for i in k:lu.n
absi = abs(lu.A[i,k])
if absi > amax
kp = i
amax = absi
end
end
end
lu.pivots[k] = kp
lu.perms[k], lu.perms[kp] = lu.perms[kp], lu.perms[k]
if lu.A[kp,k] != 0
if k != kp
# Interchange
for i in 1:lu.n
tmp = lu.A[k,i]
lu.A[k,i] = lu.A[kp,i]
lu.A[kp,i] = tmp
end
end
# Scale first column
Akkinv = inv(lu.A[k,k])
for i in k+1:lu.n
lu.A[i,k] *= Akkinv
end
elseif lu.info == 0
lu.info = k
end
# Update the rest
for j in k+1:lu.n
for i in k+1:lu.n
lu.A[i,j] -= lu.A[i,k] * lu.A[k,j]
end
end
end
return lu
end
function LinearAlgebra.ldiv!(x::AbstractVector{T}, lu::LUSolver{T}, b::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
@assert axes(x,1) == axes(b,1) == axes(lu.A,1) == axes(lu.A,2)
@inbounds for i in 1:lu.n
x[i] = b[lu.perms[i]]
end
@inbounds for i in 2:lu.n
s = zero(T)
for j in 1:i-1
s += lu.A[i,j] * x[j]
end
x[i] -= s
end
x[lu.n] /= lu.A[lu.n,lu.n]
@inbounds for i in lu.n-1:-1:1
s = zero(T)
for j in i+1:lu.n
s += lu.A[i,j] * x[j]
end
x[i] -= s
x[i] /= lu.A[i,i]
end
return x
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1971 |
import LinearAlgebra: checksquare
import LinearAlgebra.BLAS: BlasFloat, BlasInt, liblapack, @blasfunc
struct LUSolverLAPACK{T<:BlasFloat} <: LinearSolver{T}
n::BlasInt
A::Matrix{T}
pivots::Vector{BlasInt}
info::BlasInt
end
function LUSolverLAPACK(A::Matrix{T}) where {T}
n = checksquare(A)
lu = LUSolverLAPACK{T}(n, zero(A), zeros(BlasInt, n), 0)
factorize!(lu, A)
end
LUSolverLAPACK{T}(n::BlasInt) where {T} = LUSolverLAPACK(zeros(T, n, n))
## LAPACK LU factorization and solver for general matrices (GE)
for (getrf, getrs, elty) in
((:dgetrf_,:dgetrs_,:Float64),
(:sgetrf_,:sgetrs_,:Float32),
(:zgetrf_,:zgetrs_,:ComplexF64),
(:cgetrf_,:cgetrs_,:ComplexF32))
@eval begin
function factorize!(lu::LUSolverLAPACK{$elty}, A::AbstractMatrix{$elty})
copy!(lu.A, A)
ccall((@blasfunc($getrf), liblapack), Nothing,
(Ptr{BlasInt}, Ptr{BlasInt}, Ptr{$elty},
Ptr{BlasInt}, Ptr{BlasInt}, Ptr{BlasInt}),
Ref(lu.n), Ref(lu.n), lu.A, Ref(lu.n), lu.pivots, Ref(lu.info))
if lu.info > 0
throw(SingularException(lu.info))
elseif lu.info < 0
throw(ArgumentError(lu.info))
end
return lu
end
function LinearAlgebra.ldiv!(x::AbstractVector{$elty}, lu::LUSolverLAPACK{$elty}, b::AbstractVector{$elty})
copy!(x, b)
trans = UInt8('N')
nrhs = BlasInt(1)
ccall((@blasfunc($getrs), liblapack), Nothing,
(Ptr{UInt8}, Ptr{BlasInt}, Ptr{BlasInt}, Ptr{$elty}, Ptr{BlasInt},
Ptr{BlasInt}, Ptr{$elty}, Ptr{BlasInt}, Ptr{BlasInt}),
Ref(trans), Ref(lu.n), Ref(nrhs), lu.A, Ref(lu.n), lu.pivots, x, Ref(lu.n), Ref(lu.info))
if lu.info < 0
throw(ArgumentError(lu.info))
end
return x
end
end
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1269 |
using Printf
const DEFAULT_ARMIJO_α₀ = 1.0
const DEFAULT_ARMIJO_σ₀ = 0.1
const DEFAULT_ARMIJO_σ₁ = 0.5
const DEFAULT_ARMIJO_p = 0.5
struct BacktrackingState{OPT,T} <: LinesearchState where {OPT <: Options, T <: Number}
config::OPT
α₀::T
ϵ::T
p::T
function BacktrackingState(; config = Options(),
α₀::T = DEFAULT_ARMIJO_α₀,
ϵ::T = DEFAULT_WOLFE_ϵ,
p::T = DEFAULT_ARMIJO_p) where {T}
new{typeof(config), T}(config, α₀, ϵ, p)
end
end
Base.show(io::IO, ls::BacktrackingState) = print(io, "Backtracking")
LinesearchState(algorithm::Backtracking; kwargs...) = BacktrackingState(; kwargs...)
function (ls::BacktrackingState)(obj::AbstractUnivariateObjective, α = ls.α₀)
local y₀ = value!(obj, zero(α))
local d₀ = derivative!(obj, zero(α))
for _ in 1:ls.config.max_iterations
if value!(obj, α) ≥ y₀ + ls.ϵ * α * d₀
α *= ls.p
else
break
end
end
return α
end
backtracking(o::AbstractUnivariateObjective, args...; kwargs...) = BacktrackingState(; kwargs...)(o, args...)
backtracking(f::Callable, g::Callable, args...; kwargs...) = BacktrackingState(; kwargs...)(TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, g), args...)
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1900 |
function bisection(f, xmin::T, xmax::T; config = Options()) where {T <: Number}
local x₀ = xmin
local x₁ = xmax
local x = zero(T)
x₀ < x₁ || begin x₀, x₁ = x₁, x₀ end
local y₀ = f(x₀)
local y₁ = f(x₁)
local y = zero(y₀)
# y₀ * y₁ ≤ 0 || error("Either no or multiple real roots in [xmin,xmax]")
for j in 1:config.max_iterations
x = (x₀ + x₁) / 2
y = f(x)
# println("j = ", j, " , x₀ = ", x₀, " , x₁ = ", x₁)
!isapprox(y, zero(y), atol=config.f_abstol) || break
if y₀ * y > 0
x₀ = x # Root is in the right half of [x₀,x₁].
y₀ = y
else
x₁ = x # Root is in the left half of [x₀,x₁].
y₁ = y
end
!isapprox(x₁ - x₀, zero(x), atol=config.x_abstol) || break
end
# println("α=", x, ", f(α)=", y, ", ftol=", config.f_abstol, ", abs(x₁-x₀)=", abs(x₁-x₀), ", xtol=", config.x_abstol)
# i != ls.nmax || error("Max iteration number exceeded")
return x
end
bisection(f, x::Number; kwargs...) = bisection(f, bracket_minimum(f, x)...; kwargs...)
"""
simple bisection line search
"""
mutable struct BisectionState{OPT} <: LinesearchState where {OPT <: Options}
config::OPT
function BisectionState(config)
new{typeof(config)}(config)
end
end
function BisectionState(; config = Options())
BisectionState(config)
end
# function BisectionState(objective::MultivariateObjective; config = Options())
# cache = LinesearchCache(objective.x_f)
# ls_objective = linesearch_objective(objective, cache)
# BisectionState(ls_objective, config)
# end
Base.show(io::IO, ls::BisectionState) = print(io, "Bisection")
LinesearchState(algorithm::Bisection; kwargs...) = BisectionState(; kwargs...)
function (ls::BisectionState)(obj::AbstractUnivariateObjective)
bisection(obj, 0., 1.; config = ls.config)
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 2292 |
const DEFAULT_LINESEARCH_nmax=100
const DEFAULT_LINESEARCH_rmax=100
const DEFAULT_WOLFE_ϵ = 1E-4
abstract type LinesearchState end
# LinesearchState(algorithm, f::Callable, x::Number; kwargs...) = LinesearchState(algorithm, UnivariateObjective(f, x); kwargs...)
# LinesearchState(algorithm, f::Callable, g::Callable, x::Number; kwargs...) = LinesearchState(algorithm, UnivariateObjective(f, g, x); kwargs...)
# LinesearchState(algorithm, f::Callable, x::AbstractVector; kwargs...) = LinesearchState(algorithm, MultivariateObjective(f, x); kwargs...)
(ls::LinesearchState)(f::Callable; kwargs...) = ls(TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, missing); kwargs...)
(ls::LinesearchState)(f::Callable, x::Number; kwargs...) = ls(TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, missing), x; kwargs...)
(ls::LinesearchState)(f::Callable, g::Callable; kwargs...) = ls(TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, g); kwargs...)
(ls::LinesearchState)(f::Callable, g::Callable, x::Number; kwargs...) = ls(TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, g), x; kwargs...)
# solve!(x, δx, ls::LinesearchState) = ls(x, δx)
# solve!(x, δx, g, ls::LinesearchState) = ls(x, δx, g)
struct Linesearch{ALG <: LinesearchMethod, OPT <: Options, OST <: LinesearchState}
algorithm::ALG
config::OPT
state::OST
function Linesearch(algorithm, config, state)
new{typeof(algorithm), typeof(config), typeof(state)}(algorithm, config, state)
end
end
function Linesearch(; algorithm = Static(), config = Options(), kwargs...)
state = LinesearchState(algorithm; kwargs...)
Linesearch(algorithm, config, state)
end
# function Linesearch(x::Number, F::Callable; D = nothing, kwargs...)
# objective = UnivariateObjective(F, D, x)
# Linesearch(x, objective; kwargs...)
# end
# function Linesearch(x::AbstractVector, F::Callable; D = nothing, kwargs...)
# objective = MultivariateObjective(F, D, x)
# Linesearch(x, objective; kwargs...)
# end
(ls::Linesearch)(args...; kwargs...) = ls.state(args...; kwargs...)
# (ls::Linesearch)(f::Callable, args...; kwargs...) = ls(TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, missing), args...; kwargs...)
# (ls::Linesearch)(f::Callable, g::Callable, args...; kwargs...) = ls(TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, g), args...; kwargs...)
# solve!(x, δx, ls::Linesearch) = solve!(x, δx, ls.state)
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1917 | """
Quadratic Polynomial line search
"""
struct QuadraticState{OPT,T} <: LinesearchState where {OPT <: Options, T <: Number}
config::OPT
α₀::T
σ₀::T
σ₁::T
ϵ::T
function QuadraticState(; config = Options(),
α₀::T = DEFAULT_ARMIJO_α₀,
σ₀::T = DEFAULT_ARMIJO_σ₀,
σ₁::T = DEFAULT_ARMIJO_σ₁,
ϵ::T = DEFAULT_WOLFE_ϵ) where {T}
new{typeof(config), T}(config, α₀, σ₀, σ₁, ϵ)
end
end
Base.show(io::IO, ls::QuadraticState) = print(io, "Polynomial quadratic")
LinesearchState(algorithm::Quadratic; kwargs...) = QuadraticState(; kwargs...)
function (ls::QuadraticState)(obj::AbstractUnivariateObjective, α::T = ls.α₀) where {T}
local αₜ::T
local y₁::T
local p₀::T
local p₁::T
local p₂::T
# determine constant coefficients of polynomial p(α) = p₀ + p₁α + p₂α²
# p₀ = f(x₀) # value of initial solution
# p₁ = f'(x₀) # derivative of initial solution
y₀ = value!(obj, zero(α))
d₀ = derivative!(obj, zero(α))
p₀ = y₀
p₁ = d₀
for _ in 1:ls.config.max_iterations
# compute value of new solution
y₁ = value!(obj, α)
if y₁ ≥ y₀ + ls.ϵ * α * d₀
# determine nonconstant coefficient of polynomial p(α) = p₀ + p₁α + p₂α²
p₂ = (y₁^2 - p₀ - p₁*α) / α^2
# compute minimum αₜ of p(α)
αₜ = - p₁ / (2p₂)
if αₜ < ls.σ₀ * α
α = ls.σ₀ * α
elseif αₜ > ls.σ₁ * α
α = ls.σ₁ * α
else
α = αₜ
end
else
break
end
end
return α
end
quadratic(o::AbstractUnivariateObjective, args...; kwargs...) = QuadraticState(; kwargs...)(o, args...)
quadratic(f::Callable, g::Callable, args...; kwargs...) = QuadraticState(; kwargs...)(TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, g), args...)
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 535 |
struct StaticState{T} <: LinesearchState
alpha::T
StaticState(alpha::T = 1.0) where {T} = new{T}(alpha)
end
StaticState(args...; alpha = 1.0, kwargs...) = StaticState(alpha)
LinesearchState(algorithm::Static; kwargs...) = StaticState(algorithm.alpha)
Base.show(io::IO, ls::StaticState) = print(io, "Static Linesearch")
(ls::StaticState)(x::Number = 0) = ls.alpha
(ls::StaticState)(o::AbstractUnivariateObjective, x::Number = 0) = ls.alpha
# (ls::StaticState)(x::AbstractVector, δx::AbstractVector) = x .+= ls.alpha .* δx
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 2320 |
struct NewtonSolverCache{T, AT <: AbstractVector{T}, JT <: AbstractMatrix{T}}
x₀::AT
x₁::AT
δx::AT
rhs::AT
y::AT
J::JT
function NewtonSolverCache(x::AT, y::AT) where {T, AT <: AbstractArray{T}}
J = alloc_j(x,y)
new{T, AT, typeof(J)}(zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), zero(y), zero(y), J)
end
end
function update!(cache::NewtonSolverCache, x::AbstractVector)
cache.x₀ .= x
cache.x₁ .= x
cache.δx .= 0
return cache
end
function initialize!(cache::NewtonSolverCache, x::AbstractVector)
cache.x₀ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
cache.x₁ .= x
cache.δx .= eltype(x)(NaN)
cache.rhs .= eltype(x)(NaN)
cache.y .= eltype(x)(NaN)
cache.J .= eltype(x)(NaN)
return cache
end
"create univariate objective for linesearch algorithm"
function linesearch_objective(objective!, jacobian!, cache::NewtonSolverCache)
function f(α)
cache.x₁ .= cache.x₀ .+ α .* cache.δx
objective!(cache.y, cache.x₁)
l2norm(cache.y)
end
function d(α)
cache.x₁ .= cache.x₀ .+ α .* cache.δx
objective!(cache.y, cache.x₁)
jacobian!(cache.J, cache.x₁, objective!)
-2*dot(cache.y, cache.J, cache.δx)
end
TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, d)
end
abstract type AbstractNewtonSolver{T,AT} <: NonlinearSolver end
@define newton_solver_variables begin
jacobian::TJ
linear::TL
linesearch::TLS
cache::NewtonSolverCache{T,AT,JT}
config::Options{T}
status::TST
end
cache(solver::AbstractNewtonSolver) = solver.cache
config(solver::AbstractNewtonSolver) = solver.config
status(solver::AbstractNewtonSolver) = solver.status
jacobian(solver::AbstractNewtonSolver) = solver.jacobian
compute_jacobian!(s::AbstractNewtonSolver, x, f::Callable) = compute_jacobian!(s, x, f, missing)
compute_jacobian!(s::AbstractNewtonSolver, x, f::Callable, ::Missing) = s.jacobian(s.cache.J, x, f)
compute_jacobian!(s::AbstractNewtonSolver, x, f::Callable, j::Callable) = s.jacobian(s.cache.J, x, j)
check_jacobian(s::AbstractNewtonSolver) = check_jacobian(s.jacobian)
print_jacobian(s::AbstractNewtonSolver) = print_jacobian(s.jacobian)
initialize!(s::AbstractNewtonSolver, x₀::AbstractArray, f) = initialize!(status(s), x₀, f)
update!(s::AbstractNewtonSolver, x₀::AbstractArray) = update!(cache(s), x₀)
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1434 |
struct NewtonSolver{T, AT, JT, TJ, TL, TLS <: LinesearchState, TST <: NonlinearSolverStatus{T}} <: AbstractNewtonSolver{T,AT}
@newton_solver_variables
function NewtonSolver{T,AT,JT,TJ,TL,TS}(x, jacobian, linear_solver, linesearch, cache, config) where {T,AT,JT,TJ,TL,TS}
status = NonlinearSolverStatus{T}(length(x))
new{T,AT,JT,TJ,TL,TS, typeof(status)}(jacobian, linear_solver, linesearch, cache, config, status)
end
end
function NewtonSolver(x::AT, y::AT; J! = missing, linesearch = Backtracking(), config = Options()) where {T, AT <: AbstractVector{T}}
n = length(y)
jacobian = Jacobian{T}(J!, n)
cache = NewtonSolverCache(x, y)
linear_solver = LinearSolver(y)
ls = LinesearchState(linesearch)
options = Options(T, config)
NewtonSolver{T, AT, typeof(cache.J), typeof(jacobian), typeof(linear_solver), typeof(ls)}(x, jacobian, linear_solver, ls, cache, options)
end
function solver_step!(x, f, forj, s::NewtonSolver)
# shortcuts
rhs = s.cache.rhs
δ = s.cache.δx
# update Newton solver cache
update!(s, x)
# compute Jacobian
compute_jacobian!(s, x, forj)
# factorize linear solver
factorize!(s.linear, s.cache.J)
# compute RHS
f(rhs, x)
rmul!(rhs, -1)
# solve J δx = -f(x)
ldiv!(δ, s.linear, rhs)
# apply line search
α = s.linesearch(linesearch_objective(f, jacobian(s), cache(s)))
x .+= α .* δ
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1828 |
import NLsolve: OnceDifferentiable, NewtonCache, newton_
import LineSearches
struct NLsolveNewton{T, AT, JT, FT, DT, CT, LST, LT, TST} <: AbstractNewtonSolver{T,AT}
x::AT
f::AT
J::JT
F!::FT
DF::DT
line_search::LST
linear_solver::LT
cache::CT
config::Options{T}
status::TST
function NLsolveNewton(x::AT, f::AT, J::JT, F!::FT, DF::DT, cache::CT,
line_search::ST, linear_solver::LT, config = Options()) where {
T, AT <: AbstractVector{T}, JT <: AbstractMatrix{T}, FT, DT, CT, ST, LT
}
status = NonlinearSolverStatus{T}(length(x))
options = Options(T, config)
new{T,AT,JT,FT,DT,CT,ST,LT, typeof(status)}(x, f, J, F!, DF, line_search, linear_solver, cache, options, status)
end
end
function NLsolveNewton(x::AbstractVector{T}, f::AbstractVector{T}, F!::Function; J!::Union{Callable,Nothing,Missing} = nothing, mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :forward) where {T}
linear_solver = LinearSolver(x)
df = linear_solver.A
if J! === nothing || ismissing(J!) || mode == :autodiff
DF = OnceDifferentiable(F!, x, f, df; autodiff=diff_type, inplace=true)
else
DF = OnceDifferentiable(F!, J!, x, f, df; inplace=true)
end
NLsolveNewton(x, f, df, F!, DF, NewtonCache(DF), LineSearches.Static(), linear_solver)
end
function linsolve!(s::NLsolveNewton, x, A, b)
factorize!(s.linear_solver, A)
ldiv!(x, s.linear_solver, b)
end
function solve!(x, f, forj, s::NLsolveNewton)
res = newton_(s.DF, x, s.config.x_abstol, s.config.f_abstol, s.config.max_iterations, false, false, false,
s.line_search, (x, A, b) -> linsolve!(s, x, A, b), s.cache)
copyto!(x, res.zero)
s.status.i = res.iterations
s.status.rfₐ = res.residual_norm
return x
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1458 |
using Printf
abstract type NonlinearSolver <: AbstractSolver end
config(s::NonlinearSolver) = error("config not implemented for $(typeof(s))")
status(s::NonlinearSolver) = error("status not implemented for $(typeof(s))")
initialize!(s::NonlinearSolver, ::AbstractArray) = error("initialize! not implemented for $(typeof(s))")
solver_step!(s::NonlinearSolver) = error("solver_step! not implemented for $(typeof(s))")
function solve!(x, f, forj, s::NonlinearSolver)
initialize!(s, x, f)
while !meets_stopping_criteria(status(s), config(s))
next_iteration!(status(s))
solver_step!(x, f, forj, s)
update!(status(s), x, f)
residual!(status(s))
end
warn_iteration_number(status(s), config(s))
return x
end
solve!(x, f, s::NonlinearSolver) = solve!(x, f, f, s)
struct NonlinearSolverException <: Exception
msg::String
end
Base.showerror(io::IO, e::NonlinearSolverException) = print(io, "Nonlinear Solver Exception: ", e.msg, "!")
# get_solver_status!(solver::NonlinearSolver{T}, status_dict::Dict) where {T} =
# get_solver_status!(status(solver), params(solver), status_dict)
# get_solver_status(solver::NonlinearSolver{T}) where {T} = get_solver_status!(solver,
# Dict(:nls_niter => 0,
# :nls_atol => zero(T),
# :nls_rtol => zero(T),
# :nls_stol => zero(T),
# :nls_converged => false)
# )
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 5610 |
mutable struct NonlinearSolverStatus{XT,YT,AXT,AYT}
i::Int # iteration number
rxₐ::XT # residual (absolute)
rxᵣ::XT # residual (relative)
rxₛ::XT # residual (successive)
rfₐ::YT # residual (absolute)
rfᵣ::YT # residual (relative)
rfₛ::YT # residual (successive)
x::AXT # initial solution
x̄::AXT # previous solution
δ::AXT # change in solution
x̃::AXT # temporary variable similar to x
f::AYT # initial function
f̄::AYT # previous function
γ::AYT # initial function
f̃::AYT # temporary variable similar to f
x_converged::Bool
f_converged::Bool
g_converged::Bool
f_increased::Bool
NonlinearSolverStatus{T}(n::Int) where {T} = new{T,T,Vector{T},Vector{T}}(
0,
zero(T), zero(T), zero(T),
zero(T), zero(T), zero(T),
zeros(T,n), zeros(T,n), zeros(T,n), zeros(T,n),
zeros(T,n), zeros(T,n), zeros(T,n), zeros(T,n),
false, false, false, false)
end
solution(status::NonlinearSolverStatus) = status.x
function clear!(status::NonlinearSolverStatus{XT,YT}) where {XT,YT}
status.i = 0
status.rxₐ = XT(NaN)
status.rxᵣ = XT(NaN)
status.rxₛ = XT(NaN)
status.rfₐ = YT(NaN)
status.rfᵣ = YT(NaN)
status.rfₛ = YT(NaN)
status.x̄ .= XT(NaN)
status.x .= XT(NaN)
status.δ .= XT(NaN)
status.x̃ .= XT(NaN)
status.f̄ .= YT(NaN)
status.f .= YT(NaN)
status.γ .= YT(NaN)
status.f̃ .= YT(NaN)
status.x_converged = false
status.f_converged = false
status.f_increased = false
end
Base.show(io::IO, status::NonlinearSolverStatus) = print(io,
(@sprintf " i=%4i" status.i), ", ",
(@sprintf "rxₐ=%14.8e" status.rxₐ), ", ",
(@sprintf "rxᵣ=%14.8e" status.rxᵣ), ", ",
(@sprintf "rfₐ=%14.8e" status.rfₐ), ", ",
(@sprintf "rfᵣ=%14.8e" status.rfᵣ))
function print_status(status::NonlinearSolverStatus, config::Options)
if (config.verbosity ≥ 1 && !(assess_convergence!(status, config) && status.i ≤ config.max_iterations)) ||
config.verbosity > 1
println(status)
end
end
increase_iteration_number!(status::NonlinearSolverStatus) = status.i += 1
isconverged(status::NonlinearSolverStatus) = status.x_converged || status.f_converged
function assess_convergence!(status::NonlinearSolverStatus, config::Options)
x_converged = status.rxₐ ≤ config.x_abstol ||
status.rxᵣ ≤ config.x_reltol ||
status.rxₛ ≤ config.x_suctol
f_converged = status.rfₐ ≤ config.f_abstol ||
status.rfᵣ ≤ config.f_reltol ||
status.rfₛ ≤ config.f_suctol
status.x_converged = x_converged
status.f_converged = f_converged
status.f_increased = norm(status.f) > norm(status.f̄)
return isconverged(status)
end
function meets_stopping_criteria(status::NonlinearSolverStatus, config::Options)
assess_convergence!(status, config)
( isconverged(status) && status.i ≥ config.min_iterations ) ||
( status.f_increased && !config.allow_f_increases ) ||
status.i ≥ config.max_iterations ||
status.rxₐ > config.x_abstol_break ||
status.rxᵣ > config.x_reltol_break ||
status.rfₐ > config.f_abstol_break ||
status.rfᵣ > config.f_reltol_break ||
any(isnan, status.x) ||
any(isnan, status.f)
end
# function check_solver_status(status::NonlinearSolverStatus, config::Options)
# if any(x -> isnan(x), status.xₚ)
# throw(NonlinearSolverException("Detected NaN"))
# end
# if status.rₐ > config.f_abstol_break
# throw(NonlinearSolverException("Absolute error ($(status.rₐ)) larger than allowed ($(config.f_abstol_break))"))
# end
# if status.rᵣ > config.f_reltol_break
# throw(NonlinearSolverException("Relative error ($(status.rᵣ)) larger than allowed ($(config.f_reltol_break))"))
# end
# end
# function get_solver_status!(status::NonlinearSolverStatus, config::Options, status_dict::Dict)
# status_dict[:nls_niter] = status.i
# status_dict[:nls_atol] = status.rₐ
# status_dict[:nls_rtol] = status.rᵣ
# status_dict[:nls_stol] = status.rₛ
# status_dict[:nls_converged] = assess_convergence(status, config)
# return status_dict
# end
function warn_iteration_number(status::NonlinearSolverStatus, config::Options)
if config.warn_iterations > 0 && status.i ≥ config.warn_iterations
@warn "Solver took $(status.i) iterations."
end
nothing
end
function residual!(status::NonlinearSolverStatus)
status.rxₐ = norm(status.x)
status.rxᵣ = status.rxₐ / norm(status.x)
status.x̃ .= status.δ ./ status.x
status.rxₛ = norm(status.x̃)
status.rfₐ = norm(status.f)
status.rfᵣ = status.rfₐ / norm(status.f)
status.f̃ .= status.γ ./ status.f
status.rfₛ = norm(status.f̃)
nothing
end
function initialize!(status::NonlinearSolverStatus, x, f)
clear!(status)
copyto!(status.x, x)
f(status.f, x)
return status
end
function update!(status::NonlinearSolverStatus, x, f)
copyto!(status.x, x)
f(status.f, x)
status.δ .= status.x .- status.x̄
status.γ .= status.f .- status.f̄
return status
end
function next_iteration!(status::NonlinearSolverStatus)
increase_iteration_number!(status)
status.x̄ .= status.x
status.f̄ .= status.f
status.δ .= 0
status.γ .= 0
return status
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1579 |
struct QuasiNewtonSolver{T, AT, JT, TJ, TL, TLS <: LinesearchState, TST <: NonlinearSolverStatus{T}} <: AbstractNewtonSolver{T,AT}
@newton_solver_variables
refactorize::Int
function QuasiNewtonSolver{T,AT,JT,TJ,TL,TS}(x, jacobian, linear_solver, linesearch, cache, config, refactorize) where {T,AT,JT,TJ,TL,TS}
status = NonlinearSolverStatus{T}(length(x))
new{T,AT,JT,TJ,TL,TS, typeof(status)}(jacobian, linear_solver, linesearch, cache, config, status, refactorize)
end
end
function QuasiNewtonSolver(x::AT, y::AT; J! = missing, linesearch = Backtracking(), config = Options(), refactorize=5) where {T, AT <: AbstractVector{T}}
n = length(y)
jacobian = Jacobian{T}(J!, n)
cache = NewtonSolverCache(x, y)
linear_solver = LinearSolver(y)
ls = LinesearchState(linesearch)
options = Options(T, config)
QuasiNewtonSolver{T, AT, typeof(cache.J), typeof(jacobian), typeof(linear_solver), typeof(ls)}(x, jacobian, linear_solver, ls, cache, options, refactorize)
end
function solver_step!(x, f, forj, s::QuasiNewtonSolver)
# shortcuts
rhs = s.cache.rhs
δ = s.cache.δx
# update Newton solver cache
update!(s, x)
# compute Jacobian and factorize
if mod(s.status.i-1, s.refactorize) == 0
compute_jacobian!(s, x, forj)
factorize!(s.linear, s.cache.J)
end
# compute RHS
f(rhs, x)
rmul!(rhs, -1)
# solve J δx = -f(x)
ldiv!(δ, s.linear, rhs)
# apply line search
α = s.linesearch(linesearch_objective(f, jacobian(s), cache(s)))
x .+= α .* δ
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1971 |
struct HessianBFGS{T,VT,MT,OBJ} <: Hessian{T}
objective::OBJ
x̄::VT # previous solution
x::VT # current solution
δ::VT # difference of current and previous solution
ḡ::VT # previous gradient
g::VT # current gradient
γ::VT # difference of current and previous gradient
Q::MT
T1::MT
T2::MT
T3::MT
δγ::MT
δδ::MT
function HessianBFGS(objective::MultivariateObjective, x::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
Q = alloc_h(x)
T1 = zero(Q)
T2 = zero(Q)
T3 = zero(Q)
δγ = zero(Q)
δδ = zero(Q)
new{T,typeof(x),typeof(Q),typeof(objective)}(objective, zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), Q, T1, T2, T3, δγ, δδ)
end
end
HessianBFGS(F, x) = HessianBFGS(MultivariateObjective(F, x), x)
function initialize!(H::HessianBFGS, x::AbstractVector)
H.Q .= Matrix(1.0I, size(H.Q)...)
H.x̄ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
H.δ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
H.ḡ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
H.γ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
H.x .= x
H.g .= gradient!(H.objective, x)
return H
end
function update!(H::HessianBFGS, x::AbstractVector)
# copy previous data and compute new gradient
H.ḡ .= H.g
H.x̄ .= H.x
H.x .= x
H.g .= gradient!(H.objective, x)
# δ = x - x̄
H.δ .= H.x .- H.x̄
# γ = g - ḡ
H.γ .= H.g .- H.ḡ
# δγ = δᵀγ
δγ = H.δ ⋅ H.γ
# BFGS
# Q = Q - ... + ...
# H.Q .-= (H.δ * H.γ' * H.Q .+ H.Q * H.γ * H.δ') ./ δγ .-
# (1 + dot(H.γ, H.Q, H.γ) ./ δγ) .* (H.δ * H.δ') ./ δγ
if δγ ≠ 0
outer!(H.δγ, H.δ, H.γ)
outer!(H.δδ, H.δ, H.δ)
mul!(H.T1, H.δγ, H.Q)
mul!(H.T2, H.Q, H.δγ')
H.T3 .= (1 + dot(H.γ, H.Q, H.γ) ./ δγ) .* H.δδ
H.Q .-= (H.T1 .+ H.T2 .- H.T3) ./ δγ
end
end
Base.inv(H::HessianBFGS) = H.Q
Base.:\(H::HessianBFGS, b) = inv(H) * b
LinearAlgebra.ldiv!(x, H::HessianBFGS, b) = mul!(x, inv(H), b)
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1894 |
struct HessianDFP{T,VT,MT,OBJ} <: Hessian{T}
objective::OBJ
x̄::VT # previous solution
x::VT # current solution
δ::VT # difference of current and previous solution
ḡ::VT # previous gradient
g::VT # current gradient
γ::VT # difference of current and previous gradient
Q::MT
T1::MT
T2::MT
γγ::MT
δδ::MT
function HessianDFP(objective::MultivariateObjective, x::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
Q = alloc_h(x)
T1 = zero(Q)
T2 = zero(Q)
γγ = zero(Q)
δδ = zero(Q)
new{T,typeof(x),typeof(Q),typeof(objective)}(objective, zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), Q, T1, T2, γγ, δδ)
end
end
HessianDFP(F, x) = HessianDFP(MultivariateObjective(F, x), x)
function initialize!(H::HessianDFP, x::AbstractVector)
H.Q .= Matrix(1.0I, size(H.Q)...)
H.x̄ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
H.δ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
H.ḡ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
H.γ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
H.x .= x
H.g .= gradient!(H.objective, x)
return H
end
function update!(H::HessianDFP, x::AbstractVector)
# copy previous data and compute new gradient
H.ḡ .= H.g
H.x̄ .= H.x
H.x .= x
H.g .= gradient!(H.objective, x)
# δ = x - x̄
H.δ .= H.x .- H.x̄
# γ = g - ḡ
H.γ .= H.g .- H.ḡ
# γQγ = γᵀQγ
γQγ = dot(H.γ, H.Q, H.γ)
# δγ = δᵀγ
δγ = H.δ ⋅ H.γ
# DFP
# Q = Q - ... + ...
# H.Q .-= H.Q * H.γ * H.γ' * H.Q / (H.γ' * H.Q * H.γ) .-
# H.δ * H.δ' ./ δγ
if δγ ≠ 0 && γQγ ≠ 0
outer!(H.γγ, H.γ, H.γ)
outer!(H.δδ, H.δ, H.δ)
mul!(H.T1, H.γγ, H.Q)
mul!(H.T2, H.Q, H.T1)
H.Q .-= H.T2 ./ γQγ
H.Q .+= H.δδ ./ δγ
end
end
Base.inv(H::HessianDFP) = H.Q
Base.:\(H::HessianDFP, b) = inv(H) * b
LinearAlgebra.ldiv!(x, H::HessianDFP, b) = mul!(x, inv(H), b)
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 3836 |
struct NewtonOptimizerCache{T, AT <: AbstractArray{T}}
x̄::AT
x::AT
δ::AT
g::AT
rhs::AT
function NewtonOptimizerCache(x::AT) where {T, AT <: AbstractArray{T}}
new{T,AT}(zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), zero(x), zero(x))
end
end
function update!(cache::NewtonOptimizerCache, x::AbstractVector)
cache.x̄ .= x
cache.x .= x
cache.δ .= 0
return cache
end
function update!(cache::NewtonOptimizerCache, x::AbstractVector, g::AbstractVector)
update!(cache, x)
cache.g .= g
cache.rhs .= -g
return cache
end
function initialize!(cache::NewtonOptimizerCache, x::AbstractVector)
cache.x̄ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
cache.x .= x
cache.δ .= eltype(x)(NaN)
cache.g .= eltype(x)(NaN)
cache.rhs .= eltype(x)(NaN)
return cache
end
"create univariate objective for linesearch algorithm"
function linesearch_objective(objective::MultivariateObjective, cache::NewtonOptimizerCache{T}) where {T}
function f(α)
cache.x .= cache.x̄ .+ α .* cache.δ
value(objective, cache.x)
end
function d(α)
cache.x .= cache.x̄ .+ α .* cache.δ
dot(gradient!(objective, cache.x), cache.δ)
end
UnivariateObjective(f, d, one(T))
end
struct NewtonOptimizerState{OBJ <: MultivariateObjective, HES <: Hessian, LS <: LinesearchState, LSO, NOC <: NewtonOptimizerCache} <: OptimizationAlgorithm
objective::OBJ
hessian::HES
linesearch::LS
ls_objective::LSO
cache::NOC
function NewtonOptimizerState(objective::OBJ, hessian::HES, linesearch::LS, ls_objetive::LSO, cache::NOC) where {OBJ, HES, LS, LSO, NOC}
new{OBJ,HES,LS,LSO,NOC}(objective, hessian, linesearch, ls_objetive, cache)
end
end
function NewtonOptimizerState(x::VT, objective::MultivariateObjective; hessian = HessianAutodiff, linesearch = Backtracking()) where {XT, VT <: AbstractVector{XT}}
cache = NewtonOptimizerCache(x)
hess = hessian(objective, x)
ls = LinesearchState(linesearch)
lso = linesearch_objective(objective, cache)
NewtonOptimizerState(objective, hess, ls, lso, cache)
end
NewtonOptimizer(args...; kwargs...) = NewtonOptimizerState(args...; kwargs...)
BFGSOptimizer(args...; kwargs...) = NewtonOptimizerState(args...; hessian = HessianBFGS, kwargs...)
DFPOptimizer(args...; kwargs...) = NewtonOptimizerState(args...; hessian = HessianDFP, kwargs...)
OptimizerState(algorithm::Newton, objective, x, y; kwargs...) = NewtonOptimizerState(x, objective; kwargs...)
OptimizerState(algorithm::BFGS, objective, x, y; kwargs...) = NewtonOptimizerState(x, objective; hessian = HessianBFGS, kwargs...)
OptimizerState(algorithm::DFP, objective, x, y; kwargs...) = NewtonOptimizerState(x, objective; hessian = HessianDFP, kwargs...)
cache(newton::NewtonOptimizerState) = newton.cache
direction(newton::NewtonOptimizerState) = cache(newton).δ
gradient(newton::NewtonOptimizerState) = newton.cache.g
hessian(newton::NewtonOptimizerState) = newton.hessian
linesearch(newton::NewtonOptimizerState) = newton.linesearch
objective(newton::NewtonOptimizerState) = newton.objective
rhs(newton::NewtonOptimizerState) = newton.cache.rhs
function initialize!(newton::NewtonOptimizerState, x::AbstractVector)
initialize!(cache(newton), x)
initialize!(hessian(newton), x)
end
function update!(newton::NewtonOptimizerState, x::AbstractVector)
update!(cache(newton), x, gradient!(objective(newton), x))
update!(hessian(newton), x)
end
function solver_step!(x::AbstractVector, newton::NewtonOptimizerState)
# shortcut for Newton direction
δ = direction(newton)
# update cache and Hessian
update!(newton, x)
# solve H δx = - ∇f
ldiv!(δ, hessian(newton), rhs(newton))
# apply line search
α = newton.linesearch(newton.ls_objective)
# compute new minimizer
x .= x .+ α .* δ
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 5370 |
const SOLUTION_MAX_PRINT_LENGTH = 10
"""
An `OptimizationAlgorithm` is a datastructe that is used to dispatch on different algorithms.
It needs to implement three important methods,
```
initialize!(alg::OptimizationAlgorithm, ::AbstractVector)
update!(alg::OptimizationAlgorithm, ::AbstractVector)
solver_step!(::AbstractVector, alg::OptimizationAlgorithm)
```
that initialize and update the state of the algorithm and perform an actual optimization step.
Further the following convenience methods should be implemented,
```
objective(alg::OptimizationAlgorithm)
gradient(alg::OptimizationAlgorithm)
hessian(alg::OptimizationAlgorithm)
linesearch(alg::OptimizationAlgorithm)
```
which return the objective to optimize, its gradient and (approximate) Hessian as well as the
linesearch algorithm used in conjunction with the optimization algorithm if any.
"""
abstract type OptimizationAlgorithm end
OptimizerState(alg::OptimizationAlgorithm, args...; kwargs...) = error("OptimizerState not implemented for $(typeof(alg))")
"""
Verifies if an object implements the [`OptimizationAlgorithm`](@ref) interface.
"""
function isaOptimizationAlgorithm(alg)
x = rand(3)
applicable(gradient, alg) &&
applicable(hessian, alg) &&
applicable(linesearch, alg) &&
applicable(objective, alg) &&
applicable(initialize!, alg, x) &&
applicable(update!, alg, x) &&
applicable(solver_step!, x, alg)
end
struct Optimizer{ALG <: NonlinearMethod,
OBJ <: MultivariateObjective,
OPT <: Options,
RES <: OptimizerResult,
AST <: OptimizationAlgorithm} <: NonlinearSolver
algorithm::ALG
objective::OBJ
config::OPT
result::RES
state::AST
end
function Optimizer(x::VT, objective::MultivariateObjective; algorithm = BFGS(), linesearch = Backtracking(), config = Options()) where {XT, VT <: AbstractVector{XT}}
y = value(objective, x)
result = OptimizerResult(x, y)
astate = OptimizerState(algorithm, objective, x, y; linesearch = linesearch)
options = Options(XT, config)
Optimizer{typeof(algorithm), typeof(objective), typeof(options), typeof(result), typeof(astate)}(algorithm, objective, options, result, astate)
end
function Optimizer(x::AbstractVector, F::Function; ∇F! = nothing, kwargs...)
G = Gradient(∇F!, F, x)
objective = MultivariateObjective(F, G, x)
Optimizer(x, objective; kwargs...)
end
config(opt::Optimizer) = opt.config
result(opt::Optimizer) = opt.result
status(opt::Optimizer) = opt.result.status
state(opt::Optimizer) = opt.state
objective(opt::Optimizer) = opt.objective
algorithm(opt::Optimizer) = opt.algorithm
linesearch(opt::Optimizer) = linesearch(opt.state)
Base.minimum(opt::Optimizer) = minimum(result(opt))
minimizer(opt::Optimizer) = minimizer(result(opt))
function Base.show(io::IO, opt::Optimizer)
c = config(opt)
s = status(opt)
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " * Algorithm: %s \n" algorithm(opt)
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " * Linesearch: %s\n" linesearch(opt)
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " * Iterations\n"
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " n = %i\n" iterations(s)
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " * Convergence measures\n"
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " |x - x'| = %.2e %s %.1e\n" x_abschange(s) x_abschange(s) ≤ x_abstol(c) ? "≤" : "≰" x_abstol(c)
@printf io " |x - x'|/|x'| = %.2e %s %.1e\n" x_relchange(s) x_relchange(s) ≤ x_reltol(c) ? "≤" : "≰" x_reltol(c)
@printf io " |f(x) - f(x')| = %.2e %s %.1e\n" f_abschange(s) f_abschange(s) ≤ f_abstol(c) ? "≤" : "≰" f_abstol(c)
@printf io " |f(x) - f(x')|/|f(x')| = %.2e %s %.1e\n" f_relchange(s) f_relchange(s) ≤ f_reltol(c) ? "≤" : "≰" f_reltol(c)
@printf io " |g(x)| = %.2e %s %.1e\n" g_residual(s) g_residual(s) ≤ g_restol(c) ? "≤" : "≰" g_restol(c)
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " * Candidate solution\n"
@printf io "\n"
length(minimizer(opt)) > SOLUTION_MAX_PRINT_LENGTH || @printf io " Final solution value: [%s]\n" join([@sprintf "%e" x for x in minimizer(opt)], ", ")
@printf io " Final objective value: %e\n" minimum(opt)
@printf io "\n"
end
check_gradient(opt::Optimizer) = check_gradient(gradient(objective(opt)))
print_gradient(opt::Optimizer) = print_gradient(gradient(objective(opt)))
print_status(opt::Optimizer) = print_status(status(opt), config(opt))
assess_convergence(opt::Optimizer) = assess_convergence(status(opt), config(opt))
meets_stopping_criteria(opt::Optimizer) = meets_stopping_criteria(status(opt), config(opt))
function initialize!(opt::Optimizer, x::AbstractVector)
clear!(objective(opt))
initialize!(result(opt), x, value!(objective(opt), x), gradient!(objective(opt), x))
initialize!(state(opt), x)
end
"compute objective and gradient at new solution and update result"
function update!(opt::Optimizer, x::AbstractVector)
update!(result(opt), x, value!(objective(opt), x), gradient!(objective(opt), x))
end
function solve!(x, opt::Optimizer)
initialize!(opt, x)
while !meets_stopping_criteria(opt)
next_iteration!(result(opt))
solver_step!(x, state(opt))
update!(opt, x)
end
warn_iteration_number(status(opt), config(opt))
print_status(status(opt), config(opt))
return x
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1810 |
mutable struct OptimizerResult{XT, YT, VT <: AbstractArray{XT}, OST <: OptimizerStatus{XT,YT}}
status::OST # iteration number, residuals and convergence info
x::VT # current solution
f::YT # current function
g::VT # current gradient
end
function OptimizerResult(x::VT, y::YT) where {XT, YT, VT <: AbstractVector{XT}}
status = OptimizerStatus{XT,YT}()
result = OptimizerResult{XT,YT,VT,typeof(status)}(status, zero(x), zero(y), zero(x))
clear!(result)
end
status(result::OptimizerResult) = result.status
solution(result::OptimizerResult) = result.x
minimizer(result::OptimizerResult) = result.x
Base.minimum(result::OptimizerResult) = result.f
function clear!(result::OptimizerResult{XT,YT}) where {XT,YT}
clear!(result.status)
result.x .= XT(NaN)
result.f = YT(NaN)
result.g .= XT(NaN)
return result
end
function residual!(result::OptimizerResult, x, f, g)
status = result.status
status.rxₐ = sqeuclidean(x, result.x)
status.rxᵣ = status.rxₐ / norm(x)
status.rfₐ = norm(f - result.f)
status.rfᵣ = status.rfₐ / norm(f)
status.rgₐ = norm(g - result.g)
status.rg = norm(g)
status.Δf = f - result.f
status.Δf̃ = result.g ⋅ x - result.g ⋅ result.x
status.f_increased = abs(f) > abs(result.f)
status.x_isnan = any(isnan, x)
status.f_isnan = any(isnan, f)
status.g_isnan = any(isnan, g)
return status
end
function update!(result::OptimizerResult, x, f, g)
residual!(result, x, f, g)
result.x .= x
result.f = f
result.g .= g
return result
end
function initialize!(result::OptimizerResult, x, f, g)
clear!(result)
update!(result, x, f, g)
end
function next_iteration!(result::OptimizerResult)
increase_iteration_number!(status(result))
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 6618 |
mutable struct OptimizerStatus{XT,YT}
i::Int # iteration number
rxₐ::XT # absolute change in x
rxᵣ::XT # relative change in x
rfₐ::YT # absolute change in f
rfᵣ::YT # relative change in f
rgₐ::YT # absolute change in g
rg::XT # residual of g
Δf::YT # change of function
Δf̃::YT
x_converged::Bool
f_converged::Bool
g_converged::Bool
f_increased::Bool
x_isnan::Bool
f_isnan::Bool
g_isnan::Bool
end
OptimizerStatus{XT,YT}() where {XT,YT} = OptimizerStatus{XT,YT}(
0, XT(NaN), XT(NaN), YT(NaN), YT(NaN), XT(NaN), XT(NaN), YT(NaN), YT(NaN),
false, false, false, false, true, true, true)
OptimizerStatus{T}() where {T} = OptimizerStatus{T,T}()
function OptimizerStatus(x, y)
XT = typeof(norm(x))
YT = typeof(norm(y))
OptimizerStatus{XT,YT}()
end
iterations(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.i
x_abschange(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.rxₐ
x_relchange(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.rxᵣ
f_abschange(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.rfₐ
f_relchange(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.rfᵣ
f_change(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.Δf
f_change_approx(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.Δf̃
g_abschange(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.rgₐ
g_residual(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.rg
function clear!(status::OptimizerStatus{XT,YT}) where {XT,YT}
status.i = 0
status.rxₐ = XT(NaN)
status.rxᵣ = XT(NaN)
status.rfₐ = YT(NaN)
status.rfᵣ = YT(NaN)
status.rgₐ = YT(NaN)
status.rg = XT(NaN)
status.Δf = YT(NaN)
status.Δf̃ = YT(NaN)
status.x_converged = false
status.f_converged = false
status.g_converged = false
status.f_increased = false
status.x_isnan = true
status.f_isnan = true
status.g_isnan = true
end
function Base.show(io::IO, s::OptimizerStatus)
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " * Iterations\n"
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " n = %i\n" iterations(s)
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " * Convergence measures\n"
@printf io "\n"
@printf io " |x - x'| = %.2e\n" x_abschange(s)
@printf io " |x - x'|/|x'| = %.2e\n" x_relchange(s)
@printf io " |f(x) - f(x')| = %.2e\n" f_abschange(s)
@printf io " |f(x) - f(x')|/|f(x')| = %.2e\n" f_relchange(s)
@printf io " |g(x) - g(x')| = %.2e\n" g_abschange(s)
@printf io " |g(x)| = %.2e\n" g_residual(s)
@printf io "\n"
end
function print_status(status::OptimizerStatus, config::Options)
if (verbosity(config) ≥ 1 && !(assess_convergence!(status, config) && status.i ≤ config.max_iterations)) ||
verbosity(config) > 1
println(status)
end
end
increase_iteration_number!(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.i += 1
isconverged(status::OptimizerStatus) = status.x_converged || status.f_converged || status.g_converged
function assess_convergence!(status::OptimizerStatus, config::Options)
x_converged = x_abschange(status) ≤ x_abstol(config) ||
x_relchange(status) ≤ x_reltol(config)
f_converged = f_abschange(status) ≤ f_abstol(config) ||
f_relchange(status) ≤ f_reltol(config)
f_converged_strong = f_change(status) ≤ f_mindec(config) * f_change_approx(status)
g_converged = g_residual(status) ≤ g_restol(config)
status.x_converged = x_converged
status.f_converged = f_converged && f_converged_strong
status.g_converged = g_converged
# println(x_abschange(status))
# println(x_relchange(status))
# println(x_converged)
# println(f_converged)
# println(g_converged)
return isconverged(status)
end
function meets_stopping_criteria(status::OptimizerStatus, config::Options)
converged = assess_convergence!(status, config)
# println(converged && status.i ≥ config.min_iterations )
# println(status.f_increased && !config.allow_f_increases )
# println(status.i ≥ config.max_iterations)
# println(status.rxₐ > config.x_abstol_break)
# println(status.rxᵣ > config.x_reltol_break)
# println(status.rfₐ > config.f_abstol_break)
# println(status.rfᵣ > config.f_reltol_break)
# println(status.rg > config.g_restol_break)
# println(status.x_isnan)
# println(status.f_isnan)
# println(status.g_isnan)
( converged && status.i ≥ config.min_iterations ) ||
( status.f_increased && !config.allow_f_increases ) ||
status.i ≥ config.max_iterations ||
status.rxₐ > config.x_abstol_break ||
status.rxᵣ > config.x_reltol_break ||
status.rfₐ > config.f_abstol_break ||
status.rfᵣ > config.f_reltol_break ||
status.rg > config.g_restol_break ||
status.x_isnan ||
status.f_isnan ||
status.g_isnan
end
# function check_solver_status(status::OptimizerStatus, config::Options)
# if any(isnan, status.x) || isnan(status.f) || any(isnan, status.g)
# throw(NonlinearSolverException("Detected NaN"))
# end
# if status.rfₐ > config.f_abstol_break
# throw(NonlinearSolverException("Absolute error ($(status.rfₐ)) larger than allowed ($(config.f_abtol_break))"))
# end
# if status.rfᵣ > config.f_reltol_break
# throw(NonlinearSolverException("Relative error ($(status.rfᵣ)) larger than allowed ($(config.f_reltol_break))"))
# end
# end
# function get_solver_status!(status::OptimizerStatus, params::NonlinearSolverParameters, status_dict::Dict)
# status_dict[:niter] = status.i
# status_dict[:xatol] = status.rxₐ
# status_dict[:xrtol] = status.rxᵣ
# status_dict[:yatol] = status.rfₐ
# status_dict[:yrtol] = status.rfᵣ
# status_dict[:gatol] = status.rgₐ
# status_dict[:grtol] = status.rgᵣ
# status_dict[:converged] = assess_convergence(status, params)
# return status_dict
# end
# get_solver_status!(solver::OptimizerStatus{T}, status_dict::Dict) where {T} =
# get_solver_status!(status(solver), params(solver), status_dict)
# get_solver_status(solver::OptimizerStatus{T}) where {T} = get_solver_status!(solver,
# Dict(:niter => 0,
# :xatol => zero(T),
# :xrtol => zero(T),
# :yatol => zero(T),
# :yrtol => zero(T),
# :gatol => zero(T),
# :grtol => zero(T),
# :converged => false)
# )
function warn_iteration_number(status::OptimizerStatus, config::Options)
if config.warn_iterations > 0 && status.i ≥ config.warn_iterations
println("WARNING: Optimizer took ", status.i, " iterations.")
end
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1307 |
using SimpleSolvers
using Test
n = 2
x = rand(n)
g = 2x
T = eltype(x)
function F(x::Vector)
1 + sum(x.^2)
end
function ∇F!(g::Vector, x::Vector)
g .= 0
for i in eachindex(x,g)
g[i] = 2x[i]
end
end
∇PAD = Gradient{T}(F, n; mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :forward)
∇PFD = Gradient{T}(F, n; mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :finite)
∇PUS = Gradient{T}(∇F!, n; mode = :user)
@test typeof(∇PAD) <: GradientAutodiff
@test typeof(∇PFD) <: GradientFiniteDifferences
@test typeof(∇PUS) <: GradientFunction
function test_grad(g1, g2, atol)
for i in eachindex(g1,g2)
@test g1[i] ≈ g2[i] atol=atol
end
end
gad = zero(g)
gfd = zero(g)
gus = zero(g)
compute_gradient!(gad, x, ∇PAD)
compute_gradient!(gfd, x, ∇PFD)
compute_gradient!(gus, x, ∇PUS)
test_grad(gad, g, eps())
test_grad(gfd, g, 1E-7)
test_grad(gus, g, 0)
gad1 = zero(g)
gfd1 = zero(g)
gus1 = zero(g)
compute_gradient!(gad1, x, F; mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :forward)
compute_gradient!(gfd1, x, F; mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :finite)
compute_gradient!(gus1, x, ∇F!; mode = :user)
test_grad(gad, gad1, 0)
test_grad(gfd, gfd1, 0)
test_grad(gus, gus1, 0)
gad2 = zero(g)
gfd2 = zero(g)
compute_gradient_ad!(gad2, x, F)
compute_gradient_fd!(gfd2, x, F)
test_grad(gad, gad2, 0)
test_grad(gfd, gfd2, 0)
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 921 |
using SimpleSolvers
using Test
n = 2
x = rand(n)
h = zeros(n,n)
T = eltype(x)
function F(x::Vector)
1 + sum(x.^2)
end
function H!(h::Matrix, x::Vector)
h .= 0
for i in eachindex(x)
h[i,i] = 2
end
end
H!(h,x)
HPAD = Hessian{T}(F, n; mode = :autodiff)
HPUS = Hessian{T}(H!, n; mode = :user)
@test typeof(HPAD) <: HessianAutodiff
@test typeof(HPUS) <: HessianFunction
function test_hessian(h1, h2, atol)
for i in eachindex(h1,h2)
@test h1[i] ≈ h2[i] atol=atol
end
end
had = zero(h)
hus = zero(h)
compute_hessian!(had, x, HPAD)
compute_hessian!(hus, x, HPUS)
test_hessian(had, h, eps())
test_hessian(hus, h, 0)
had1 = zero(h)
hus1 = zero(h)
compute_hessian!(had1, x, F; mode = :autodiff)
compute_hessian!(hus1, x, H!; mode = :user)
test_hessian(had, had1, 0)
test_hessian(hus, hus1, 0)
had2 = zero(h)
compute_hessian_ad!(had2, x, F)
test_hessian(had, had2, 0)
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1604 |
using SimpleSolvers
using Test
n = 1
T = Float64
x = [T(π),]
j = reshape(2x, 1, 1)
function F!(f::AbstractVector, x::AbstractVector)
f .= x.^2
end
function J!(g::AbstractMatrix, x::AbstractVector)
g .= 0
for i in eachindex(x)
g[i,i] = 2x[i]
end
end
JPAD = Jacobian{T}(n; mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :forward)
JPFD = Jacobian{T}(n; mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :finite)
JPUS = Jacobian{T}(n; mode = :user)
@test typeof(JPAD) <: JacobianAutodiff
@test typeof(JPFD) <: JacobianFiniteDifferences
@test typeof(JPUS) <: JacobianFunction
jad = zero(j)
jfd = zero(j)
jus = zero(j)
JPAD(jad, x, F!)
JPFD(jfd, x, F!)
JPUS(jus, x, J!)
@test jad ≈ j atol = eps()
@test jfd ≈ j atol = 1E-7
@test jus ≈ j atol = 0
jad1 = zero(j)
jfd1 = zero(j)
jus1 = zero(j)
compute_jacobian!(jad1, x, F!, JPAD)
compute_jacobian!(jfd1, x, F!, JPFD)
compute_jacobian!(jus1, x, J!, JPUS)
@test jad1 == jad
@test jfd1 == jfd
@test jus1 == jus
jad2 = zero(j)
jfd2 = zero(j)
jus2 = zero(j)
JPAD = Jacobian{T}(nothing, F!, n; diff_type = :forward)
JPFD = Jacobian{T}(nothing, F!, n; diff_type = :finite)
JPUS = Jacobian{T}(J!, F!, n)
compute_jacobian!(jad2, x, F!, JPAD)
compute_jacobian!(jfd2, x, F!, JPFD)
compute_jacobian!(jus2, x, J!, JPUS)
@test jad2 == jad
@test jfd2 == jfd
@test jus2 == jus
jad3 = zero(j)
jfd3 = zero(j)
jus3 = zero(j)
compute_jacobian!(jad3, x, F!; mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :forward)
compute_jacobian!(jfd3, x, F!; mode = :autodiff, diff_type = :finite)
compute_jacobian!(jus3, x, J!; mode = :user)
@test jad3 == jad
@test jfd3 == jfd
@test jus3 == jus
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 7146 |
using SimpleSolvers
using SimpleSolvers: LinesearchState, StaticState
using Test
# include("optimizers_problems.jl")
f(x) = x^2-1
g(x) = 2x
function F(x)
# sum(x.^2) - 1
y = - one(eltype(x))
for _x in x
y += _x^2
end
return y
end
function test_linesearch(algorithm, method; kwargs...)
x₀ = -3.0
x₁ = +3.0
xₛ = 0.0
δx = x₁ .- x₀
_f = α -> f(x₀ + α * δx)
_d = α -> g(x₀ + α * δx)
o1 = UnivariateObjective(_f, xₛ)
o2 = UnivariateObjective(_f, _d, xₛ)
options = Options(x_abstol = zero(x₀))
ls = Linesearch(; algorithm = algorithm, config = options, kwargs...)
α1 = ls(o1)
α2 = ls(o2)
α3 = ls(_f, _d)
@test x₀ + α1 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
@test x₀ + α2 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
@test x₀ + α3 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
α1 = ls(o1, one(xₛ))
α2 = ls(o2, one(xₛ))
α3 = ls(_f, _d, one(xₛ))
@test x₀ + α1 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
@test x₀ + α2 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
@test x₀ + α3 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
α1 = method(o1; config = config = options, kwargs...)
α2 = method(o2; config = config = options, kwargs...)
α3 = method(_f, _d; config = options, kwargs...)
@test x₀ + α1 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
@test x₀ + α2 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
@test x₀ + α3 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
α1 = method(o1, one(xₛ); config = options, kwargs...)
α2 = method(o2, one(xₛ); config = options, kwargs...)
α3 = method(_f, _d, one(xₛ); config = options, kwargs...)
@test x₀ + α1 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
@test x₀ + α2 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
@test x₀ + α3 * δx ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
end
@testset "$(rpad("Bracketing",80))" begin
@test bracket_minimum(x -> x^2) == (-SimpleSolvers.DEFAULT_BRACKETING_s, +SimpleSolvers.DEFAULT_BRACKETING_s)
@test bracket_minimum(x -> (x-1)^2) == (0.64, 2.56)
end
@testset "$(rpad("Static",80))" begin
x₀ = -3.
x₁ = +1.
δx = x₁ - x₀
x = copy(x₀)
o = UnivariateObjective(f, x)
ls = StaticState()
@test ls == LinesearchState(Static())
@test ls == LinesearchState(Static(1.0))
# x1 = copy(x₀); x2 = copy(x₀); @test solve!(x1, δx, ls) == ls(x2, δx) == x₁
@test ls() == 1.
o1 = UnivariateObjective(f, x)
o2 = UnivariateObjective(f, g, x)
ls1 = Linesearch(algorithm = Static())
ls2 = Linesearch(algorithm = Static(1.0))
ls3 = Linesearch(algorithm = Static(0.8))
# @test ls1 == Linesearch(x, F; algorithm = Static())
# @test ls2 == Linesearch(x, F; algorithm = Static(), D = D)
# x1 = copy(x₀); x2 = copy(x₀); @test solve!(x1, δx, ls1) == ls1(x2, δx) == x₁
# x1 = copy(x₀); x2 = copy(x₀); @test solve!(x1, δx, ls2) == ls2(x2, δx) == x₁
# x1 = copy(x₀); x2 = copy(x₀); @test solve!(x1, δx, ls3) == ls3(x2, δx) == x₁
@test ls1(o1) == ls1(o2) == ls1(f,g) == 1
@test ls2(o1) == ls2(o2) == ls2(f,g) == 1
@test ls3(o1) == ls3(o2) == ls3(f,g) == 0.8
end
@testset "$(rpad("Bisection",80))" begin
x₀ = -3.0
x₁ = +0.5
δx = x₁ .- x₀
x = copy(x₀)
o = UnivariateObjective(f, x)
x1 = bisection(f, x₀, x₁; config = Options(x_abstol = zero(x)))
x2 = bisection(f, x; config = Options(x_abstol = zero(x)))
@test x1 ≈ -1 atol=∛(2eps())
@test x2 ≈ -1 atol=∛(2eps())
x1 = bisection(f, x₀, x₁; config = Options(f_abstol = zero(f(x))))
x2 = bisection(f, x; config = Options(f_abstol = zero(f(x))))
@test x1 ≈ -1 atol=2eps()
@test x2 ≈ -1 atol=2eps()
# x₀ = [-3.0]
# x₁ = [+0.5]
# xₛ = [-1.0]
# δx = x₁ .- x₀
# x = copy(x₀)
x_abstol = zero(eltype(x))
f_abstol = zero(F(x))
ls = Linesearch(algorithm = Bisection(), config = Options(x_abstol = x_abstol))
@test ls(o) == ls(f,g) == 1.0
# x1 = copy(x₀)
# x2 = copy(x₀)
# x3 = copy(x₀)
# ls(x1, δx)
# solve!(x2, δx, ls)
# solve!(x3, δx, ls.state)
# @test x1 ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
# @test x2 ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
# @test x3 ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
ls = Linesearch(algorithm = Bisection(), config = Options(f_abstol = f_abstol))
@test ls(o) == ls(f,g) == 1.0
# x1 = copy(x₀)
# x2 = copy(x₀)
# x3 = copy(x₀)
# ls(x1, δx)
# solve!(x2, δx, ls)
# solve!(x3, δx, ls.state)
# @test x1 ≈ xₛ atol=2eps()
# @test x2 ≈ xₛ atol=2eps()
# @test x3 ≈ xₛ atol=2eps()
end
@testset "$(rpad("Backtracking",80))" begin
test_linesearch(Backtracking(), backtracking)
# x₀ = [-3.0]
# x₁ = [+3.0]
# xₛ = [ 0.0]
# δx = x₁ .- x₀
# x = copy(x₀)
# x1 = copy(x₀)
# x2 = copy(x₀)
# x3 = copy(x₀)
# ls = Linesearch(x, F; algorithm = Backtracking(), config = Options(x_abstol = zero(eltype(x))))
# ls(x1, δx)
# solve!(x2, δx, ls)
# backtracking(F, x3, δx; config = Options(x_abstol = zero(eltype(x))))
# @test x1 ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
# @test x2 ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
# @test x3 ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
# n = 1
# x₀ = -0.5*ones(n)
# x₁ = +1.0*ones(n)
# x = copy(x₀)
# f = zeros(n)
# g = zeros(n,n)
# ls = Solver(F!, x, f)
# F!(f,x)
# J!(g,x)
# solve!(x, f, g, x₀, x₁, ls)
# F!(f,x)
# @test x ≈ zero(x) atol=4E-1
# @test f ≈ zero(f) atol=8E-2
# @test solve!(x, f, g, x₀, x₁, ls) == ls(x, f, g, x₀, x₁) == SFunc(F!, x, f, g, x₀, x₁)
# n = 3
# x₀ = -ones(n)
# x₁ = +ones(n)
# x = copy(x₀)
# f = zeros(n)
# g = zeros(n,n)
# ls = Solver(F!, x, f)
# F!(f,x)
# J!(g,x)
# solve!(x, f, g, x₀, x₁, ls)
# F!(f,x)
# @test x == zero(x)
# @test f == zero(f)
# @test solve!(x, f, g, x₀, x₁, ls) == ls(x, f, g, x₀, x₁) == SFunc(F!, x, f, g, x₀, x₁)
end
@testset "$(rpad("Polynomial Linesearch",80))" begin
test_linesearch(Quadratic(), quadratic; σ₀=0.5, σ₁=0.8)
# x₀ = [-3.0]
# x₁ = [+3.0]
# xₛ = [ 0.0]
# δx = x₁ .- x₀
# x = copy(x₀)
# x1 = copy(x₀)
# x2 = copy(x₀)
# x3 = copy(x₀)
# ls = Linesearch(x, F; algorithm = Quadratic(), config = Options(x_abstol = zero(eltype(x))))
# ls(x1, δx)
# solve!(x2, δx, ls)
# quadratic(F, x3, δx; config = Options(x_abstol = zero(eltype(x))))
# @test x1 ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
# @test x2 ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
# @test x3 ≈ xₛ atol=∛(2eps())
# n = 1
# x₀ = -0.5*ones(n)
# x₁ = +1.0*ones(n)
# x = copy(x₀)
# f = zeros(n)
# g = zeros(n,n)
# ls = Solver(F!, x, f)
# F!(f,x)
# J!(g,x)
# solve!(x, f, g, x₀, x₁, ls)
# F!(f,x)
# @test x ≈ zero(x) atol=4E-1
# @test f ≈ zero(f) atol=8E-2
# @test solve!(x, f, g, x₀, x₁, ls) == ls(x, f, g, x₀, x₁) == SFunc(F!, x, f, g, x₀, x₁)
# n = 3
# x₀ = -ones(n)
# x₁ = +ones(n)
# x = copy(x₀)
# f = zeros(n)
# g = zeros(n,n)
# ls = Solver(F!, x, f)
# F!(f,x)
# J!(g,x)
# solve!(x, f, g, x₀, x₁, ls)
# F!(f,x)
# @test x == zero(x)
# @test f == zero(f)
# @test solve!(x, f, g, x₀, x₁, ls) == ls(x, f, g, x₀, x₁) == SFunc(F!, x, f, g, x₀, x₁)
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 924 |
using LinearAlgebra: ldiv!
using SimpleSolvers
using Test
struct LinearSolverTest{T} <: LinearSolver{T} end
test_solver = LinearSolverTest{Float64}()
@test_throws ErrorException factorize!(test_solver)
@test_throws ErrorException ldiv!(test_solver)
A = [[+4. +5. -2.]
[+7. -1. +2.]
[+3. +1. +4.]]
x = [+4., -4., +5.]
b = [-14., +42., +28.]
function test_lu_solver(solver, A, b, x)
for T in (Float64, ComplexF64, Float32, ComplexF32)
AT = convert(Matrix{T}, A)
bT = convert(Vector{T}, b)
xT = convert(Vector{T}, x)
lu1 = solver(AT)
x1 = ldiv!(zero(xT), lu1, bT)
@test x1 ≈ xT atol=8*eps(real(T))
lu2 = solver(rand(T, size(A)...))
x2 = zero(xT)
factorize!(lu2, AT)
ldiv!(x2, lu2, bT)
@test x2 ≈ xT atol=8*eps(real(T))
end
end
test_lu_solver(LUSolverLAPACK, A, b, x)
test_lu_solver(LUSolver, A, b, x)
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1690 |
using SimpleSolvers
using SimpleSolvers: initialize!, solver_step!
using Test
struct NonlinearSolverTest{T} <: NonlinearSolver end
test_solver = NonlinearSolverTest{Float64}()
@test_throws ErrorException config(test_solver)
@test_throws ErrorException status(test_solver)
@test_throws ErrorException initialize!(test_solver, rand(3))
@test_throws ErrorException solver_step!(test_solver)
function F!(f, x)
f .= tan.(x)
end
function J!(g, x)
g .= 0
for i in eachindex(x)
g[i,i] = sec(x[i])^2
end
end
for (Solver, kwarguments) in (
(NewtonSolver, (linesearch = Static(),)),
(NewtonSolver, (linesearch = Backtracking(),)),
(NewtonSolver, (linesearch = Quadratic(),)),
(NewtonSolver, (linesearch = Bisection(),)),
(QuasiNewtonSolver, (linesearch = Static(),)),
(QuasiNewtonSolver, (linesearch = Backtracking(),)),
(QuasiNewtonSolver, (linesearch = Quadratic(),)),
(QuasiNewtonSolver, (linesearch = Bisection(),)),
# (NLsolveNewton, NamedTuple()),
)
for T in (Float64, Float32)
n = 1
x = ones(T, n)
y = zero(x)
nl = Solver(x, y; kwarguments...)
@test config(nl) == nl.config
@test status(nl) == nl.status
solve!(x, F!, nl)
# println(status(nl))
for _x in x
@test _x ≈ 0 atol = eps(T)
end
x = ones(T, n)
nl = Solver(x, y; J! = J!, kwarguments...)
solve!(x, F!, J!, nl)
# println(status(nl))
for _x in x
@test _x ≈ 0 atol = eps(T)
end
end
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 4032 |
using SimpleSolvers
using Test
f = x -> 1 + x^2
d = x -> 2x
x = Float64(π)
y = f(x)
z = d(x)
obj1 = UnivariateObjective(f, x)
obj2 = UnivariateObjective(f, d, x)
obj3 = TemporaryUnivariateObjective(f, d, x)
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 0
@test value(obj1, x) == value(obj2, x) == value(obj3, x) == y
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 1
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 0
@test value!(obj1, x) == value!(obj2, x) == value!(obj3, x) == y
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 2
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 0
@test value!(obj1, x) == value!(obj2, x) == value!(obj3, x) == y
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 2
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 0
@test value!!(obj1, x) == value!!(obj2, x) == y
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 3
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 0
@test value!(obj1, 2x) == value!(obj2, 2x) == value!(obj3, 2x)
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 4
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 0
@test obj1(2x) == obj2(2x) == obj3(2x)
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 4
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 0
SimpleSolvers.clear!(obj1)
SimpleSolvers.clear!(obj2)
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 0
@test derivative(obj1, x) == derivative(obj2, x) == derivative(obj3, x) == z
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 1
@test derivative!(obj1, x) == derivative!(obj2, x) == derivative!(obj3, x) == z
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 2
@test derivative!(obj1, x) == derivative!(obj2, x) == derivative!(obj3, x) == z
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 2
@test derivative!!(obj1, x) == derivative!!(obj2, x) == z
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 3
@test derivative!(obj1, 2x) == derivative!(obj2, 2x) == derivative!(obj3, 2x)
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test d_calls(obj1) == d_calls(obj2) == 4
function F(x)
1 + sum(x.^2)
end
function G!(g, x)
g .= 0
for i in eachindex(x,g)
g[i] = 2x[i]
end
end
n = 2
x = rand(n)
f = F(x)
g = SimpleSolvers.alloc_g(x)
G!(g, x)
obj1 = MultivariateObjective(F, x)
obj2 = MultivariateObjective(F, G!, x)
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 0
@test value(obj1, x) == value(obj2, x) == f
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 1
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 0
@test value!(obj1, x) == value!(obj2, x) == f
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 2
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 0
@test value!(obj1, x) == value!(obj2, x) == f
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 2
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 0
@test value!!(obj1, x) == value!!(obj2, x) == f
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 3
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 0
@test value!(obj1, 2x) == value!(obj2, 2x)
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 4
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 0
@test obj1(2x) == obj2(2x)
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 4
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 0
SimpleSolvers.clear!(obj1)
SimpleSolvers.clear!(obj2)
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 0
@test gradient(obj1, x) == gradient(obj2, x) == g
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 1
@test gradient!(obj1, x) == gradient!(obj2, x) == g
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 2
@test gradient!(obj1, x) == gradient!(obj2, x) == g
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 2
@test gradient!!(obj1, x) == gradient!!(obj2, x) == g
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 3
@test gradient!(obj1, 2x) == gradient!(obj2, 2x)
@test f_calls(obj1) == f_calls(obj2) == 0
@test g_calls(obj1) == g_calls(obj2) == 4
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 215 |
using SimpleSolvers
using Test
include("optimizers_problems.jl")
n = 1
x = ones(n)
nl = QuasiNewtonOptimizer(x, F)
@test config(nl) == nl.config
@test status(nl) == nl.status
solve!(x, nl)
println(status(nl))
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 244 |
function F(x)
# 1 + sum(x.^2)
y = one(eltype(x))
for _x in x
y += _x^2
end
return y
end
function ∇F!(g, x)
g .= 2 .* x
end
function H!(g, x)
g .= 0
for i in eachindex(x)
g[i,i] = 2
end
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 2016 |
using LinearAlgebra
using SimpleSolvers
using SimpleSolvers: gradient, hessian, linesearch, objective, initialize!, update!, solver_step!
using Test
include("optimizers_problems.jl")
struct OptimizerTest{T} <: OptimizationAlgorithm end
test_optim = OptimizerTest{Float64}()
test_x = zeros(3)
test_obj = MultivariateObjective(F, test_x)
@test_throws MethodError gradient(test_optim)
@test_throws MethodError hessian(test_optim)
@test_throws MethodError linesearch(test_optim)
@test_throws MethodError objective(test_optim)
@test_throws MethodError initialize!(test_optim, test_x)
@test_throws MethodError update!(test_optim, test_x)
@test_throws MethodError solver_step!(test_x, test_optim)
@test isaOptimizationAlgorithm(test_optim) == false
@test isaOptimizationAlgorithm(NewtonOptimizer(test_x, test_obj)) == true
@test isaOptimizationAlgorithm(BFGSOptimizer(test_x, test_obj)) == true
@test isaOptimizationAlgorithm(DFPOptimizer(test_x, test_obj)) == true
for method in (Newton(), BFGS(), DFP())
for linesearch in (Static(0.8), Backtracking(), Quadratic(), Bisection())
for T in (Float64, Float32)
n = 1
x = ones(T, n)
opt = Optimizer(x, F; algorithm = method, linesearch = linesearch)
@test config(opt) == opt.config
@test status(opt) == opt.result.status
if !(method == BFGS() && linesearch == Quadratic() && T == Float32)
# TODO: Investigate why this combination always fails.
solve!(x, opt)
# println(opt)
@test norm(minimizer(opt)) ≈ 0 atol=1E-7
@test norm(minimum(opt)) ≈ F(0) atol=1E-7
x = ones(T, n)
opt = Optimizer(x, F; ∇F! = ∇F!, algorithm = method, linesearch = linesearch)
solve!(x, opt)
# println(opt)
@test norm(minimizer(opt)) ≈ 0 atol=1E-7
@test norm(minimum(opt)) ≈ F(0) atol=1E-7
end
end
end
end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | code | 1123 | using SafeTestsets
@safetestset "Gradients " begin include("gradient_tests.jl") end
@safetestset "Jacobians " begin include("jacobian_tests.jl") end
@safetestset "Hessians " begin include("hessian_tests.jl") end
@safetestset "Objectives " begin include("objectives_tests.jl") end
@safetestset "Linear Solvers " begin include("linear_solvers_tests.jl") end
@safetestset "Line Searches " begin include("line_searches_tests.jl") end
@safetestset "Nonlinear Solvers " begin include("nonlinear_solvers_tests.jl") end
@safetestset "Optimizers " begin include("optimizers_tests.jl") end
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | docs | 1804 | # SimpleSolvers
[](https://JuliaGNI.github.io/SimpleSolvers.jl/stable)
[](https://JuliaGNI.github.io/SimpleSolvers.jl/latest)
[](https://juliaci.github.io/NanosoldierReports/pkgeval_badges/S/SimpleSolvers.html)
[](https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl/actions)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl)
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4317189)
This package provides simple linear and nonlinear solvers such as LU decomposition and Newton's method. Under a unified interface, it provides low-overhead implementations in pure Julia, applicable to a wide range of data types, and wraps methods from other Julia libraries. Nonlinear solvers can be used with linesearch algorithms. Jacobians can be computed via automatic differentiation, finite differences or manually.
## References
If you use SimpleSolvers.jl in your work, please consider citing it by
```
@misc{Kraus:2020:SimpleSolvers,
title={SimpleSolvers.jl: Simple linear and nonlinear solvers in Julia},
author={Kraus, Michael},
year={2020},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl}},
doi={10.5281/zenodo.4317189}
}
```
## Development
We are using git hooks, e.g., to enforce that all tests pass before pushing.
In order to activate these hooks, the following command must be executed once:
```
git config core.hooksPath .githooks
```
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.3.6 | 26000b0fbcbe3f05f89338f49988b99fd261c6eb | docs | 119 | ```@meta
CurrentModule = SimpleSolvers
```
# SimpleSolvers
```@index
```
```@autodocs
Modules = [SimpleSolvers]
```
| SimpleSolvers | https://github.com/JuliaGNI/SimpleSolvers.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 1799 | using Devito, BenchmarkTools
const SUITE = BenchmarkGroup()
nz,ny,nx = 102,101,100
grd = Grid(shape=(nz,ny,nx))
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grd, space_order=8)
d = data(f)
dhalo = data_with_halo(f)
dinhalo = data_with_inhalo(f)
dalloc = data_allocated(f)
_d = zeros(eltype(d), size(d))
_dhalo = zeros(eltype(dhalo), size(dhalo))
_dinhalo = zeros(eltype(dinhalo), size(dinhalo))
_dalloc = zeros(eltype(dalloc), size(dalloc))
SUITE["function"] = BenchmarkGroup()
SUITE["function"]["data"] = @benchmarkable data($f)
SUITE["function"]["data with halo"] = @benchmarkable data_with_halo($f)
SUITE["function"]["data with inhalo"] = @benchmarkable data_with_inhalo($f)
SUITE["function"]["data allocated"] = @benchmarkable data_allocated($f)
SUITE["function"]["data copy!"] = @benchmarkable copy!($_d, $d)
SUITE["function"]["data with halo copy!"] = @benchmarkable copy!($_dhalo, $dhalo)
SUITE["function"]["data with inhalo copy!"] = @benchmarkable copy!($_dinhalo, $dinhalo)
SUITE["function"]["data allocated copy!"] = @benchmarkable copy!($_dalloc, $dalloc)
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", grid=grd, npoint=1, nt=1000, coordinates=[50 50 50])
tf = TimeFunction(name="tf", grid=grd, time_order=8, space_order=8)
SUITE["sparse time function"] = BenchmarkGroup()
SUITE["sparse time function"]["data"] = @benchmarkable data($stf)
SUITE["sparse time function"]["data with halo"] = @benchmarkable data_with_halo($stf)
SUITE["sparse time function"]["data with inhalo"] = @benchmarkable data_with_inhalo($stf)
SUITE["sparse time function"]["data allocated"] = @benchmarkable data_allocated($stf)
SUITE["sparse time function"]["inject"] = @benchmarkable inject($stf; field=$(forward(tf)), expr=$stf)
SUITE["sparse time function"]["interpolate"] = @benchmarkable interpolate($stf; expr=tf)
SUITE
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 2357 | using Revise
using Devito
configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
configuration!("language", "openmp")
# configuration!("mpi", false)
x = SpaceDimension(name="x", spacing=Spacing(name="h_x", is_const=true))
z = SpaceDimension(name="z", spacing=Spacing(name="h_z", is_const=true))
function ricker!(src, f, _t, t₀)
t = reshape(_t, size(src))
src .= (1.0 .- 2.0 * (pi * f * (t .- t₀)).^2) .* exp.(-(pi * f * (t .- t₀)).^2)
end
grid = Grid(
dimensions = (z,x),
shape = (501,251),
origin = (0.0,0.0),
extent = (2500.0,1250.0),
dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=8)
v = Devito.Function(name="v", grid=grid, space_order=8)
q = Devito.Function(name="woverq", grid=grid, space_order=8)
b_data = data(b)
v_data = data(v)
q_data = data(q)
b_data .= 1
v_data .= 1.5
q_data .= 1/1000
time_range = 0.0f0:0.5f0:1000.0f0
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=8)
z,x,t = dimensions(p)
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=grid, npoint=1, nt=length(time_range))
src_coords = coordinates_data(src)
src_coords .= [625.0; 5.0]
src_data = data(src)
ricker!(src_data, 0.01, collect(time_range), 125)
src_term = inject(src; field=forward(p), expr=src*spacing(t)^2*v^2/b)
nz,nx,δz,δx = size(grid)...,spacing(grid)...
rec = SparseTimeFunction(name="rec", grid=grid, npoint=nx, nt=length(time_range))
rec_coords = coordinates_data(rec)
rec_coords[1,:] .= δx*(0:nx-1)
rec_coords[2,:] .= 10.0
rec_term = interpolate(rec, expr=p)
g1(field) = dx(field,x0=x+spacing(x)/2)
g3(field) = dz(field,x0=z+spacing(z)/2)
g1_tilde(field) = dx(field,x0=x-spacing(x)/2)
g3_tilde(field) = dz(field,x0=z-spacing(z)/2)
update_p = spacing(t)^2 * v^2 / b *
(g1_tilde(b * g1(p)) + g3_tilde(b * g3(p))) +
(2 - spacing(t) * q) * p +
(spacing(t) * q - 1) * backward(p)
stencil_p = Eq(forward(p), update_p)
dt = step(time_range)
smap = spacing_map(grid)
smap[spacing(t)] = dt
op = Operator([stencil_p, src_term, rec_term], subs=smap, name="OpExampleIso")
summary = apply(op)
@show summary
_p = data(p)
d = data(rec)
using PyPlot
_p = data(p)
d = data(rec)
figure();imshow(_p[:,:,1])
display(gcf())
savefig("p.png", bbox_inches="tight", dpi=150)
figure();imshow(d, aspect="auto",cmap="gray",clim=.1*[-1,1]*maximum(abs,d))
display(gcf())
savefig("d.png", bbox_inches="tight", dpi=150)
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 2341 | using Revise
using Devito
configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
configuration!("language", "openmp")
configuration!("mpi", false)
function ricker(f, _t, t₀)
t = reshape(_t, length(_t), 1)
(1.0 .- 2.0 * (pi * f * (t .- t₀)).^2) .* exp.(-(pi * f * (t .- t₀)).^2)
end
grid = Grid(
shape = (121,121,121),
origin = (0.0,0.0,0.0),
extent = (1210.0,1210.0,1210.0),
dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=8)
v = Devito.Function(name="v", grid=grid, space_order=8)
q = Devito.Function(name="woverq", grid=grid, space_order=8)
b_data = data(b)
v_data = data(v)
q_data = data(q)
# note that the folowing is faster if we include the halo
# i.e. use the data_with_halo method rather than the data method.
b_data .= 1
v_data .= 1.5
q_data .= 1/1000
time_range = 0.0f0:1.0f0:750.0f0
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=8)
z,y,x,t = dimensions(p)
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=grid, f0=0.01f0, npoint=1, nt=length(time_range), coordinates=[605.0 605.0 10.0])
src_data = data(src)
w = ricker(0.01, collect(time_range), 125)
copy!(src_data, w)
src_term = inject(src; field=forward(p), expr=src*spacing(t)^2*v^2/b)
nz,ny,nx,δz,δy,δx = size(grid)...,spacing(grid)...
rec = SparseTimeFunction(name="rec", grid=grid, npoint=nx, nt=length(time_range))
rec_coords = coordinates_data(rec)
rec_coords[1,:] .= δx*(0:nx-1)
rec_coords[2,:] .= 605
rec_coords[3,:] .= 20
rec_term = interpolate(rec, expr=p)
g1(field) = dx(field,x0=x+spacing(x)/2)
g2(field) = dy(field,x0=y+spacing(y)/2)
g3(field) = dz(field,x0=z+spacing(z)/2)
g1_tilde(field) = dx(field,x0=x-spacing(x)/2)
g2_tilde(field) = dy(field,x0=y-spacing(y)/2)
g3_tilde(field) = dz(field,x0=z-spacing(z)/2)
update_p = spacing(t)^2 * v^2 / b *
(g1_tilde(b * g1(p)) + g2_tilde(b * g2(p)) + g3_tilde(b * g3(p))) +
(2 - spacing(t) * q) * p +
(spacing(t) * q - 1) * backward(p)
stencil_p = Eq(forward(p), update_p)
dt = step(time_range)
smap = spacing_map(grid)
smap[spacing(t)] = dt
op = Operator([stencil_p, src_term, rec_term], subs=smap, name="OpExampleIso")
summary = apply(op)
using PyPlot
_p = data_with_halo(p)
extrema(_p)
d = data(rec)
extrema(d)
figure();imshow(_p[:,:,60,1])
display(gcf())
figure();imshow(d, aspect="auto",cmap="gray",clim=.1*[-1,1]*maximum(abs,d))
display(gcf()) | Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 3327 | using Revise
using Distributed, MPIClusterManagers
manager = MPIWorkerManager(4)
addprocs(manager)
@everywhere ENV["OMP_NUM_THREADS"] = 4
@everywhere using Revise
@everywhere using Devito
@everywhere using MPI
@everywhere configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
@everywhere configuration!("language", "openmp")
@everywhere configuration!("mpi", true)
@everywhere function ricker(f, _t, t₀)
t = reshape(_t, length(_t), 1)
(1.0 .- 2.0 * (pi * f * (t .- t₀)).^2) .* exp.(-(pi * f * (t .- t₀)).^2)
end
@everywhere function model()
write(stdout, "inside model()\n")
grid = Grid(
shape = (121,121,121),
origin = (0.0,0.0,0.0),
extent = (1210.0,1210.0,1210.0),
dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=8)
v = Devito.Function(name="vel", grid=grid, space_order=8)
q = Devito.Function(name="woverq", grid=grid, space_order=8)
b_data = data(b)
v_data = data(v)
q_data = data(q)
b_data .= 1
v_data .= 1.5
q_data .= 1/1000
time_range = 0.0f0:1.0f0:750.0f0
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=8)
z,y,x,t = dimensions(p)
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=grid, f0=0.01f0, npoint=1, nt=length(time_range), coordinates=[605.0 605.0 10.0])
src_data = data(src)
w = zeros(Float32, 1, length(time_range))
w[1,:] .= ricker(0.01, collect(time_range), 125)[:]
copy!(src_data, w)
src_term = inject(src; field=forward(p), expr=src * spacing(t)^2 * v^2 / b)
nz,ny,nx,δz,δy,δx = size(grid)...,spacing(grid)...
rec = SparseTimeFunction(name="rec", grid=grid, npoint=nx, nt=length(time_range))
rec_coords = coordinates_data(rec)
_rec_coords = zeros(Float32, length(dimensions(p))-1, nx)
_rec_coords[1,:] .= δx*(0:nx-1)
_rec_coords[2,:] .= 605
_rec_coords[3,:] .= 20
copy!(rec_coords, _rec_coords)
rec_term = interpolate(rec, expr=p)
g1(field) = dx(field,x0=x+spacing(x)/2)
g2(field) = dy(field,x0=y+spacing(y)/2)
g3(field) = dz(field,x0=z+spacing(z)/2)
g1_tilde(field) = dx(field,x0=x-spacing(x)/2)
g2_tilde(field) = dy(field,x0=y-spacing(y)/2)
g3_tilde(field) = dz(field,x0=z-spacing(z)/2)
# write the time update equation for u_x
update_p = spacing(t)^2 * v^2 / b *
(g1_tilde(b * g1(p)) + g2_tilde(b * g2(p)) + g3_tilde(b * g3(p))) +
(2 - spacing(t) * q) * p +
(spacing(t) * q - 1) * backward(p)
stencil_p = Eq(forward(p), update_p)
# update the dimension spacing_map to include the time dimension
# these symbols will be replaced with the relevant scalars by the Operator
dt = step(time_range)
smap = spacing_map(grid)
smap[spacing(t)] = dt
op = Operator([stencil_p, src_term, rec_term], subs=smap, name="OpExampleIso")
bx,by = 19,8
t_apply = @elapsed begin
summary = apply(op; x0_blk0_size=bx, y0_blk0_size=by)
end
write(stdout, "t_appy=$t_apply\n")
_p = data_with_halo(p)
_d = data(rec)
__d = convert(Array, _d)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
write("d.bin", __d)
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
nothing
end
@mpi_do manager model()
d = read!("d.bin", Array{Float32}(undef,751,121))
using PyPlot
figure(); imshow(d); display(gcf())
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 3131 | using Revise
using Distributed, AzManagers
ENV["OMP_NUM_THREADS"] = 4
addprocs("cbox120", 1; group="tqff-devito7", mpi_ranks_per_worker=16)
@everywhere using Revise
@everywhere using Devito
@everywhere using MPI
@everywhere configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
@everywhere configuration!("language", "openmp")
@everywhere configuration!("mpi", true)
@everywhere function ricker(f, _t, t₀)
t = reshape(_t, length(_t), 1)
(1.0 .- 2.0 * (pi * f * (t .- t₀)).^2) .* exp.(-(pi * f * (t .- t₀)).^2)
end
@everywhere function model()
MPI.Initialized() || MPI.Init()
write(stdout, "inside model()\n")
grid = Grid(
shape = (601,1201,1201),
origin = (0.0,0.0,0.0),
extent = (6000.0,12000.0,12000.0),
dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=8)
v = Devito.Function(name="vel", grid=grid, space_order=8)
q = Devito.Function(name="wOverQ", grid=grid, space_order=8)
b_data = data(b)
v_data = data(v)
q_data = data(q)
b_data .= 1
v_data .= 1.5
q_data .= 1/1000
time_range = 0.0f0:1.0f0:250.0f0
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=8)
z,y,x,t = dimensions(p)
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=grid, f0=0.01f0, npoint=1, nt=length(time_range), coordinates=[6500.0 6500.0 10.0])
src_data = data(src)
w = zeros(Float32, 1, length(time_range))
w[1,:] .= ricker(0.01, collect(time_range), 125)[:]
copy!(src_data, w)
src_term = inject(src; field=forward(p), expr=src * spacing(t)^2 * v^2 / b)
nz,ny,nx,δz,δy,δx = size(grid)...,spacing(grid)...
rec_coords = zeros(nx,3)
rec_coords[:,1] .= δx*[0:nx-1;]
rec_coords[:,2] .= 6500.0
rec_coords[:,3] .= 20.0
rec = SparseTimeFunction(name="rec", grid=grid, npoint=nx, nt=length(time_range), coordinates=rec_coords)
rec_term = interpolate(rec, expr=p)
g1(field) = dx(field,x0=x+spacing(x)/2)
g2(field) = dy(field,x0=y+spacing(y)/2)
g3(field) = dz(field,x0=z+spacing(z)/2)
g1_tilde(field) = dx(field,x0=x-spacing(x)/2)
g2_tilde(field) = dy(field,x0=y-spacing(y)/2)
g3_tilde(field) = dz(field,x0=z-spacing(z)/2)
# write the time update equation for u_x
update_p = spacing(t)^2 * v^2 / b *
(g1_tilde(b * g1(p)) + g2_tilde(b * g2(p)) + g3_tilde(b * g3(p))) +
(2 - spacing(t) * q) * p +
(spacing(t) * q - 1) * backward(p)
stencil_p = Eq(forward(p), update_p)
# update the dimension spacing_map to include the time dimension
# these symbols will be replaced with the relevant scalars by the Operator
dt = step(time_range)
smap = spacing_map(grid)
smap[spacing(t)] = dt
op = Operator([stencil_p, src_term, rec_term], subs=smap, name="OpExampleIso")
bx,by = 19,8
t_apply = @elapsed apply(op; x0_blk0_size=bx, y0_blk0_size=by)
write(stdout, "t_appy=$t_apply\n")
_p = data_with_halo(p)
_d = data(rec)
__d = convert(Array, _d)
__d
end
d = remotecall_fetch(model, workers()[1])
using PyPlot
figure(); imshow(d); display(gcf())
rmprocs(workers())
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 2821 | using Conda
dpro_repo = get(ENV, "DEVITO_PRO", "")
which_devito = get(ENV,"DEVITO_BRANCH", "")
try
Conda.pip_interop(true)
# optional devito pro installation
# note that the submodules do not install correctly from a URL, so we need install from local cloned repo
# 2024-07-29 this is totally hacked for nvidia HPCX and Open MPI 4.1.7a1
# using nvidia HPC SDK 24.7 and cuda 12.5
if dpro_repo != ""
@info "Building devitopro from latest release"
Conda.pip("uninstall -y", "devitopro")
Conda.pip("uninstall -y", "devito")
Conda.pip("uninstall -y", "numpy")
# clone the devitopro repository and init submodules
dir = "$(tempname())-devitopro"
_pwd = pwd()
Sys.which("git") === nothing && error("git is not installed")
run(`git clone $(dpro_repo) $(dir)`)
cd(dir)
run(`git submodule update --init`)
cd(_pwd)
# use nvc compiler
ENV["CC"] = "nvc"
# devitopro
Conda.pip("install", "$(dir)")
rm(dir, recursive=true, force=true)
# devito requirements
Conda.pip("install --no-cache-dir -r", "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/devitocodes/devito/master/requirements.txt")
# nvida requirements
Conda.pip("install --no-cache-dir -r", "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/devitocodes/devito/master/requirements-nvidia.txt")
# mpi requirements
ENV["CFLAGS"] = "-noswitcherror -tp=px"
Conda.pip("install --no-cache-dir -r", "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/devitocodes/devito/master/requirements-mpi.txt")
delete!(ENV,"CFLAGS")
# and finally ... mpi4py
# ENV["CFLAGS"] = "-noswitcherror -tp=px"
# Conda.pip("uninstall -y", "mpi4py")
# Conda.pip("install --no-cache-dir", "mpi4py")
elseif which_devito != ""
@info "Building devito from branch $(which_devito)"
Conda.pip("install", "devito[tests,extras,mpi]@git+https://github.com/devitocodes/devito@$(which_devito)")
else
@info "Building devito from latest release"
Conda.pip("uninstall -y", "devitopro")
Conda.pip("uninstall -y", "devito")
dir = "$(tempname())-devito"
Sys.which("git") === nothing && error("git is not installed")
run(`git clone https://github.com/devitocodes/devito $(dir)`)
Conda.pip("install", "$(dir)[tests,extras,mpi]")
rm(dir, recursive=true, force=true)
ENV["CC"] = "gcc"
ENV["CFLAGS"] = ""
ENV["MPICC"] = "mpicc"
Conda.pip("uninstall -y", "mpi4py")
Conda.pip("install", "mpi4py")
end
catch e
if get(ENV, "JULIA_REGISTRYCI_AUTOMERGE", "false") == "true"
@warn "unable to build"
else
throw(e)
end
end
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 136 | using Documenter, Devito
makedocs(sitename="Devito", modules=[Devito])
deploydocs(
repo = "github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git",
) | Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 74731 | module Devito
using MPI, PyCall, Strided
const numpy = PyNULL()
const sympy = PyNULL()
const devito = PyNULL()
const devitopro = PyNULL()
const seismic = PyNULL()
const utils = PyNULL()
const enriched = PyNULL()
has_devitopro() = devitopro != devito
function __init__()
try
copy!(numpy, pyimport("numpy"))
copy!(sympy, pyimport("sympy"))
copy!(devito, pyimport("devito"))
try
copy!(devitopro, pyimport("devitopro"))
catch e
copy!(devitopro, pyimport("devito"))
end
copy!(seismic, pyimport("examples.seismic"))
if has_devitopro()
copy!(enriched, pyimport("devitopro.types.enriched"))
end
# Utilities. Need to both load and also add to PYTHONPATH
# so that spawned python subprocesses find it as well
ppath = get(ENV, "PYTHONPATH", "")
upath = join(split(@__DIR__, "/")[1:end-1], "/")
pushfirst!(PyVector(pyimport("sys")."path"), upath)
copy!(utils, pyimport("src"))
catch e
if get(ENV, "JULIA_REGISTRYCI_AUTOMERGE", "false") == "true"
@warn "unable to pyimport"
else
throw(e)
end
end
end
PyCall.PyObject(::Type{Float32}) = numpy.float32
PyCall.PyObject(::Type{Float64}) = numpy.float64
PyCall.PyObject(::Type{Int8}) = numpy.int8
PyCall.PyObject(::Type{Int16}) = numpy.int16
PyCall.PyObject(::Type{Int32}) = numpy.int32
PyCall.PyObject(::Type{Int64}) = numpy.int64
PyCall.PyObject(::Type{ComplexF32}) = numpy.complex64
PyCall.PyObject(::Type{ComplexF64}) = numpy.complex128
function numpy_eltype(dtype)
if dtype == numpy.float32
return Float32
elseif dtype == numpy.float64
return Float64
elseif dtype == numpy.int8
return Int8
elseif dtype == numpy.int16
return Int16
elseif dtype == numpy.int32
return Int32
elseif dtype == numpy.int64
return Int64
elseif dtype == numpy.complex64
return ComplexF32
elseif dtype == numpy.complex128
return ComplexF64
else
error("Unsupported NumPy data type: $(dtype)")
end
end
"""
configuration!(key, value)
Configure Devito. Examples include
```julia
configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
configuration!("language", "openmp")
configuration!("mpi", false)
```
"""
function configuration!(key, value)
set!(devito."configuration", key, value)
get(devito."configuration", key)
end
configuration(key) = get(devito."configuration", key)
configuration() = devito.configuration
_reverse(argument::Tuple) = reverse(argument)
_reverse(argument) = argument
function reversedims(arguments)
_arguments = collect(arguments)
keys = first.(_arguments)
values = @. _reverse(last(_arguments))
(; zip(keys, values)...)
end
struct DevitoArray{T,N,A<:AbstractArray{T,N}} <: AbstractArray{T,N}
o::PyObject # Python object for the numpy array
p::A # copy-free
end
function DevitoArray{T,N}(o) where {T,N}
p = unsafe_wrap(Array{T,N}, Ptr{T}(o.__array_interface__["data"][1]), reverse(o.shape); own=false)
DevitoArray{T,N,Array{T,N}}(o, p)
end
function DevitoArray(o)
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
N = length(o.shape)
DevitoArray{T,N}(o)
end
Base.size(x::DevitoArray{T,N}) where {T,N} = size(x.p)
Base.parent(x::DevitoArray) = x.p
Base.getindex(x::DevitoArray{T,N,A}, i) where {T,N,A<:Array} = getindex(parent(x), i)
Base.getindex(x::DevitoArray{T,N,A}, I::Vararg{Int,N}) where {T,N,A<:StridedView} = getindex(parent(x), I...)
Base.setindex!(x::DevitoArray{T,N,A}, v, i) where {T,N,A<:Array} = setindex!(parent(x), v, i)
Base.setindex!(x::DevitoArray{T,N,A}, v, I::Vararg{Int,N}) where {T,N,A<:StridedView} = setindex!(parent(x), v, I...)
Base.IndexStyle(::Type{<:DevitoArray{<:Any,<:Any,<:Array}}) = IndexLinear()
Base.IndexStyle(::Type{<:DevitoArray{<:Any,<:Any,<:StridedView}}) = IndexCartesian()
Base.view(x::DevitoArray{T,N,Array{T,N}}, I::Vararg{Any}) where {T,N} = DevitoArray(x.o, sview(x.p, I...))
abstract type DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,N} <: AbstractArray{T,N} end
Base.parent(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray) = x.p
localsize(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,N}) where {T,N} = ntuple(i->size(x.local_indices[i])[1], N)
localindices(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,N}) where {T,N} = x.local_indices
decomposition(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray) = x.decomposition
topology(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray) = x.topology
function _size_from_local_indices(local_indices::NTuple{N,UnitRange{Int64}}) where {N}
n = ntuple(i->(size(local_indices[i])[1] > 0 ? local_indices[i][end] : 0), N)
MPI.Allreduce(n, max, MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
Base.size(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray) = x.size
function counts(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray)
[count(x, mycoords) for mycoords in CartesianIndices(topology(x))][:]
end
function Base.fill!(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray, v)
parent(x) .= v
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
x
end
Base.IndexStyle(::Type{<:DevitoMPIAbstractArray}) = IndexCartesian()
struct DevitoMPIArray{T,N,A<:AbstractArray{T,N},D} <: DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,N}
o::PyObject
p::A
local_indices::NTuple{N,UnitRange{Int}}
decomposition::D
topology::NTuple{N,Int}
size::NTuple{N,Int}
end
function DevitoMPIArray{T,N}(o, idxs, decomp::D, topo) where {T,N,D}
p = unsafe_wrap(Array{T,N}, Ptr{T}(o.__array_interface__["data"][1]), length.(idxs); own=false)
n = _size_from_local_indices(idxs)
DevitoMPIArray{T,N,Array{T,N},D}(o, p, idxs, decomp, topo, n)
end
function convert_resort_array!(_y::Array{T,N}, y::Vector{T}, topology, decomposition) where {T,N}
i = 1
for block_idx in CartesianIndices(topology)
idxs = CartesianIndices(ntuple(idim->decomposition[idim] === nothing ? size(_y, idim) : length(decomposition[idim][block_idx.I[idim]]), N))
for _idx in idxs
idx = CartesianIndex(ntuple(idim->decomposition[idim] === nothing ? _idx.I[idim] : decomposition[idim][block_idx.I[idim]][_idx.I[idim]], N))
_y[idx] = y[i]
i += 1
end
end
_y
end
function Base.convert(::Type{Array}, x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,N}) where {T,N}
local y
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
y = zeros(T, length(x))
y_vbuffer = VBuffer(y, counts(x))
else
y = Array{T}(undef, ntuple(_->0, N))
y_vbuffer = VBuffer(nothing)
end
_x = zeros(T, size(parent(x)))
copyto!(_x, parent(x))
MPI.Gatherv!(_x, y_vbuffer, 0, MPI.COMM_WORLD)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
_y = convert_resort_array!(Array{T,N}(undef, size(x)), y, x.topology, x.decomposition)
else
_y = Array{T,N}(undef, ntuple(_->0, N))
end
_y
end
function copyto_resort_array!(_y::Vector{T}, y::Array{T,N}, topology, decomposition) where {T,N}
i = 1
for block_idx in CartesianIndices(topology)
idxs = CartesianIndices(ntuple(idim->decomposition[idim] === nothing ? size(y, idim) : length(decomposition[idim][block_idx.I[idim]]), N))
for _idx in idxs
idx = CartesianIndex(ntuple(idim->decomposition[idim] === nothing ? _idx.I[idim] : decomposition[idim][block_idx.I[idim]][_idx.I[idim]], N))
_y[i] = y[idx]
i += 1
end
end
_y
end
function Base.copyto!(dst::DevitoMPIArray{T,N}, src::AbstractArray{T,N}) where {T,N}
_counts = counts(dst)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
_y = copyto_resort_array!(Vector{T}(undef, length(src)), src, dst.topology, dst.decomposition)
data_vbuffer = VBuffer(_y, _counts)
else
data_vbuffer = VBuffer(nothing)
end
_dst = MPI.Scatterv!(data_vbuffer, Vector{T}(undef, _counts[MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)+1]), 0, MPI.COMM_WORLD)
copyto!(parent(dst), _dst)
end
struct DevitoMPITimeArray{T,N,A<:AbstractArray{T,N},NM1,D} <: DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,N}
o::PyObject
p::A
local_indices::NTuple{N,UnitRange{Int}}
decomposition::D
topology::NTuple{NM1,Int}
size::NTuple{N,Int}
end
function DevitoMPITimeArray{T,N}(o, idxs, decomp::D, topo::NTuple{NM1,Int}) where {T,N,D,NM1}
p = unsafe_wrap(Array{T,N}, Ptr{T}(o.__array_interface__["data"][1]), length.(idxs); own=false)
n = _size_from_local_indices(idxs)
DevitoMPITimeArray{T,N,Array{T,N},NM1,D}(o, p, idxs, decomp, topo, n)
end
function Base.convert(::Type{Array}, x::DevitoMPITimeArray{T,N}) where {T,N}
local y
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
y = zeros(T, length(x))
y_vbuffer = VBuffer(y, counts(x))
else
y = Vector{T}(undef, 0)
y_vbuffer = VBuffer(nothing)
end
MPI.Gatherv!(convert(Array, parent(x)), y_vbuffer, 0, MPI.COMM_WORLD)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
_y = convert_resort_array!(Array{T,N}(undef, size(x)), y, x.topology, x.decomposition)
else
_y = zeros(T, ntuple(_->0, N))
end
_y
end
function Base.copy!(dst::DevitoMPIAbstractArray, src::AbstractArray)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
axes(dst) == axes(src) || throw(ArgumentError(
"arrays must have the same axes for copy! (consider using `copyto!`)"))
end
copyto!(dst, src)
end
function Base.copy!(dst::DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,1}, src::AbstractVector) where {T}
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
axes(dst) == axes(src) || throw(ArgumentError(
"arrays must have the same axes for copy! (consider using `copyto!`)"))
end
copyto!(dst, src)
end
function Base.copyto!(dst::DevitoMPITimeArray{T,N}, src::AbstractArray{T,N}) where {T,N}
_counts = counts(dst)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
_y = copyto_resort_array!(Vector{T}(undef, length(src)), src, dst.topology, dst.decomposition)
data_vbuffer = VBuffer(_y, _counts)
else
data_vbuffer = VBuffer(nothing)
end
_dst = MPI.Scatterv!(data_vbuffer, Vector{T}(undef, _counts[MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)+1]), 0, MPI.COMM_WORLD)
copyto!(parent(dst), _dst)
end
struct DevitoMPISparseTimeArray{T,N,NM1,D} <: DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,NM1}
o::PyObject
p::Array{T,NM1}
local_indices::NTuple{NM1,Vector{Int}}
decomposition::D
topology::NTuple{NM1,Int}
size::NTuple{NM1,Int}
end
function DevitoMPISparseTimeArray{T,N}(o, idxs, decomp::D, topo::NTuple{NM1,Int}) where {T,N,D,NM1}
local p
if length(idxs) == 0
p = Array{T,N}(undef, ntuple(_->0, N))
else
p = unsafe_wrap(Array{T,N}, Ptr{T}(o.__array_interface__["data"][1]), length.(idxs); own=false)
end
DevitoMPISparseTimeArray{T,N,NM1,D}(o, p, idxs, decomp, topo, globalsize(decomp))
end
localsize(x::DevitoMPISparseTimeArray) = length.(x.local_indices)
struct DevitoMPISparseArray{T,N,NM1,D} <: DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,N}
o::PyObject
p::Array{T,NM1}
local_indices::NTuple{NM1,Vector{Int}}
decomposition::D
topology::NTuple{NM1,Int}
size::NTuple{NM1,Int}
end
function DevitoMPISparseArray{T,N}(o, idxs, decomp::D, topo::NTuple{NM1,Int}) where {T,N,D,NM1}
local p
if prod(length.(idxs)) == 0
p = Array{T,N}(undef, ntuple(_->0, N))
else
p = unsafe_wrap(Array{T,N}, Ptr{T}(o.__array_interface__["data"][1]), length.(idxs); own=false)
end
DevitoMPISparseArray{T,N,NM1,D}(o, p, idxs, decomp, topo, globalsize(decomp))
end
localsize(x::DevitoMPISparseArray) = length.(x.local_indices)
globalsize(decomp) = ntuple( i -> max(cat(decomp[i]..., dims=1)...) - min(cat(decomp[i]..., dims=1)...) + 1 , length(decomp))
function count(x::Union{DevitoMPIArray,DevitoMPITimeArray,DevitoMPISparseArray,DevitoMPISparseTimeArray}, mycoords)
d = decomposition(x)
n = size(x)
mapreduce(idim->d[idim] === nothing ? n[idim] : length(d[idim][mycoords[idim]]), *, 1:length(d))
end
function Base.convert(::Type{Array}, x::Union{DevitoMPISparseTimeArray{T,N},DevitoMPISparseArray{T,N}}) where {T,N}
local y
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
y = zeros(T, length(x))
y_vbuffer = VBuffer(y, counts(x))
else
y = Array{T,N}(undef, ntuple(_->0, N))
y_vbuffer = VBuffer(nothing)
end
_x = zeros(T, size(parent(x)))
copyto!(_x, parent(x))
MPI.Gatherv!(_x, y_vbuffer, 0, MPI.COMM_WORLD)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
_y = convert_resort_array!(Array{T,N}(undef, size(x)), y, x.topology, x.decomposition)
else
_y = Array{T,N}(undef, ntuple(_->0, N))
end
_y
end
function Base.copyto!(dst::Union{DevitoMPISparseTimeArray{T,N},DevitoMPISparseArray{T,N}}, src::Array{T,N}) where {T,N}
_counts = counts(dst)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
_y = copyto_resort_array!(Vector{T}(undef, length(src)), src, dst.topology, dst.decomposition)
data_vbuffer = VBuffer(_y, _counts)
else
data_vbuffer = VBuffer(nothing)
end
_dst = MPI.Scatterv!(data_vbuffer, Vector{T}(undef, _counts[MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)+1]), 0, MPI.COMM_WORLD)
copyto!(parent(dst), _dst)
end
function in_range(i::Int, ranges)
for rang in enumerate(ranges)
if i ∈ rang[2]
return rang[1]
end
end
error("Outside Valid Ranges")
end
function helix_helper(tup::NTuple{N,Int}) where {N}
wrapper = (1,)
for i in 2:N
wrapper = (wrapper..., wrapper[1]*tup[i-1])
end
return wrapper
end
function find_rank(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,N}, I::Vararg{Int,N}) where {T,N}
decomp = decomposition(x)
rank_position = in_range.(I,decomp)
helper = helix_helper(topology(x))
rank = sum((rank_position .- 1) .* helper)
return rank
end
shift_localindicies(i::Int, indices::Union{UnitRange{Int},Vector{Int}}) = i - indices[1] + 1
shift_localindicies(i::Int, indices::Int) = i - indices + 1
function Base.getindex(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,N}, I::Vararg{Int,N}) where {T,N}
v = nothing
wanted_rank = find_rank(x, I...)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == wanted_rank
J = ntuple(idim-> shift_localindicies( I[idim], localindices(x)[idim]), N)
v = getindex(x.p, J...)
end
v = MPI.bcast(v, wanted_rank, MPI.COMM_WORLD)
v
end
function Base.setindex!(x::DevitoMPIAbstractArray{T,N}, v::T, I::Vararg{Int,N}) where {T,N}
myrank = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
if myrank == 0
@warn "`setindex!` for Devito MPI Arrays has suboptimal performance. consider using `copy!`"
end
wanted_rank = find_rank(x, I...)
if wanted_rank == 0
received_v = v
else
message_tag = 2*MPI.Comm_size(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
source_rank = 0
send_mesg = [v]
recv_mesg = 0 .* send_mesg
rreq = ( myrank == wanted_rank ? MPI.Irecv!(recv_mesg, source_rank, message_tag, MPI.COMM_WORLD) : MPI.Request())
sreq = ( myrank == source_rank ? MPI.Isend(send_mesg, wanted_rank, message_tag, MPI.COMM_WORLD) : MPI.Request() )
stats = MPI.Waitall!([rreq, sreq])
received_v = recv_mesg[1]
end
if myrank == wanted_rank
J = ntuple(idim-> shift_localindicies( I[idim], localindices(x)[idim]), N)
setindex!(x.p, received_v, J...)
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
#
# Dimension
#
abstract type AbstractDimension end
# here is Devito's dimension type hierarchy:
# https://github.com/devitocodes/devito/blob/02bbefb7e380d299a2508fef2923c1a4fbd5c59d/devito/types/dimension.py
# Python <-> Julia quick-and-dirty type/struct for dimensions
for (M,F) in ((:devito,:SpaceDimension),
(:devito,:SteppingDimension),
(:devito,:TimeDimension),
(:devito,:ConditionalDimension),
(:devito,:Dimension),
(:devito,:Spacing),
(:devito,:DefaultDimension))
@eval begin
struct $F <: AbstractDimension
o::PyObject
end
PyCall.PyObject(x::$F) = x.o
Base.convert(::Type{$F}, x::PyObject) = $F(x)
$F(args...; kwargs...) = pycall($M.$F, $F, args...; kwargs...)
export $F
end
end
# subdimensions, generated using subdimension helper functions for simplicity
abstract type AbstractSubDimension <: AbstractDimension end
for (M,F,G) in ((:devito,:SubDimensionLeft,:left),
(:devito,:SubDimensionRight, :right),
(:devito,:SubDimensionMiddle, :middle))
@eval begin
struct $F <: AbstractSubDimension
o::PyObject
end
PyCall.PyObject(x::$F) = x.o
Base.convert(::Type{$F}, x::PyObject) = $F(x)
$F(args...; kwargs...) = pycall($M.SubDimension.$G, $F, args...; kwargs...)
export $F
end
end
"""
SubDimensionLeft(args...; kwargs...)
Creates middle a SubDimension. Equivalent to devito.SubDimension.left helper function.
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
xm = SubDimensionLeft(name="xl", parent=x, thickness=2)
```
"""
function SubDimensionLeft end
"""
SubDimensionRight(args...; kwargs...)
Creates right a SubDimension. Equivalent to devito.SubDimension.right helper function.
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
xr = SubDimensionRight(name="xr", parent=x, thickness=3)
```
"""
function SubDimensionRight end
"""
SubDimensionMiddle(args...; kwargs...)
Creates middle a SubDimension. Equivalent to devito.SubDimension.middle helper function.
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
xm = SubDimensionMiddle(name="xm", parent=x, thickness_left=2, thickness_right=3)
```
"""
function SubDimensionMiddle end
"""
thickness(x::AbstractSubDimension)
Returns a tuple of a tuple containing information about the left and right thickness of a SubDimension and a symbol corresponding to each side's thickness.
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
xr = SubDimensionRight(name="xr", parent=x, thickness=2)
thickness(xr)
```
"""
thickness(x::AbstractSubDimension) = x.o.thickness
"""
parent(x::AbstractSubDimension)
Returns the parent dimension of a subdimension.
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
xr = SubDimensionRight(name="xr", parent=x, thickness=2)
parent(xr)
````
"""
Base.parent(x::AbstractSubDimension) = x.o.parent
# Python <-> Julia quick-and-dirty type/struct mappings
for (M,F) in ((:devito,:Eq), (:devito,:Injection), (:devito, :Inc))
@eval begin
struct $F
o::PyObject
end
PyCall.PyObject(x::$F) = x.o
Base.convert(::Type{$F}, x::PyObject) = $F(x)
$F(args...; kwargs...) = pycall($M.$F, $F, args...; kwargs...)
export $F
end
end
Base.:(==)(x::Eq,y::Eq) = x.o == y.o
struct Operator
o::PyObject
function Operator(args...; kwargs...)
if :name ∈ keys(kwargs)
new(pycall(devito.Operator, PyObject, args...; kwargs...))
else
new(pycall(devito.Operator, PyObject, args...; name="Kernel", kwargs...))
end
end
function Operator(op::PyObject)
if (:apply ∈ propertynames(op)) && (:ccode ∈ propertynames(op))
new(op)
else
error("PyObject is not an operator")
end
end
end
PyCall.PyObject(x::Operator) = x.o
Base.convert(::Type{Operator}, x::PyObject) = Operator(x)
export Operator
"""
Operator(expressions...[; optional named arguments])
Generate, JIT-compile and run C code starting from an ordered sequence of symbolic expressions,
and where you provide a list of `expressions` defining the computation.
See: https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/operator.html?highlight=operator#devito.operator.operator.Operator""
# Optional named arguments
* `name::String` Name of the Operator, defaults to “Kernel”.
* `subs::Dict` Symbolic substitutions to be applied to expressions.
* `opt::String` The performance optimization level. Defaults to configuration["opt"].
* `language::String` The target language for shared-memory parallelism. Defaults to configuration["language"].
* `platform::String` The architecture the code is generated for. Defaults to configuration["platform"].
* `compiler::String` The backend compiler used to jit-compile the generated code. Defaults to configuration["compiler"].
# Example
Assuming that one has constructed the following Devito expressions: `stencil_p`, `src_term` and `rec_term`,
```julia
op = Operator([stencil_p, src_term, rec_term]; name="opIso")
```
"""
function Operator end
struct Constant{T}
o::PyObject
end
"""
Constant(args...; kwargs...)
Symbol representing a constant, scalar value in symbolic equations.
A Constant carries a scalar value.
# kwargs
* `name::String` Name of the symbol.
* `value::Real` Value associated with the symbol. Defaults to 0.
* `dtype::Type{AbstractFloat}` choose from `Float32` or `Float64`. Default is `Float32`
"""
function Constant(args...; kwargs...)
o = pycall(devito.Constant, PyObject, args...; kwargs...)
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
Constant{T}(o)
end
function Constant(o::PyObject)
if (:is_const ∈ propertynames(o) ) && (o.is_const)
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
Constant{T}(o)
else
error("PyObject is not a Constant")
end
end
PyCall.PyObject(x::Constant{T}) where {T} = x.o
Base.convert(::Type{Constant}, x::PyObject) = Constant(x)
"""
data(x::Constant{T})
Returns `value(x::Constant{T})`. See `value` documentation for more information.
"""
data(x::Constant) = value(x)
"""
value(x::Constant)
Returns the value of a devito constant. Can not be used to change constant value, for that use value!(x,y)
"""
value(x::Constant{T}) where {T} = convert(T,x.o._value)
"""
isconst(x::Constant)
True if the symbol value cannot be modified within an Operator (and thus its value is provided by the user directly from Python-land), False otherwise.
"""
Base.isconst(x::Constant) = x.o.is_const
"""
value!(x::Constant{T},y::T)
Change the numerical value of a constant, x, after creation to y, after converting y to datatype T of constant x.
"""
function value!(x::Constant{T},y::Real) where {T}
x.o.data = PyObject(convert(T,y))
end
"""
SpaceDimension(;kwargs...)
Construct a space dimension that defines the extend of a physical grid.
See https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/dimension.html?highlight=spacedimension#devito.types.dimension.SpaceDimension.
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x", spacing=Constant(name="h_x", value=5.0))
````
"""
function SpaceDimension end
Base.:(==)(x::AbstractDimension,y::AbstractDimension) = x.o == y.o
PyCall.PyObject(x::AbstractDimension) = x.o
"""
ConditionalDimension(;kwargs)
Symbol defining a non-convex iteration sub-space derived from a parent Dimension, implemented by the compiler generating conditional “if-then” code within the parent Dimension’s iteration space.
See: https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/dimension.html?highlight=conditional#devito.types.dimension.ConditionalDimension
# Example
```julia
size, factor = 16, 4
i = SpaceDimension(name="i")
grid = Grid(shape=(size,),dimensions=(i,))
ci = ConditionalDimension(name="ci", parent=i, factor=factor)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=grid, shape=(size,), dimensions=(i,))
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid, shape=(div(size,factor),), dimensions=(ci,))
op = Operator([Eq(g, 1), Eq(f, g)],name="Cond")
```
"""
function ConditionalDimension end
factor(x::ConditionalDimension) = x.o.factor
export factor
Base.parent(x::Union{ConditionalDimension,SteppingDimension}) = x.o.parent
#
# Grid
#
struct Grid{T,N}
o::PyObject
end
"""
Grid(; shape[, optional key-word arguments...])
Construct a grid that can be used in the construction of a Devito Functions.
See: https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/grid.html?highlight=grid#devito.types.Grid
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x", spacing=Constant(name="h_x", value=5.0))
z = SpaceDimension(name="z", spacing=Constant(name="h_z", value=5.0))
grid = Grid(
dimensions = (x,z), # z is fast (row-major)
shape = (251,501),
origin = (0.0,0.0),
extent = (1250.0,2500.0),
dtype = Float32)
```
"""
function Grid(args...; kwargs...)
o = pycall(devito.Grid, PyObject, args...; reversedims(kwargs)...)
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
N = length(o.shape)
Grid{T,N}(o)
end
PyCall.PyObject(x::Grid) = x.o
Base.:(==)(x::Grid{T,N},y::Grid{T,N}) where{T,N} = x.o == y.o
Base.size(grid::Grid{T,N}) where {T,N} = reverse((grid.o.shape)::NTuple{N,Int})
extent(grid::Grid{T,N}) where {T,N} = reverse((grid.o.extent)::NTuple{N,Float64})
"""
origin(grid)
returns the tuple corresponding to the grid's origin
"""
origin(grid::Grid{T,N}) where {T,N} = reverse((grid.o.origin)::NTuple{N,Float64})
size_with_halo(grid::Grid{T,N}, h) where {T,N} = ntuple(i->size(grid)[i] + h[i][1] + h[i][2], N)
Base.size(grid::Grid, i::Int) = size(grid)[i]
Base.ndims(grid::Grid{T,N}) where {T,N} = N
Base.eltype(grid::Grid{T}) where {T} = T
spacing(x::Grid{T,N}) where {T,N} = reverse(x.o.spacing)
spacing_map(x::Grid{T,N}) where {T,N} = Dict( key => convert( T, val) for (key, val) in pairs(PyDict(x.o."spacing_map")))
#
# SubDomain
#
abstract type AbstractSubDomain{N} end
struct SubDomain{N} <: AbstractSubDomain{N}
o::PyObject
end
PyCall.PyObject(x::AbstractSubDomain) = x.o
"""
subdomains(grid)
returns subdomains associated with a Devito grid
"""
function subdomains(x::Grid{T,N}) where {T,N}
dictpre = x.o.subdomains
dict = Dict()
for key in keys(dictpre)
dict[key] = SubDomain{N}(dictpre[key])
end
return dict
end
"""
interior(x::grid)
returns the interior subdomain of a Devito grid
"""
interior(x::Grid{T,N}) where {T,N} = SubDomain{N}(x.o.interior)
Base.:(==)(x::AbstractSubDomain,y::AbstractSubDomain) = x.o == y.o
#
# Functions
#
abstract type DevitoMPI end
struct DevitoMPITrue <: DevitoMPI end
struct DevitoMPIFalse <: DevitoMPI end
abstract type DiscreteFunction{T,N,M} end
struct Function{T,N,M} <: DiscreteFunction{T,N,M}
o::PyObject
end
ismpi_distributed(o::PyObject) = (o._distributor === nothing) || (o._distributor.nprocs == 1) ? DevitoMPIFalse : DevitoMPITrue
"""
Devito.Function(; kwargs...)
Tensor symbol representing a discrete function in symbolic equations.
See: https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/function.html?highlight=function#devito.types.Function
# Example
```
x = SpaceDimension(name="x", spacing=Constant(name="h_x", value=5.0))
z = SpaceDimension(name="z", spacing=Constant(name="h_z", value=5.0))
grid = Grid(
dimensions = (x,z),
shape = (251,501), # assume x is first, z is second (i.e. z is fast in python)
origin = (0.0,0.0),
extent = (1250.0,2500.0),
dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=8)
```
"""
function Function(args...; kwargs...)
o = pycall(devitopro.Function, PyObject, args...; reversedims(kwargs)...)
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
N = length(o.dimensions)
M = ismpi_distributed(o)
Function{T,N,M}(o)
end
function Function(o::PyObject)
# ensure pyobject corresponds to a devito function
isafunction = (:is_Function ∈ propertynames(o)) && (o.is_Function == true)
isatimefunction = ((:is_TimeFunction ∈ propertynames(o)) && (o.is_TimeFunction == true))
isasparsefunction = ((:is_SparseFunction ∈ propertynames(o)) && (o.is_SparseFunction == true))
if (isafunction && ~(isatimefunction || isasparsefunction))
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
N = length(o.dimensions)
M = ismpi_distributed(o)
return Function{T,N,M}(o)
else
error("PyObject is not a devito.Function")
end
end
struct SubFunction{T,N,M} <: DiscreteFunction{T,N,M}
o::PyObject
end
struct TimeFunction{T,N,M} <: DiscreteFunction{T,N,M}
o::PyObject
end
"""
TimeFunction(; kwargs...)
Tensor symbol representing a discrete function in symbolic equations.
See https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/timefunction.html?highlight=timefunction#devito.types.TimeFunction.
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x", spacing=Constant(name="h_x", value=5.0))
z = SpaceDimension(name="z", spacing=Constant(name="h_z", value=5.0))
grid = Grid(
dimensions = (x,z),
shape = (251,501), # assume x is first, z is second (i.e. z is fast in python)
origin = (0.0,0.0),
extent = (1250.0,2500.0),
dtype = Float32)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=8)
```
"""
# function TimeFunction(args...; kwargs...)
# local o
# o = pycall(devitopro.TimeFunction, PyObject, args...; reversedims(kwargs)...)
# T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
# N = length(o.dimensions)
# M = ismpi_distributed(o)
# TimeFunction{T,N,M}(o)
# end
function TimeFunction(args...; lazy=false, kwargs...)
if lazy
o = pycall(devitopro.TimeFunction, PyObject, args...; reversedims(kwargs)...)
else
if ~has_devitopro()
@error "Automatic serialization only supported with devito pro"
end
# this is inelegant, TODO: find better way to handle layers.
# Issue is that PyCall interpets the layers as tuple, eliminating key metadata.
# TODO: Generate MFE and submit as issue to PyCall
o = utils."serializedtimefunc"(; Devito.reversedims(kwargs)...)
end
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
N = length(o.dimensions)
M = ismpi_distributed(o)
TimeFunction{T,N,M}(o)
end
function TimeFunction(o::PyObject)
# ensure pyobject corresponds to a devito timefunction
isatimefunction = ((:is_TimeFunction ∈ propertynames(o)) && (o.is_TimeFunction == true))
if (isatimefunction)
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
N = length(o.dimensions)
M = ismpi_distributed(o)
return TimeFunction{T,N,M}(o)
else
error("PyObject is not a devito.TimeFunction")
end
end
function serial2str(x::TimeFunction)
mypath = ""
if hasproperty(x.o, :_fnbase)
mypath = py"str"(x.o._fnbase)
else
@warn "Object doesn't have serialized path!"
end
return mypath
end
str2serial(y::String) = utils."str2path"(y)
abstract type SparseDiscreteFunction{T,N,M} <: DiscreteFunction{T,N,M} end
struct SparseTimeFunction{T,N,M} <: SparseDiscreteFunction{T,N,M}
o::PyObject
end
"""
SparseTimeFunction(; kwargs...)
Tensor symbol representing a space- and time-varying sparse array in symbolic equations.
See: https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/sparsetimefunction.html?highlight=sparsetimefunction
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x", spacing=Constant(name="h_x", value=5.0))
z = SpaceDimension(name="z", spacing=Constant(name="h_z", value=5.0))
grid = Grid(
dimensions = (x,z),
shape = (251,501), # assume x is first, z is second (i.e. z is fast in python)
origin = (0.0,0.0),
extent = (1250.0,2500.0),
dtype = Float32)
time_range = 0.0f0:0.5f0:1000.0f0
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=grid, npoint=1, nt=length(time_range))
```
"""
function SparseTimeFunction(args...; kwargs...)
o = pycall(devito.SparseTimeFunction, PyObject, args...; reversedims(kwargs)...)
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
N = length(o.shape)
M = ismpi_distributed(o)
SparseTimeFunction{T,N,M}(o)
end
function SparseTimeFunction(o::PyObject)
if (:is_SparseTimeFunction ∈ propertynames(o)) && (o.is_SparseTimeFunction == true)
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
N = length(o.shape)
M = ismpi_distributed(o)
return SparseTimeFunction{T,N,M}(o)
else
error("PyObject is not a devito.SparseTimeFunction")
end
end
struct SparseFunction{T,N,M} <: SparseDiscreteFunction{T,N,M}
o::PyObject
end
"""
SparseFunction(; kwargs...)
Tensor symbol representing a sparse array in symbolic equations.
See: https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/sparsefunction.html
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x", spacing=Constant(name="h_x", value=5.0))
z = SpaceDimension(name="z", spacing=Constant(name="h_z", value=5.0))
grid = Grid(
dimensions = (x,z),
shape = (251,501), # assume x is first, z is second (i.e. z is fast in python)
origin = (0.0,0.0),
extent = (1250.0,2500.0),
dtype = Float32)
src = SparseFunction(name="src", grid=grid, npoint=1)
```
"""
function SparseFunction(args...; kwargs...)
o = pycall(devito.SparseFunction, PyObject, args...; reversedims(kwargs)...)
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
N = length(o.shape)
M = ismpi_distributed(o)
SparseFunction{T,N,M}(o)
end
function SparseFunction(o::PyObject)
if ((:is_SparseFunction ∈ propertynames(o)) && (o.is_SparseFunction == true)) && ~((:is_SparseTimeFunction ∈ propertynames(o)) && (o.is_SparseTimeFunction == true))
T = numpy_eltype(o.dtype)
N = length(o.shape)
M = ismpi_distributed(o)
return SparseFunction{T,N,M}(o)
else
error("PyObject is not a devito.SparseFunction")
end
end
function CoordSlowSparseFunction(args...; kwargs...)
@pydef mutable struct coordslowsparse <: devito.SparseFunction
_sparse_position = 0
end
return SparseFunction(coordslowsparse(args...; reversedims(kwargs)...))
end
PyCall.PyObject(x::DiscreteFunction) = x.o
"""
grid(f::DiscreteFunction)
Return the grid corresponding to the discrete function `f`.
"""
grid(x::Function{T,N}) where {T,N} = Grid{T,N}(x.o.grid)
grid(x::TimeFunction{T,N}) where {T,N} = Grid{T,N-1}(x.o.grid)
function grid(x::SparseDiscreteFunction{T}) where {T}
N = length(x.o.grid.shape)
Grid{T,N}(x.o.grid)
end
"""
halo(x::DiscreteFunction)
Return the Devito "outer" halo size corresponding to the discrete function `f`.
"""
halo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N}) where {T,N} = reverse(x.o.halo)::NTuple{N,Tuple{Int,Int}}
"""
inhalo(x::DiscreteFunction)
Return the Devito "inner" halo size used for domain decomposition, and corresponding to
the discrete function `f`.
"""
inhalo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N}) where {T,N} = reverse(x.o._size_inhalo)::NTuple{N,Tuple{Int,Int}}
"""
size(x::DiscreteFunction)
Return the shape of the grid for the discrete function `x`.
"""
Base.size(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N}) where {T,N} = reverse(x.o.shape)::NTuple{N,Int}
"""
ndims(x::DiscreteFunction)
Return the number of dimensions corresponding to the discrete function `x`.
"""
Base.ndims(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N}) where {T,N} = N
"""
size_with_halo(x::DiscreteFunction)
Return the size of the grid associated with `x`, inclusive of the Devito "outer" halo.
"""
size_with_halo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N}) where{T,N} = reverse(convert.(Int, x.o.shape_with_halo))::NTuple{N,Int}
"""
size_with_inhalo(x::DiscreteFunction)
Return the size of the grid associated with `z`, inclusive the the Devito "inner" and "outer" halos.
"""
size_with_inhalo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N}) where {T,N} = reverse(x.o._shape_with_inhalo)::NTuple{N,Int}
Base.size(x::SparseDiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N} = size(data(x))
size_with_halo(x::SparseDiscreteFunction) = size(x)
localmask(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N}) where {T,N} = ntuple(i->convert(Int,x.o._mask_domain[N-i+1].start)+1:convert(Int,x.o._mask_domain[N-i+1].stop), N)::NTuple{N,UnitRange{Int}}
localmask_with_halo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N}) where {T,N} = ntuple(i->convert(Int,x.o._mask_outhalo[N-i+1].start)+1:convert(Int,x.o._mask_outhalo[N-i+1].stop), N)::NTuple{N,UnitRange{Int}}
localmask_with_inhalo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N}) where {T,N} = ntuple(i->convert(Int,x.o._mask_inhalo[N-i+1].start)+1:convert(Int,x.o._mask_inhalo[N-i+1].stop), N)::NTuple{N,UnitRange{Int}}
localindices(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPIFalse}) where {T,N} = localmask(x)
localindices_with_halo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPIFalse}) where {T,N} = localmask_with_halo(x)
localindices_with_inhalo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPIFalse}) where {T,N} = localmask_with_inhalo(x)
"""
space_order(x::Union{TimeFunction,Function})
Returns the space order for spatial derivatives defined on the associated TimeFunction or Function
"""
space_order(x::Union{TimeFunction,Function}) = x.o.space_order
"""
forward(x::TimeFunction)
Returns the symbol for the time-forward state of the `TimeFunction`.
See: https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/timefunction.html?highlight=forward#devito.types.TimeFunction.forward
"""
forward(x::TimeFunction) = x.o.forward
"""
backward(x::TimeFunction)
Returns the symbol for the time-backward state of the `TimeFunction`.
See: https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/timefunction.html?highlight=forward#devito.types.TimeFunction.backward
"""
backward(x::TimeFunction) = x.o.backward
"""
time_dim(x::Union{Grid,TimeFunction})
Returns the time dimension for the associated object.
"""
time_dim(x::Union{Grid,TimeFunction}) = dimension(x.o.time_dim)
"""
stepping_dim(x::Grid)
Returns the stepping dimension for the associated grid.
"""
stepping_dim(x::Grid) = dimension(x.o.stepping_dim)
export time_dim, stepping_dim
"""
subs(f::DiscreteFunction{T,N,M},dict::Dict)
Perform substitution on the dimensions of Devito Discrete Function f based on a dictionary.
# Example
```julia
grid = Grid(shape=(10,10,10))
z,y,x = dimensions(grid)
f = Devito.Function(grid=grid, name="f", staggered=x)
subsdict = Dict(x=>x-spacing(x)/2)
g = subs(f,subsdict)
```
"""
subs(f::DiscreteFunction{T,N,M},dict::Dict) where {T,N,M} = f.o.subs(dict)
"""
evaluate(x::PyObject)
Evaluate a PyCall expression
"""
evaluate(x::PyObject) = x.evaluate
"""
data(x::DiscreteFunction)
Return the data associated with the grid that corresponds to the discrete function `x`. This is the
portion of the grid that excludes the halo. In the case of non-MPI Devito, this returns an array
of type `DevitoArray`. In the case of the MPI Devito, this returns an array of type `DevitoMPIArray`.
The `data` can be converted to an `Array` via `convert(Array, data(x))`. In the case where `data(x)::DevitoMPIArray`,
this also *collects* the data onto MPI rank 0.
"""
data(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPIFalse}) where {T,N} = view(DevitoArray{T,N}(x.o."_data_allocated"), localindices(x)...)
"""
data_with_halo(x::DiscreteFunction)
Return the data associated with the grid that corresponds to the discrete function `x`. This is the
portion of the grid that excludes the inner halo and includes the outer halo. In the case of non-MPI
Devito, this returns an array of type `DevitoArray`. In the case of the MPI Devito, this returns an
array of type `DevitoMPIArray`.
The `data` can be converted to an `Array` via `convert(Array, data(x))`. In the case where `data(x)::DevitoMPIArray`,
this also *collects* the data onto MPI rank 0.
"""
data_with_halo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPIFalse}) where {T,N} = view(DevitoArray{T,N}(x.o."_data_allocated"), localindices_with_halo(x)...)
"""
data_with_inhalo(x::DiscreteFunction)
Return the data associated with the grid that corresponds to the discrete function `x`. This is the
portion of the grid that includes the inner halo and includes the outer halo. In the case of non-MPI
Devito, this returns an array of type `DevitoArray`. In the case of the MPI Devito, this returns an
array of type `DevitoMPIArray`.
The `data` can be converted to an `Array` via `convert(Array, data(x))`. In the case where `data(x)::DevitoMPIArray`,
this also *collects* the data onto MPI rank 0.
"""
data_with_inhalo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPIFalse}) where {T,N} = view(data_allocated(x), localindices_with_inhalo(x)...)
"""
data_allocated(x::DiscreteFunction)
Return the data associated with the grid that corresponds to the discrete function `x`. This is the
portion of the grid that includes the inner halo and includes the outer halo. We expect this to be
equivalent to `data_with_inhalo`.
The `data` can be converted to an `Array` via `convert(Array, data(x))`. In the case where `data(x)::DevitoMPIArray`,
this also *collects* the data onto MPI rank 0.
"""
data_allocated(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPIFalse}) where {T,N} = DevitoArray{T,N}(x.o."_data_allocated")
function localindices(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
localinds = PyCall.trygetproperty(x.o,"local_indices",nothing)
if localinds === nothing
return ntuple(i -> 0:-1, N)
else
return ntuple(i->convert(Int,localinds[N-i+1].start)+1:convert(Int,localinds[N-i+1].stop), N)
end
end
function one_based_decomposition(decomposition)
for idim = 1:length(decomposition)
if decomposition[idim] !== nothing
for ipart = 1:length(decomposition[idim])
decomposition[idim][ipart] .+= 1
end
end
end
decomposition
end
function getdecomp(x::DiscreteFunction)
decomppre = reverse(x.o._decomposition)
funcshape = reverse(x.o.shape)
decompout = ()
# if the decomp at a level is nothing, replace it with decomp over whole dim
for i in 1:length(decomppre)
if decomppre[i] === nothing
decompout = (decompout..., ([0:funcshape[i]-1;],))
else
decompout = (decompout..., decomppre[i])
end
end
return decompout
end
function getdecompwithhalo(x::DiscreteFunction)
decomppre = reverse(x.o._decomposition_outhalo)
funcshape = reverse(x.o.shape_with_halo)
decompout = ()
# if the decomp at a level is nothing, replace it with decomp over whole dim
for i in 1:length(decomppre)
if decomppre[i] === nothing
decompout = (decompout..., ([0:funcshape[i]-1;],))
else
decompout = (decompout..., decomppre[i])
end
end
return decompout
end
function topology(x::DiscreteFunction)
# this checks for non-distributor dimensions and tacks them on in the right position
distributordims = reverse(x.o._distributor.dimensions)
functiondims = reverse(x.o.dimensions)
topopre = reverse(x.o._distributor.topology)
topoout = ()
j = 1
for i in 1:length(functiondims)
if (j <= length(distributordims)) && (functiondims[i] == distributordims[j])
topoout = (topoout..., topopre[j])
j = j+1
else
topoout = (topoout..., 1)
end
end
return topoout
end
function mycoords(x::DiscreteFunction)
# this checks for non-distributor dimensions and tacks them on in the right position
distributordims = reverse(x.o._distributor.dimensions)
functiondims = reverse(x.o.dimensions)
mycoordspre = reverse(x.o._distributor.mycoords) .+ 1
mycoordsout = ()
j = 1
for i in 1:length(functiondims)
if (j <= length(distributordims)) && (functiondims[i] == distributordims[j])
mycoordsout = (mycoordsout..., mycoordspre[j])
j = j+1
else
mycoordsout = (mycoordsout..., 1)
end
end
return mycoordsout
end
decomposition(x::DiscreteFunction) = one_based_decomposition(getdecomp(x))
decomposition_with_halo(x::DiscreteFunction) = one_based_decomposition(getdecompwithhalo(x))
function decomposition_with_inhalo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
_decomposition = getdecomp(x)
h = inhalo(x)
ntuple(
idim->begin
if _decomposition[idim] === nothing
nothing
else
M = length(_decomposition[idim])
ntuple(
ipart->begin
n = length(_decomposition[idim][ipart])
strt = _decomposition[idim][ipart][1] + (h[idim][1] + h[idim][2])*(ipart-1) + 1
stop = _decomposition[idim][ipart][end] + (h[idim][1] + h[idim][2])*ipart + 1
[strt:stop;]
end,
M
)
end
end,
N
)
end
function localindices_with_inhalo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
h = inhalo(x)
localidxs = localindices(x)
n = size_with_inhalo(x)
_mycoords = mycoords(x)
_decomposition = decomposition(x)
ntuple(idim->begin
local strt,stop
if _decomposition[idim] == nothing
strt = 1
stop = n[idim]
else
strt = localidxs[idim][1] + (_mycoords[idim]-1)*(h[idim][1] + h[idim][2])
stop = strt + length(localidxs[idim]) - 1 + h[idim][1] + h[idim][2]
end
strt:stop
end, N)
end
function localindices_with_halo(x::DiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
h = halo(x)
localidxs = localindices(x)
n = size_with_halo(x)
_mycoords = mycoords(x)
_topology = topology(x)
_decomposition = decomposition(x)
ntuple(idim->begin
local strt,stop
if _decomposition[idim] == nothing
strt = 1
stop = n[idim]
else
strt = _mycoords[idim] == 1 ? localidxs[idim][1] : localidxs[idim][1] + h[idim][1]
stop = _mycoords[idim] == _topology[idim] ? localidxs[idim][end] + h[idim][1] + h[idim][2] : localidxs[idim][end] + h[idim][1]
end
strt:stop
end, N)
end
function data(x::Function{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
p = sview(parent(data_allocated(x)), localmask(x)...)
d = decomposition(x)
t = topology(x)
idxs = localindices(x)
n = _size_from_local_indices(idxs)
DevitoMPIArray{T,N,typeof(p),typeof(d)}(x.o."_data_allocated", p, idxs, d, t, n)
end
function data_with_halo(x::Function{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
p = sview(parent(data_allocated(x)), localmask_with_halo(x)...)
d = decomposition_with_halo(x)
t = topology(x)
idxs = localindices_with_halo(x)
n = _size_from_local_indices(idxs)
DevitoMPIArray{T,N,typeof(p),typeof(d)}(x.o."_data_allocated", p, idxs, d, t, n)
end
function data_with_inhalo(x::Function{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
p = sview(parent(data_allocated(x)), localmask_with_inhalo(x)...)
d = decomposition_with_inhalo(x)
t = topology(x)
idxs = localindices_with_inhalo(x)
n = _size_from_local_indices(idxs)
DevitoMPIArray{T,N,typeof(p),typeof(d)}(x.o."_data_allocated", p, idxs, d, t, n)
end
function data_allocated(x::Function{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
DevitoMPIArray{T,N}(x.o."_data_allocated", localindices_with_inhalo(x), decomposition(x), topology(x))
end
function data(x::TimeFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
p = sview(parent(data_allocated(x)), localmask(x)...)
d = decomposition(x)
t = topology(x)
idxs = localindices(x)
n = _size_from_local_indices(idxs)
DevitoMPITimeArray{T,N,typeof(p),length(t),typeof(d)}(x.o."_data_allocated", p, idxs, d, t, n)
end
function data_with_halo(x::TimeFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
p = sview(parent(data_allocated(x)), localmask_with_halo(x)...)
d = decomposition_with_halo(x)
t = topology(x)
idxs = localindices_with_halo(x)
n = _size_from_local_indices(idxs)
DevitoMPITimeArray{T,N,typeof(p),length(t),typeof(d)}(x.o."_data_allocated", p, idxs, d, t, n)
end
function data_with_inhalo(x::TimeFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
p = sview(parent(data_allocated(x)), localmask_with_inhalo(x)...)
d = decomposition_with_inhalo(x)
t = topology(x)
idxs = localindices_with_inhalo(x)
n = _size_from_local_indices(idxs)
DevitoMPITimeArray{T,N,typeof(p),length(t),typeof(d)}(x.o."_data_allocated", p, idxs, d, t, n)
end
function data_allocated(x::TimeFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
DevitoMPITimeArray{T,N}(x.o."_data_allocated", localindices_with_inhalo(x), decomposition(x), topology(x))
end
function data_allocated(x::SubFunction{T,2,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T}
topo = (1, MPI.Comm_size(MPI.COMM_WORLD)) # topo is not defined for sparse decompositions
d = DevitoMPIArray{T,2}(x.o."_data_allocated", localindices(x), decomposition(x), topo)
end
sparsetopo(x::Union{SparseFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue},SparseTimeFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}}) where {T,N} = ntuple(i-> length(decomposition(x)[i]) > 1 ? MPI.Comm_size(MPI.COMM_WORLD) : 1, N)
localindxhelper(x) = length(x) > 1 ? x[MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)+1] : x[1]
sparseindices(x::Union{SparseFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue},SparseTimeFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}}) where {T,N} = localindxhelper.(decomposition(x))
function data_with_inhalo(x::SparseFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
d = DevitoMPISparseArray{T,N}(x.o."_data_allocated", sparseindices(x), decomposition(x), sparsetopo(x))
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
d
end
# TODO - needed? <--
function data_with_inhalo(x::SparseTimeFunction{T,N,DevitoMPITrue}) where {T,N}
d = DevitoMPISparseTimeArray{T,N}(x.o."_data_allocated", sparseindices(x), decomposition(x), sparsetopo(x))
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
d
end
function data_with_inhalo(x::SparseDiscreteFunction{T,N,DevitoMPIFalse}) where {T,N}
d = DevitoArray{T,N}(x.o."_data_allocated")
d
end
data_with_halo(x::SparseDiscreteFunction{T,N,M}) where {T,N,M} = data_with_inhalo(x)
data(x::SparseDiscreteFunction{T,N,M}) where {T,N,M} = data_with_inhalo(x)
data(x::SubFunction{T,N,M}) where {T,N,M} = data_allocated(x)
# -->
"""
coordinates(x::SparseDiscreteFunction)
Returns a Devito function associated with the coordinates of a sparse time function.
Note that contrary to typical Julia convention, coordinate order is from slow-to-fast (Python ordering).
Thus, for a 3D grid, the sparse time function coordinates would be ordered x,y,z.
"""
coordinates(x::SparseDiscreteFunction{T,N,M}) where {T,N,M} = SubFunction{T,2,M}(x.o.coordinates)
"""
coordinates_data(x::SparseDiscreteFunction)
Returns a Devito array associated with the coordinates of a sparse time function.
Note that contrary to typical Julia convention, coordinate order is from slow-to-fast (Python ordering).
Thus, for a 3D grid, the sparse time function coordinates would be ordered x,y,z.
"""
coordinates_data(x::SparseDiscreteFunction{T,N,M}) where {T,N,M} = data(coordinates(x))
export DevitoArray, localindices, SubFunction
function dimension(o::PyObject)
if :is_Dimension ∈ propertynames(o)
if o.is_Conditional
return ConditionalDimension(o)
elseif o.is_Stepping
return SteppingDimension(o)
elseif o.is_Space
return SpaceDimension(o)
elseif o.is_Time
return TimeDimension(o)
elseif o.is_Default
return DefaultDimension(o)
elseif o.is_Dimension
return Dimension(o)
end
end
error("not implemented")
end
"""
dimensions(x::Union{Grid,DiscreteFunction})
Returns a tuple with the dimensions associated with the Devito grid.
"""
function dimensions(x::Union{Grid{T,N},DiscreteFunction{T,N},AbstractSubDomain{N}}) where {T,N}
ntuple(i->dimension(x.o.dimensions[N-i+1]), N)
end
"""
inject(x::SparseDiscreteFunction; kwargs...)
Generate equations injecting an arbitrary expression into a field.
See: Generate equations injecting an arbitrary expression into a field.
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x", spacing=Constant(name="h_x", value=5.0))
z = SpaceDimension(name="z", spacing=Constant(name="h_z", value=5.0))
grid = Grid(
dimensions = (x,z),
shape = (251,501), # assume x is first, z is second (i.e. z is fast in python)
origin = (0.0,0.0),
extent = (1250.0,2500.0),
dtype = Float32)
time_range = 0.0f0:0.5f0:1000.0f0
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=grid, npoint=1, nt=length(time_range))
src_term = inject(src; field=forward(p), expr=2*src)
```
"""
inject(x::SparseDiscreteFunction, args...; kwargs...) = pycall(PyObject(x).inject, Injection, args...; kwargs...)
"""
interpolate(x::SparseDiscreteFunction; kwargs...)
Generate equations interpolating an arbitrary expression into self.
See: https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/sparsetimefunction.html#devito.types.SparseTimeFunction.interpolate
# Example
```julia
x = SpaceDimension(name="x", spacing=Constant(name="h_x", value=5.0))
z = SpaceDimension(name="z", spacing=Constant(name="h_z", value=5.0))
grid = Grid(
dimensions = (z,x),
shape = (501,251), # assume z is first, x is second
origin = (0.0,0.0),
extent = (2500.0,1250.0),
dtype = Float32)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=8)
time_range = 0.0f0:0.5f0:1000.0f0
nz,nx,δz,δx = size(grid)...,spacing(grid)...
rec = SparseTimeFunction(name="rec", grid=grid, npoint=nx, nt=length(time_range))
rec_coords = coordinates_data(rec)
rec_coords[1,:] .= 10.0
rec_coords[2,:] .= δx*(0:nx-1)
rec_term = interpolate(rec, expr=p)
```
"""
interpolate(x::SparseDiscreteFunction; kwargs...) = pycall(PyObject(x).interpolate, PyObject; kwargs...)
"""
apply( operator::Operator; kwargs...)
Execute the Devito operator, `Operator`.
See: https://www.devitoproject.org/devito/operator.html?highlight=apply#devito.operator.operator.Operator.apply
Note that this returns a `summary::Dict` of the action of applying the operator. This contains information
such as the number of floating point operations executed per second.
"""
function apply(x::Operator, args...; kwargs...)
_summary = pycall(PyObject(x).apply, PyObject, args...; kwargs...)
summary = Dict()
for (k,v) in _summary.items()
summary[k] = Dict(
"time"=>v[1],
"gflopss"=>v[2],
"gpointss"=>v[3],
"oi"=>v[4],
"ops"=>v[5],
"itershape"=>v[6])
end
summary["globals"] = Dict()
if haskey(_summary.globals, "fdlike")
summary["globals"]["fdlike"] = Dict(
"time"=>_summary.globals["fdlike"][1],
"gflopss"=>_summary.globals["fdlike"][2],
"gpointss"=>_summary.globals["fdlike"][3],
"oi"=>_summary.globals["fdlike"][4],
"ops"=>_summary.globals["fdlike"][5],
"itershape"=>_summary.globals["fdlike"][6])
end
if haskey(_summary.globals, "vanilla")
summary["globals"]["vanilla"] = Dict(
"time"=>_summary.globals["vanilla"][1],
"gflopss"=>_summary.globals["vanilla"][2],
"gpointss"=>_summary.globals["vanilla"][3],
"oi"=>_summary.globals["vanilla"][4],
"ops"=>_summary.globals["vanilla"][5],
"itershape"=>_summary.globals["vanilla"][6])
end
summary
end
# derivative function
"""
Derivative(x::Union{Constant, Number}, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the derivative of a constant or number, which is zero.
"""
Derivative(x::Union{Constant, Number}, args...; kwargs...) = PyObject(0)
"""
Derivative(x::Union{DiscreteFunction,PyObject}, args...; kwargs...)
An unevaluated Derivative, which carries metadata (Dimensions,
derivative order, etc) describing how the derivative will be expanded
upon evaluation.
Parameters
----------
expr : expr-like
Expression for which the Derivative is produced.
dims : Dimension or tuple of Dimension
Dimenions w.r.t. which to differentiate.
fd_order : int or tuple of int, optional
Coefficient discretization order. Note: this impacts the width of
the resulting stencil. Defaults to 1.
deriv_order: int or tuple of int, optional
Derivative order. Defaults to 1.
side : Side or tuple of Side, optional
Side of the finite difference location, centered (at x), left (at x - 1)
or right (at x +1). Defaults to ``centered``.
transpose : Transpose, optional
Forward (matvec=direct) or transpose (matvec=transpose) mode of the
finite difference. Defaults to ``direct``.
subs : dict, optional
Substitutions to apply to the finite-difference expression after evaluation.
x0 : dict, optional
Origin (where the finite-difference is evaluated at) for the finite-difference
scheme, e.g. Dict(x=> x, y => y + spacing(y)/2).
Examples
--------
Creation
```julia
using Devito
grid = Grid((10, 10))
y, x = dimensions(grid)
u = Devito.Function(name="u", grid=grid, space_order=2)
Derivative(u, x)
# You can also specify the order as a keyword argument
Derivative(u, x, deriv_order=2)
# Or as a tuple
Derivative(u, (x, 2))
```
"""
Derivative(x::Union{DiscreteFunction,PyObject}, args...; kwargs...) = pycall(devito.Derivative, PyObject, PyObject(x), args...; kwargs...)
# metaprograming for various derivative shorthands
for F in (:dx,:dy,:dz,:dxr,:dyr,:dzr,:dxl,:dyl,:dzl,:dx2,:dy2,:dz2,:dxdy,:dxdz,:dydz)
@eval begin
$F(x::Union{DiscreteFunction,PyObject}, args...; kwargs...) = ( hasproperty(PyObject(x),Symbol($F)) ? pycall(PyObject(x).$F, PyObject, args...; kwargs...) : PyObject(0) )
$F(x::Union{Constant,Number}, args...; kwargs...) = PyObject(0)
export $F
end
end
"""
dx(f::Union{DiscreteFunction,PyObject,Constant,Number}, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the first derivative with respect to x if f is a Function with dimension x.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dx end
"""
dy(f::DiscreteFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the first derivative with respect to y if f is a Function with dimension y.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dy end
"""
dz(f::DiscreteFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the first derivative with respect to z if f is a Function with dimension z.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dz end
"""
dxl(f::DiscreteFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the first backward one-sided derivative with respect to x if f is a Function with dimension x.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dxl end
"""
dyl(f::DiscreteFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the first backward one-sided derivative with respect to y if f is a Function with dimension y.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dyl end
"""
dzl(f::DiscreteFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the first backward one-sided derivative with respect to z if f is a Function with dimension y.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dzl end
"""
dxr(f::DiscreteFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the first forward one-sided derivative with respect to x if f is a Function with dimension x.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dxr end
"""
dyr(f::DiscreteFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the first forward one-sided derivative with respect to y if f is a Function with dimension y.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dyr end
"""
dzr(f::DiscreteFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the first forward one-sided derivative with respect to z if f is a Function with dimension z.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dz end
"""
dx2(f::Union{DiscreteFunction,PyObject,Constant,Number}, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the second derivative with respect to x if f is a Function with dimension x.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dx2 end
"""
dy2(f::DiscreteFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the second derivative with respect to y if f is a Function with dimension y.
Otherwise returns 0. Thus, the derivative of a function with respect to a dimension it doesn't have is zero, as is the derivative of a constant.
"""
function dy2 end
# metaprograming for various derivatives
for F in (:dt,:dt2)
@eval begin
$F(x::Union{TimeFunction,PyObject}, args...; kwargs...) = pycall(PyObject(x).$F, PyObject, args...; kwargs...)
export $F
end
end
"""
dt(f::TimeFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the first time derivative of a time function
"""
function dt end
"""
dt2(f::TimeFunction, args...; kwargs...)
Returns the symbol for the second time derivative of a time function
"""
function dt2 end
# metaprogramming for basic operations
for F in ( :+, :-, :*, :/, :^)
@eval begin
Base.$F(x::Real,y::Union{DiscreteFunction,Constant,AbstractDimension}) = $F(PyObject(x),PyObject(y))
Base.$F(x::Union{DiscreteFunction,Constant,AbstractDimension}, y::Union{DiscreteFunction,Constant,AbstractDimension}) = $F(PyObject(x),PyObject(y))
Base.$F(x::Union{DiscreteFunction,Constant,Dimension}, y::PyObject) = $F(x.o,y)
Base.$F(x::PyObject, y::Union{DiscreteFunction,Constant,AbstractDimension}) = $F(x,y.o)
Base.$F(x::Union{DiscreteFunction,Constant,AbstractDimension}, y::Real) = $F(PyObject(x),PyObject(y))
end
end
Base.:(-)(x::Union{AbstractDimension,DiscreteFunction,PyObject,Constant}) = -1*x
Base.:(+)(x::Union{AbstractDimension,DiscreteFunction,PyObject,Constant}) = x
# metaprogramming to access Devito dimension boolean attributes
for F in (:is_Dimension, :is_Space, :is_Time, :is_Default, :is_Custom, :is_Derived, :is_NonlinearDerived, :is_Sub, :is_Conditional, :is_Stepping, :is_Modulo, :is_Incr)
@eval begin
$F(x::AbstractDimension) = x.o.$F::Bool
export $F
end
end
# metaprogramming for devito conditionals
for (M,F) in ((:devito,:Ne),(:devito,:Gt),(:devito,:Ge),(:devito,:Lt),(:devito,:Le),(:devito,:CondEq),(:devito,:CondNe))
@eval begin
$F(x::Union{Real,DiscreteFunction,PyObject,AbstractDimension},y::Union{Real,DiscreteFunction,PyObject,AbstractDimension}) = $M.$F(PyObject(x),PyObject(y))
export $F
end
end
# metaprogramming for symbolic operations on Devito dimensions
for F in (:symbolic_min, :symbolic_max, :spacing, :symbolic_size)
@eval begin
$F(x::AbstractDimension) = PyObject(x).$F
export $F
end
end
"""
symbolic_min(x::Dimension)
Symbol defining the minimum point of the Dimension
"""
function symbolic_min end
"""
symbolic_max(x::Dimension)
Symbol defining the maximum point of the Dimension
"""
function symbolic_max end
"""
spacing(x::Dimension)
Symbol representing the physical spacing along the Dimension.
"""
function spacing end
"""
is_Derived(x::Dimension)
Returns true when dimension is derived, false when it is not
"""
function is_Derived end
"""
symbolic_size(x::Dimension)
Symbol defining the size of the Dimension
"""
function symbolic_size end
# metaprograming for Devito functions taking variable number of arguments
for (M,F) in ((:devito,:Min), (:devito,:Max),(:sympy,:And))
@eval begin
$F(args...) = $M.$F((PyObject.(args))...)
export $F
end
end
"""
Min(args...)
Can be used in a Devito.Eq to return the minimum of a collection of arguments
Example:
```julia
eqmin = Eq(f,Min(g,1))
```
Is equivalent to f = Min(g,1) for Devito functions f,g
"""
function Min end
"""
Max(args...)
Can be used in a Devito.Eq to return the minimum of a collection of arguments
Example:
```julia
eqmax = Eq(f,Max(g,1))
```
Is equivalent to f = Max(g,1) for Devito functions f,g
"""
function Max end
# metaprograming for Devito mathematical operations ( more exist and may be added as required, find them at https://github.com/devitocodes/devito/blob/a8a33dc55ac3be008644c58a76b671028625679a/devito/finite_differences/elementary.py )
# these are broken out into four groups to help keep track of how they behave for unit testing
# functions defined on real numbers with equivalent in base
for F in (:cos, :sin, :tan, :sinh, :cosh, :tanh, :exp, :floor)
@eval begin
Base.$F(x::Union{AbstractDimension,DiscreteFunction,PyObject,Constant}) = devito.$F(PyObject(x))
end
end
# functions defined on real numbers who are written differently in base
for F in (:Abs,:ceiling)
@eval begin
$F(x::Union{AbstractDimension,DiscreteFunction,PyObject,Constant}) = devito.$F(PyObject(x))
export $F
end
end
# functions defined on positive numbers with equivalent in base
for F in (:sqrt,)
@eval begin
Base.$F(x::Union{AbstractDimension,DiscreteFunction,PyObject,Constant}) = devito.$F(PyObject(x))
end
end
# functions defined on positive numbers who are written differently in base
for F in (:ln,)
@eval begin
$F(x::Union{AbstractDimension,DiscreteFunction,PyObject,Constant}) = devito.$F(PyObject(x))
export $F
end
end
"""
Mod(x::AbstractDimension,y::Int)
Perform Modular division on a dimension
"""
Mod(x::AbstractDimension,y::Int) = sympy.Mod(PyObject(x),PyObject(y))
export Mod
"""Get symbolic representation for function index object"""
function Base.getindex(x::Union{TimeFunction,Function},args...)
return utils."indexobj"(x,reverse(args)...)
end
# helper functions for mapping arguments to python
shiftarg(x::Int) = x-1
shiftarg(x) = x
function pygetindex(x::PyObject,args...)
return utils."indexobj"(x,reverse(shiftarg.(args))...)
end
struct IndexedData
o::PyObject
end
"""
The wrapped IndexedData object.
"""
indexed(x::DiscreteFunction) = IndexedData(x)
IndexedData(x::DiscreteFunction) = IndexedData(x.o.indexed)
PyCall.PyObject(x::IndexedData) = x.o
Base.getindex(x::IndexedData,args...) = Indexed(pygetindex(x.o, args...))
struct Indexed
o::PyObject
Indexed(o) = ( hasproperty(o, :is_Indexed) && getproperty(o, :is_Indexed) ? new(o) : error("not indexed"))
end
PyCall.PyObject(x::Indexed) = x.o
"""
ccode(x::Operator; filename="")
Print the ccode associated with a devito operator.
If filename is provided, writes ccode to disk using that filename
"""
function ccode(x::Operator; filename="")
utils."ccode"(x.o,filename)
return nothing
end
"""
SubDomain(name, instructions)
Create a subdomain by passing a list of instructions for each dimension.
Using an instruction with (nothing,) implies that the whole dimension should be used for that subdomain, as will ("middle",0,0)
Examples:
```julia
instructions = ("left",2),("middle",3,3)
SubDomain("subdomain_name",instructions)
```
or
```julia
instructions = [("right",4),("middle",1,2)]
SubDomain("subdomain_name",instructions)
```
or
```julia
SubDomain("subdomain_name",("right",2),("left",1))
```
"""
SubDomain(name::String, instructions::Vector) = SubDomain(name, instructions...)
SubDomain(name::String, instructions::Tuple{Vararg{Tuple}}) = SubDomain(name, instructions...)
function SubDomain(name::String, instructions...)
# copy and reverse instructions
instructions = reverse(instructions)
N = length(instructions)
return SubDomain{N}(utils."subdom"(name,instructions))
end
struct Buffer
o::PyObject
end
"""
Buffer(value::Int)
Construct a devito buffer. This may be used as a save= keyword argument in the construction of TimeFunctions.
"""
Buffer(value::Int) = Buffer(pycall(devito.Buffer, PyObject, value))
PyCall.PyObject(x::Buffer) = x.o
"""
nsimplify(expr::PyObject; constants=(), tolerance=none, full=false, rational=none, rational_conversion="base10")
Wrapper around `sympy.nsimplify`.
Find a simple representation for a number or, if there are free symbols or
if ``rational=True``, then replace Floats with their Rational equivalents. If
no change is made and rational is not False then Floats will at least be
converted to Rationals.
# Explanation
For numerical expressions, a simple formula that numerically matches the
given numerical expression is sought (and the input should be possible
to evalf to a precision of at least 30 digits).
Optionally, a list of (rationally independent) constants to
include in the formula may be given.
A lower tolerance may be set to find less exact matches. If no tolerance
is given then the least precise value will set the tolerance (e.g. Floats
default to 15 digits of precision, so would be tolerance=10**-15).
With ``full=True``, a more extensive search is performed
(this is useful to find simpler numbers when the tolerance
is set low).
When converting to rational, if rational_conversion='base10' (the default), then
convert floats to rationals using their base-10 (string) representation.
When rational_conversion='exact' it uses the exact, base-2 representation.
See https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/52f606a503cea5e9588de14150ccb9f7f9ed4752/sympy/simplify/simplify.py .
# Examples:
```julia
nsimplify(π) # PyObject 314159265358979/100000000000000
```
```julia
nsimplify(π; tolerance=0.1) # PyObject 22/7
```
"""
nsimplify(expr::PyObject; constants=(), tolerance=nothing, full=false, rational=nothing, rational_conversion="base10") = pycall(sympy.nsimplify, PyObject, expr, constants=constants, tolerance=tolerance, full=full, rational=rational, rational_conversion=rational_conversion)
nsimplify(x::Number; kwargs...) = nsimplify(PyObject(x); kwargs...)
"""
solve(eq::PyObject, target::PyObject; kwargs...)
Algebraically rearrange an Eq w.r.t. a given symbol.
This is a wrapper around ``devito.solve``, which in turn is a wrapper around ``sympy.solve``.
# Parameters
* `eq::PyObject` expr-like. The equation to be rearranged.
* `target::PyObject` The symbol w.r.t. which the equation is rearranged. May be a `Function` or any other symbolic object.
## kwargs
* Symbolic optimizations applied while rearranging the equation. For more information. refer to `sympy.solve.__doc__`.
"""
solve(eq::PyObject, target::PyObject; kwargs...) = pycall(devito.solve, PyObject, eq, target, kwargs...)
"""
name(x::Union{SubDomain, DiscreteFunction, TimeFunction, Function, Constant, AbstractDimension, Operator})
returns the name of the Devito object
"""
name(x::Union{SubDomain, DiscreteFunction, Constant, AbstractDimension, Operator}) = x.o.name
Base.isequal(x::Union{SubDomain, DiscreteFunction, Constant, AbstractDimension, Operator, Grid, Eq, Inc, Injection, SparseDiscreteFunction}, y::Union{SubDomain, DiscreteFunction, Constant, AbstractDimension, Operator, Grid, Eq, Inc, Injection, SparseDiscreteFunction}) = isequal(PyObject(x), PyObject(y))
Base.hash(x::Union{SubDomain, DiscreteFunction, Constant, AbstractDimension, Operator, Grid, Eq, Inc, Injection}) = hash(PyObject(x))
# metaprogramming for unary ops
for F in (:Byref, :Deref, :Cast)
@eval begin
struct $F
o::PyObject
end
$F(base::Union{DiscreteFunction,IndexedData,Indexed,String}, kwargs...) = pycall(devito.symbolics.$F, $F, base, kwargs...) # Todo: support Sympy.Basic as well
PyCall.PyObject(x::$F) = x.o
Base.convert(::Type{$F}, x::PyObject) = $F(x)
export $F
end
end
"""
Symbolic representation of the C notation `&expr`.
"""
function Byref end
"""
Symbolic representation of the C notation `*expr`.
"""
function Deref end
"""
Symbolic representation of the C notation `(type)expr`.
"""
function Cast end
# metaprograming for various devito types for use in C
for F in (:Pointer,)
@eval begin
struct $F
o::PyObject
end
$F(args...; kwargs...) = pycall(devito.types.$F, $F, args...; kwargs...)
PyCall.PyObject(x::$F) = x.o
Base.convert(::Type{$F}, x::PyObject) = $F(x)
export $F
end
end
"""
Symbolic representation of a pointer in C
"""
function Pointer end
# DevitoPro Stuff
struct ABox{N} <: Devito.AbstractSubDomain{N}
o::PyObject
end
function ABox(src::Union{Devito.SparseTimeFunction,Nothing}, rcv::Union{Devito.SparseTimeFunction,Nothing}, vp::Devito.Function{T,N}, space_order::Int; kwargs...) where {T,N}
if ~has_devitopro()
@error "ABox only supported with DevitoPro"
end
o = pycall(devitopro.ABox, PyObject, src, rcv, vp, space_order; kwargs...)
ABox{N}(o)
end
intersection(box::ABox{N}, sub::Devito.SubDomain{N}) where {N} = ABox{N}(pycall(PyObject(box).intersection, PyObject, PyObject(sub)))
vp(abox::ABox) = Devito.Function(abox.o.vp)
eps(abox::ABox) = abox.o.eps
src(abox::ABox) = (typeof(abox.o.src) <: Nothing ? nothing : Devito.SparseTimeFunction(abox.o.src))
rcv(abox::ABox) = (typeof(abox.o.rcv) <: Nothing ? nothing : Devito.SparseTimeFunction(abox.o.rcv))
grid(abox::ABox) = Devito.grid(vp(abox))
function subdomains(abox::ABox{N}) where {N}
dict = Dict()
for dom in abox.o._subdomains
dict[dom.name] = SubDomain{N}(dom)
end
return dict
end
compute(abox::ABox; dt) = abox.o._compute(; dt=dt)
export ABox
struct CCall
o::PyObject
end
PyCall.PyObject(x::CCall) = x.o
function CCall(name::String; header=nothing, header_dirs = (), libs = (), lib_dirs = (), target = "host", types = ())
if ~has_devitopro()
@error "CCall only supported with DevitoPro"
end
classname = Symbol(uppercasefirst(name))
@eval begin
@pydef mutable struct $classname <: devitopro.CCall
name = $name
header = $header
header_dirs = $header_dirs
libs = $libs
lib_dirs = $lib_dirs
target = $target
types = $types
end
return CCall($classname)
end
end
name(x::CCall) = x.o.name
header(x::CCall) = x.o.header
header_dirs(x::CCall) = x.o.header_dirs
libs(x::CCall) = x.o.libs
lib_dirs(x::CCall) = x.o.lib_dirs
target(x::CCall) = x.o.target
types(x::CCall) = x.o.types
(f::CCall)(args...; kwargs...) = f.o(args...; kwargs...)
export CCall
export Buffer, Constant, CoordSlowSparseFunction, Derivative, DiscreteFunction, Grid, Function, SparseFunction, SparseTimeFunction, SubDomain, TimeFunction, apply, backward, ccode, configuration, configuration!, coordinates, coordinates_data, data, data_allocated, data_with_halo, data_with_inhalo, dimension, dimensions, dx, dy, dz, evaluate, extent, forward, grid, halo, indexed, inject, interpolate, localindices, localindices_with_halo, localindices_with_inhalo, localsize, name, nsimplify, origin, size_with_halo, simplify, solve, space_order, spacing, spacing_map, step, subdomains, subs, thickness, value, value!
end
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 556 | using Devito, PyCall, Test
const ctypes = PyNULL()
copy!(ctypes, pyimport("ctypes"))
@testset "Devito Pointer" begin
p = Pointer(name="pointer")
@test getproperty(PyObject(p), :_C_ctype) == ctypes.c_void_p
end
@testset "Devito Unary Ops" begin
g = Grid(shape=(4,4))
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=g)
bref = Byref(f)
@test getproperty(PyObject(bref), :_op) == "&"
dref = Deref(f)
@test getproperty(PyObject(dref), :_op) == "*"
cst = Cast(f, "char *")
@test getproperty(PyObject( cst), :_op) == "(char *)"
end
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 4819 | using Devito, Test
@testset "ABox Expanding Source" begin
g = Grid(shape=(8,8), extent=(7.0,7.0))
nt = 3
coords = [0.5 2.5; 2.5 2.5; 0.5 4.5; 2.5 4.5]
vp = Devito.Function(name="vp", grid=g, space_order=0)
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=g, nt=nt, npoint=size(coords)[1], coordinates=coords)
data(vp) .= 1.0
abox = ABox(src, nothing, vp, -1)
dt = 1.0
srcbox_discrete = Devito.compute(abox; dt=dt)
@test srcbox_discrete ≈ [0 4 2 2; 0 3 1 1; 0 2 0 0]
@test isequal(g, Devito.grid(abox))
@test isequal(src, Devito.src(abox))
@test isequal(nothing, Devito.rcv(abox))
@test isequal(vp, Devito.vp(abox))
end
# 2024-08-15 JKW these two ABox tests are broken -- some kind of API change?
@test_skip @testset "ABox Time Function" begin
g = Grid(shape=(5,5), extent=(4.0,4.0))
nt = 3
coords = [2. 2. ;]
space_order = 0
vp = Devito.Function(name="vp", grid=g, space_order=space_order)
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=g, nt=nt, npoint=size(coords)[1], coordinates=coords, space_order=0)
data(vp) .= 1.0
dt = 1.0
t = time_dim(g)
abox = ABox(src, nothing, vp, space_order)
u = TimeFunction(name="u", grid=g, save=nt, space_order=space_order)
op = Operator([Eq(forward(u), t+1, subdomain=abox)])
apply(op, dt=dt)
@test data(u)[:,:,1] ≈ zeros(Float32, 5 , 5)
@test data(u)[2:end-1,2:end-1,2] ≈ ones(Float32, 3, 3)
data(u)[2:end-1,2:end-1,2] .= 0
@test data(u)[:,:,2] ≈ zeros(Float32, 5 , 5)
@test data(u)[:,:,3] ≈ 2 .* ones(Float32, 5 , 5)
end
@test_skip @testset "ABox Intersection Time Function" begin
mid = SubDomain("mid",[("middle",2,2),("middle",0,0)])
g = Grid(shape=(5,5), extent=(4.0,4.0), subdomains=mid)
nt = 3
coords = [2. 2. ;]
space_order = 0
vp = Devito.Function(name="vp", grid=g, space_order=space_order)
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=g, nt=nt, npoint=size(coords)[1], coordinates=coords, space_order=0)
data(vp) .= 1.0
dt = 1.0
t = time_dim(g)
abox = ABox(src, nothing, vp, space_order)
intbox = Devito.intersection(abox,mid)
u = TimeFunction(name="u", grid=g, save=nt, space_order=space_order)
op = Operator([Eq(forward(u), t+1, subdomain=intbox)])
apply(op, dt=dt)
@test data(u)[:,:,1] ≈ zeros(Float32, 5 , 5)
@test data(u)[3,2:4,2] ≈ ones(Float32, 3)
data(u)[3,2:4,2] .= 0
@test data(u)[:,:,2] ≈ zeros(Float32, 5 , 5)
@test data(u)[3,:,3] ≈ 2 .* ones(Float32, 5)
data(u)[3,:,3] .= 0
@test data(u)[:,:,3] ≈ zeros(Float32, 5 , 5)
end
@testset "CCall with printf" begin
# CCall test written to use gcc
configuration!("compiler","gcc")
pf = CCall("printf", header="stdio.h")
@test Devito.name(pf) == "printf"
@test Devito.header(pf) == "stdio.h"
printingop = Operator([pf([""" "hello world!" """])])
ccode(printingop, filename="helloworld.c")
# read the program
code = read("helloworld.c", String)
# check to make sure header is in the program
@test occursin("#include \"stdio.h\"\n", code)
# check to make sure the printf statement is in the program
@test occursin("printf(\"hello world!\" );\n", code)
# test to make sure the operator compiles and runs
@test try apply(printingop)
true
catch
false
end
# remove the file
rm("helloworld.c", force=true)
end
# JKW: removing for now, not sure what is even being tested here
# @testset "Serialization with CCall T=$T" for T in (Float32,Float64)
# space_order = 2
# time_M = 3
# filename = "testserialization.bin"
# fo = CCall("fopen", header="stdio.h")
# fw = CCall("fwrite", header="stdio.h")
# fc = CCall("fclose", header="stdio.h")
# grid = Grid(shape=(4, 3), dtype=T)
# time = time_dim(grid)
# t = stepping_dim(grid)
# stream = Pointer(name="stream") # pointer to file object
# elesize = (T == Float32 ? 4 : 8)
# u = TimeFunction(name="u", grid=grid, space_order=space_order)
# @show size_with_halo(u)
# @show prod(size_with_halo(u)[1:end-1])
# nele = prod(size_with_halo(u)[1:end-1])
# eqnswrite = [ fo([""" "$filename" """,""" "w" """], stream),
# Eq(forward(u), u + 1.),
# fw([Byref(indexed(u)[-space_order+1, -space_order+1, t+1]), elesize, nele, stream], implicit_dims=(time,)),
# fc([stream])
# ]
# # CCall test written to use gcc
# opwrite = Operator(eqnswrite, compiler="gcc")
# apply(opwrite,time_M=time_M)
# holder = zeros(T, size_with_halo(u)[1:end-1]..., time_M)
# read!(filename, holder)
# for it in 1:time_M
# @test holder[space_order+1:end-space_order, space_order+1:end-space_order, it] ≈ it .* ones(T, size(u)[1:end-1]...)
# end
# rm(filename, force=true)
# end
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 7725 | using Devito, PyCall, Test
configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
configuration!("language", "openmp")
configuration!("mpi", false)
# test independent derivatives
function python_test_individual_derivatives()
python_code =
py"""
import numpy as np
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from devito import Grid, Function, Eq, Operator
nx,ny,nz = 11,11,11
dx,dy,dz = 10,10,10
grid = Grid(extent=(dx*(nx-1),dy*(ny-1),dz*(nz-1)), shape=(nx,ny,nz), origin=(0,0,0), dtype=np.float32)
x,y,z = grid.dimensions
fx = Function(name='fx', grid=grid, space_order=2)
fy = Function(name='fy', grid=grid, space_order=2)
fz = Function(name='fz', grid=grid, space_order=2)
gx = Function(name='gx', grid=grid, space_order=2)
gy = Function(name='gy', grid=grid, space_order=2)
gz = Function(name='gz', grid=grid, space_order=2)
a,b,c = 2,3,4
eq_x0 = Eq(fx, x.spacing * a * x)
eq_y0 = Eq(fy, y.spacing * b * y)
eq_z0 = Eq(fz, z.spacing * c * z)
eq_dx = Eq(gx, fx.dx(x0 = x + x.spacing / 2))
eq_dy = Eq(gy, fy.dy(x0 = y + y.spacing / 2))
eq_dz = Eq(gz, fz.dz(x0 = z + z.spacing / 2))
spacing_map = grid.spacing_map
op = Operator([eq_x0, eq_y0, eq_z0, eq_dx, eq_dy, eq_dz], subs=spacing_map, name="Op1")
op.apply()
print(gx.data[5,5,5])
print(gy.data[5,5,5])
print(gz.data[5,5,5])
assert_almost_equal(a, gx.data[nx//2,ny//2,nz//2], decimal=6)
assert_almost_equal(b, gy.data[nx//2,ny//2,nz//2], decimal=6)
assert_almost_equal(c, gz.data[nx//2,ny//2,nz//2], decimal=6)
f = open("operator1.python.c", "w")
print(op, file=f)
f.close()
"""
end
# test folding two discretiations in a mixed derivative
function python_test_mixed_derivatives()
python_code =
py"""
import numpy as np
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
from devito import Grid, Function, Eq, Operator
nx,ny,nz = 11,11,11
dx,dy,dz = 10,10,10
grid = Grid(extent=(dx*(nx-1),dy*(ny-1),dz*(nz-1)), shape=(nx,ny,nz), origin=(0,0,0), dtype=np.float32)
x,y,z = grid.dimensions
f = Function(name='f', grid=grid, space_order=2)
g = Function(name='g', grid=grid, space_order=2)
a,b,c = 2,3,4
eq = Eq(g, f.dx.dy.dz)
spacing_map = grid.spacing_map
op = Operator([eq], subs=spacing_map, name="Op2")
op.apply()
print(gx.data[5,5,5])
print(gy.data[5,5,5])
print(gz.data[5,5,5])
assert_almost_equal(a, gx.data[nx//2,ny//2,nz//2], decimal=6)
assert_almost_equal(b, gy.data[nx//2,ny//2,nz//2], decimal=6)
assert_almost_equal(c, gz.data[nx//2,ny//2,nz//2], decimal=6)
f = open("operator2.python.c", "w")
print(op, file=f)
f.close()
"""
end
# test subdomain creation
function python_test_subdomains()
python_code =
py"""
import numpy as np
from devito import SubDomain, Grid, Function, Eq, Operator
class fs1(SubDomain):
name = "fs"
def define(self, dimensions):
x, y = dimensions
return {x: ("middle", 0, 0), y: ("left", 1)}
grid = Grid(shape=(4,4), dtype=np.float32, subdomains=(fs1()))
fs = grid.subdomains["fs"]
all = grid.subdomains["domain"]
f = Function(name="f", grid=grid, space_order=4)
f.data[:] = 0
op1 = Operator([Eq(f, 1, subdomain=all)], name="subop1")
op1.apply()
out = open("subdomain.operator1.python.c", "w")
print(op1, file=out)
out.close()
f.data[:] = 0
op2 = Operator([Eq(f, 1, subdomain=fs)], name="subop2")
op2.apply()
out = open("subdomain.operator2.python.c", "w")
print(op2, file=out)
out.close()
"""
end
@testset "GenCodeDerivativesIndividual" begin
# python execution
python_test_individual_derivatives()
# julia with Devito.jl executionl
nz,ny,nx = 11,11,11
dz,dy,dx = 10,10,10
grid = Grid(extent=(dx*(nx-1),dy*(ny-1),dz*(nz-1)), shape=(nx,ny,nz), origin=(0,0,0), dtype=Float32)
z,y,x = dimensions(grid)
fz = Devito.Function(name="fz", grid=grid, space_order=2)
fy = Devito.Function(name="fy", grid=grid, space_order=2)
fx = Devito.Function(name="fx", grid=grid, space_order=2)
gz = Devito.Function(name="gz", grid=grid, space_order=2)
gy = Devito.Function(name="gy", grid=grid, space_order=2)
gx = Devito.Function(name="gx", grid=grid, space_order=2)
a,b,c = 2,3,4
eq_z0 = Eq(fz, spacing(z) * c * z)
eq_y0 = Eq(fy, spacing(y) * b * y)
eq_x0 = Eq(fx, spacing(x) * a * x)
eq_dz = Eq(gz, Devito.dz(fz,x0=z+spacing(z)/2))
eq_dy = Eq(gy, Devito.dy(fy,x0=y+spacing(y)/2))
eq_dx = Eq(gx, Devito.dx(fx,x0=x+spacing(x)/2))
spacing_map = Devito.spacing_map(grid)
op = Operator([eq_x0, eq_y0, eq_z0, eq_dx, eq_dy, eq_dz], subs=spacing_map, name="Op1")
apply(op)
ccode(op; filename="operator1.julia.c")
@show data(gx)[5,5,5]
@show data(gy)[5,5,5]
@show data(gz)[5,5,5]
@test data(gx)[5,5,5] == a
@test data(gy)[5,5,5] == b
@test data(gz)[5,5,5] == c
# check parity of generated code
@test success(`cmp --quiet operator1.julia.c operator1.python.c`)
rm("operator1.python.c", force=true)
rm("operator1.julia.c", force=true)
end
@testset "GenCodeDerivativesMixed" begin
# python execution
python_test_mixed_derivatives()
# julia with Devito.jl executionl
nz,ny,nx = 11,11,11
dz,dy,dx = 10,10,10
grid = Grid(extent=(dx*(nx-1),dy*(ny-1),dz*(nz-1)), shape=(nx,ny,nz), origin=(0,0,0), dtype=Float32)
z,y,x = dimensions(grid)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid, space_order=2)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=grid, space_order=2)
a,b,c = 2,3,4
eq = Eq(g, Devito.dz(Devito.dy(Devito.dx(f))))
spacing_map = Devito.spacing_map(grid)
op = Operator([eq], subs=spacing_map, name="Op2")
apply(op)
ccode(op; filename="operator2.julia.c")
# check parity of generated code
@test success(`cmp --quiet operator2.julia.c operator2.python.c`)
rm("operator1.python.c", force=true)
rm("operator1.julia.c", force=true)
end
@testset "GenCodeSubdomain" begin
# python execution
python_test_subdomains()
# julia with Devito.jl implementation
fs = SubDomain("fs", [("left",1), ("middle",0,0)])
grid = Devito.Grid(shape=(4,4), dtype=Float32, subdomains=(fs,))
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid, space_order=4)
fs = subdomains(grid)["fs"]
all = subdomains(grid)["domain"]
data(f)[:,:] .= 0
op1 = Operator([Eq(f, 1, subdomain=all)], name="subop1")
apply(op1)
ccode(op1; filename="subdomain.operator1.julia.c")
op2 = Operator([Eq(f, 1, subdomain=fs)], name="subop2")
apply(op2)
ccode(op2; filename="subdomain.operator2.julia.c")
# check parity of generated codes
@test success(`cmp --quiet subdomain.operator1.julia.c subdomain.operator1.python.c`)
@test success(`cmp --quiet subdomain.operator2.julia.c subdomain.operator2.python.c`)
# check that generated code w/o subdomains is different than that with subdomains
@test ~success(`cmp --quiet subdomain.operator1.julia.c subdomain.operator2.julia.c`)
# clean up
rm("subdomain.operator1.julia.c", force=true)
rm("subdomain.operator2.julia.c", force=true)
rm("subdomain.operator1.python.c", force=true)
rm("subdomain.operator2.python.c", force=true)
end
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 42900 | using Devito, MPI, Random, Strided, Test
MPI.Init()
configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
configuration!("language", "openmp")
configuration!("mpi", true)
@testset "DevitoMPIArray, fill!, with halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data_with_halo(b)
@test isa(b_data, Devito.DevitoMPIArray{Float32,length(n)})
if length(n) == 2
@test size(b_data) == (15,14)
else
@test size(b_data) == (16,15,14)
end
b_data .= 3.14f0
for rnk in 0:1
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == rnk
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(b_data) ≈ 3.14*ones(Float32, 15, 7)
else
@test parent(b_data) ≈ 3.14*ones(Float32, 16, 15, 7)
end
@test isa(parent(b_data), StridedView)
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
end
@testset "DevitoMPIArray, fill!, no halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data(b)
@test isa(b_data, Devito.DevitoMPIArray{Float32,length(n)})
@test size(b_data) == n
b_data .= 3.14f0
b_data_test = data(b)
for rnk in 0:1
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == rnk
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(b_data_test) ≈ 3.14*ones(Float32, 11, 5)
else
@test parent(b_data_test) ≈ 3.14*ones(Float32, 12, 11, 5)
end
@test isa(parent(b_data_test), StridedView)
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
end
@testset "DevitoMPIArray, copy!, inhalo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data_with_inhalo(b)
@test isa(b_data, Devito.DevitoMPIArray{Float32,length(n)})
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (15,18) : (16,15,18)
@test size(b_data) == _n
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test = reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
b_data_test = reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
for rnk in 0:1
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == rnk
if rnk == 0
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,1:9]
else
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,:,1:9]
end
elseif rnk == 1
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,10:18]
else
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,:,10:18]
end
end
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
end
@testset "DevitoMPIArray, copy!, halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data_with_halo(b)
@test isa(b_data, Devito.DevitoMPIArray{Float32,length(n)})
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (15,14) : (16,15,14)
@test size(b_data) == _n
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test = reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
b_data_test = reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
for rnk in 0:1
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == rnk
if rnk == 0
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,1:7]
else
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,:,1:7]
end
end
if rnk == 1
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,8:14]
else
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,:,8:14]
end
end
@test isa(parent(b_data), StridedView)
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
end
@testset "DevitoMPIArray, copy!, no halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data(b)
@test isa(b_data, Devito.DevitoMPIArray{Float32,length(n)})
@test size(b_data) == n
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test = reshape(Float32[1:prod(n);], n)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
_b_data = data(b)
b_data_test = reshape(Float32[1:prod(n);], n)
for rnk in 0:1
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == rnk
if rnk == 0
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,1:5]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,1:5]
else
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,:,1:5]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,:,1:5]
end
@test isa(parent(_b_data), StridedView)
end
if rnk == 1
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,6:10]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,6:10]
else
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,:,6:10]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,:,6:10]
end
@test isa(parent(_b_data), StridedView)
end
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray, then back, inhalo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data_with_inhalo(b)
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (15,18) : (16,15,18)
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
b_data_out = convert(Array, b_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test b_data_out ≈ b_data_test
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray, then back, halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data_with_halo(b)
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (15,14) : (16,15,14)
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
_b_data = data_with_halo(b)
b_data_out = convert(Array, _b_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test b_data_out ≈ b_data_test
end
end
@testset "Convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray then back, no halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data(b)
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(n);], n)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
_b_data = data(b)
b_data_out = convert(Array, _b_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test b_data_out ≈ b_data_test
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
@testset "DevitoMPITimeArray, copy!, data, inhalo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10))
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=2)
p_data = data_with_inhalo(p)
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (15,18,3) : (16,15,18,3)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
p_data_local = parent(p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if length(n) == 2
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,1:9,:]
else
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,:,1:9,:]
end
end
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 1
if length(n) == 2
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,10:18,:]
else
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,:,10:18,:]
end
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
@testset "DevitoMPIArray localsize, n=$n" for n in ((5,4),(6,5,4))
g = Grid(shape=n)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=g)
h = Devito.TimeFunction(name="h", grid=g, time_order=2)
for func in (f,h)
@test localsize(data(func)) == length.(Devito.localindices(data(func)))
end
end
@testset "DevitoMPISparseArray localsize, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ((5,4),(6,5,4)), npoint in (1,5,10)
g = Grid(shape=n)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", grid=g, npoint=npoint)
@test localsize(data(sf)) == length.(Devito.localindices(data(sf)))
end
@testset "DevitoMPISparseTimeArray localsize, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ((5,4),(6,5,4)), npoint in (1,5,10)
g = Grid(shape=n)
nt = 11
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", grid=g, nt=11, npoint=npoint)
@test localsize(data(stf)) == length.(Devito.localindices(data(stf)))
end
@testset "DevitoMPITimeArray, copy!, data, halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10))
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=2)
p_data = data_with_halo(p)
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (15,14,3) : (16,15,14,3)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
p_data_local = parent(p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if length(n) == 2
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,1:7,:]
else
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,:,1:7,:]
end
end
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 1
if length(n) == 2
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,8:14,:]
else
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,:,8:14,:]
end
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
@testset "DevitoMPITimeArray, copy!, data, no halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10))
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=2)
p_data = data(p)
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (11,10,3) : (12,11,10,3)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
p_data_local = parent(p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if length(n) == 2
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,1:5,:]
else
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,:,1:5,:]
end
end
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 1
if length(n) == 2
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,6:10,:]
else
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,:,6:10,:]
end
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPITimeArray, then back, inhalo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=2)
p_data = data_with_inhalo(p)
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (15,18,3) : (16,15,18,3)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
_p_data_test = convert(Array, p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test p_data_test ≈ _p_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoSparseMPIArray, then back, extra dimension n=$n, nextra=$nextra, npoint=$npoint, first=$first" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), nextra in (1,2,5), first in (true,false), npoint in (1,2,5)
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
extradim = Dimension(name="extra")
space_order = 2
prec = Dimension(name="prec")
npoint = 8
sparsedims = (extradim, prec)
sparseshape = (nextra, npoint)
if ~first
sparsedims = reverse(sparsedims)
sparseshape = reverse(sparseshape)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", grid=grid, dimensions=sparsedims, shape=sparseshape, npoint=npoint)
else
sf = CoordSlowSparseFunction(name="sf", grid=grid, dimensions=sparsedims, shape=sparseshape, npoint=npoint)
end
sf_data_test = zeros(Float32, sparseshape...)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
sf_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(sparseshape);], sparseshape)
end
copy!( data(sf), sf_data_test)
_sf_data_test = convert(Array, data(sf))
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test sf_data_test ≈ _sf_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoSparseMPITimeArray, then back, extra dimension n=$n, nextra=$nextra, npoint=$npoint, nt=$nt" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), nextra in (1,2,5), npoint in (1,2,5), nt in (1,5,10)
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
extradim = Dimension(name="extra")
space_order = 2
t = time_dim(grid)
prec = Dimension(name="prec")
npoint = 8
sparsedims = (prec, extradim, t)
sparseshape = (npoint, nextra, nt)
sf = SparseTimeFunction(name="sf", grid=grid, dimensions=sparsedims, shape=sparseshape, npoint=npoint, nt=nt)
sf_data_test = zeros(Float32, sparseshape...)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
sf_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(sparseshape);], sparseshape)
end
copy!( data(sf), sf_data_test)
_sf_data_test = convert(Array, data(sf))
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test sf_data_test ≈ _sf_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray, then back, halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=2)
p_data = data_with_halo(p)
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (15,14,3) : (16,15,14,3)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
_p_data_test = convert(Array, p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test p_data_test ≈ _p_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPITimeArray, then back, no halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=2)
p_data = data(p)
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (11,10,3) : (12,11,10,3)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
_p_data_test = convert(Array, p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test p_data_test ≈ _p_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray, then back, extra dimension, n=$n, nextra=$nextra, first=$first" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), nextra in (1,2,5), first in (true,false)
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
extradim = Dimension(name="extra")
space_order = 2
time = stepping_dim(grid)
if first
funcdims = (extradim, dimensions(grid)...)
funcshap = (nextra, n...)
else
funcdims = (dimensions(grid)..., extradim)
funcshap = (n..., nextra)
end
timedims = (funcdims..., time)
timeshap = (funcshap..., 2)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=space_order, dimensions=funcdims, shape=funcshap)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=space_order, dimensions=timedims, shape=timeshap)
b_data = data(b)
p_data = data(p)
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, funcshap)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, timeshap)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(funcshap);], funcshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timeshap);], timeshap)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(funcshap);], funcshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timeshap);], timeshap)
_b_data_test = convert(Array, b_data)
_p_data_test = convert(Array, p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test b_data_test ≈ _b_data_test
@test p_data_test ≈ _p_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray, then back, extra dimensions inhalo, n=$n, nextra=$nextra, first=$first" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), nextra in (1,2,5), first in (false,true)
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
extradim = Dimension(name="extra")
space_order = 2
time = stepping_dim(grid)
padded = (length(n) == 2 ? (15, 18) : (16, 15, 18))
if first
funcdims = (extradim, dimensions(grid)...)
funcshap = (nextra, n...)
arrayshap = (nextra, padded...)
else
funcdims = (dimensions(grid)..., extradim)
funcshap = (n..., nextra)
arrayshap = (padded..., nextra)
end
timedims = (funcdims..., time)
timeshap = (funcshap..., 2)
timearrayshap = (arrayshap..., 2)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=space_order, dimensions=funcdims, shape=funcshap)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=space_order, dimensions=timedims, shape=timeshap)
b_data = data_with_inhalo(b)
p_data = data_with_inhalo(p)
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, arrayshap)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, timearrayshap)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(arrayshap);], arrayshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timearrayshap);], timearrayshap)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(arrayshap);], arrayshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timearrayshap);], timearrayshap)
_b_data_test = convert(Array, b_data)
_p_data_test = convert(Array, p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test b_data_test ≈ _b_data_test
@test p_data_test ≈ _p_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray, then back, extra dimensions with halo, n=$n, nextra=$nextra, first=$first" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), nextra in (1,2,5), first in (false,true)
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
extradim = Dimension(name="extra")
space_order = 2
time = stepping_dim(grid)
padded = (length(n) == 2 ? (15, 14) : (16, 15, 14))
if first
funcdims = (extradim, dimensions(grid)...)
funcshap = (nextra, n...)
arrayshap = (nextra, padded...)
else
funcdims = (dimensions(grid)..., extradim)
funcshap = (n..., nextra)
arrayshap = (padded..., nextra)
end
timedims = (funcdims..., time)
timeshap = (funcshap..., 2)
timearrayshap = (arrayshap..., 2)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=space_order, dimensions=funcdims, shape=funcshap)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=space_order, dimensions=timedims, shape=timeshap)
b_data = data_with_halo(b)
p_data = data_with_halo(p)
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, arrayshap)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, timearrayshap)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(arrayshap);], arrayshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timearrayshap);], timearrayshap)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(arrayshap);], arrayshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timearrayshap);], timearrayshap)
_b_data_test = convert(Array, b_data)
_p_data_test = convert(Array, p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test b_data_test ≈ _b_data_test
@test p_data_test ≈ _p_data_test
end
end
@testset "DevitoMPITimeArray coordinates check, 2D" begin
ny,nx = 4,6
grd = Grid(shape=(ny,nx), extent=(ny-1,nx-1), dtype=Float32)
time_order = 1
fx = TimeFunction(name="fx", grid=grd, time_order=time_order, save=time_order+1, allowpro=false)
fy = TimeFunction(name="fy", grid=grd, time_order=time_order, save=time_order+1, allowpro=false)
sx = SparseTimeFunction(name="sx", grid=grd, npoint=ny*nx, nt=time_order+1)
sy = SparseTimeFunction(name="sy", grid=grd, npoint=ny*nx, nt=time_order+1)
cx = [ix-1 for iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx][:]
cy = [iy-1 for iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx][:]
coords = zeros(Float32, 2, ny*nx)
coords[1,:] .= cx
coords[2,:] .= cy
copy!(coordinates_data(sx), coords)
copy!(coordinates_data(sy), coords)
datx = reshape(Float32[ix for iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx, it = 1:time_order+1][:], nx*ny, time_order+1)
daty = reshape(Float32[iy for iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx, it = 1:time_order+1][:], nx*ny, time_order+1)
copy!(data(sx), datx)
copy!(data(sy), daty)
eqx = inject(sx, field=forward(fx), expr=sx)
eqy = inject(sy, field=forward(fy), expr=sy)
op = Operator([eqx, eqy], name="CoordOp")
apply(op)
x = convert(Array, data(fx))
y = convert(Array, data(fy))
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if VERSION >= v"1.7"
@test x ≈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0]
@test y ≈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0]
else
_x = zeros(Float32, ny, nx, 2)
_x[:,:,1] .= [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0]
_x[:,:,2] .= [1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0]
@test x ≈ _x
_y = zeros(Float32, ny, nx, 2)
_y[:,:,1] .= [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0]
_y[:,:,2] .= [1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0]
@test y ≈ _y
end
end
end
@testset "DevitoMPITimeArray coordinates check, 3D" begin
nz,ny,nx = 4,5,6
grd = Grid(shape=(nz,ny,nx), extent=(nz-1,ny-1,nx-1), dtype=Float32)
time_order = 1
fx = TimeFunction(name="fx", grid=grd, time_order=time_order, allowpro=false, save=time_order+1)
fy = TimeFunction(name="fy", grid=grd, time_order=time_order, allowpro=false, save=time_order+1)
fz = TimeFunction(name="fz", grid=grd, time_order=time_order, allowpro=false, save=time_order+1)
sx = SparseTimeFunction(name="sx", grid=grd, npoint=nz*ny*nx, nt=time_order+1)
sy = SparseTimeFunction(name="sy", grid=grd, npoint=nz*ny*nx, nt=time_order+1)
sz = SparseTimeFunction(name="sz", grid=grd, npoint=nz*ny*nx, nt=time_order+1)
cx = [ix-1 for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx][:]
cy = [iy-1 for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx][:]
cz = [iz-1 for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx][:]
coords = zeros(Float32, 3, nz*ny*nx)
coords[1,:] .= cx
coords[2,:] .= cy
coords[3,:] .= cz
copy!(coordinates_data(sx), coords)
copy!(coordinates_data(sy), coords)
copy!(coordinates_data(sz), coords)
datx = reshape(Float32[ix for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx, it = 1:time_order+1][:], nx*ny*nz, time_order+1)
daty = reshape(Float32[iy for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx, it = 1:time_order+1][:], nx*ny*nz, time_order+1)
datz = reshape(Float32[iz for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx, it = 1:time_order+1][:], nx*ny*nz, time_order+1)
copy!(data(sx), datx)
copy!(data(sy), daty)
copy!(data(sz), datz)
eqx = inject(sx, field=forward(fx), expr=sx)
eqy = inject(sy, field=forward(fy), expr=sy)
eqz = inject(sz, field=forward(fz), expr=sz)
op = Operator([eqx, eqy, eqz], name="CoordOp")
apply(op)
x = convert(Array, data(fx))
y = convert(Array, data(fy))
z = convert(Array, data(fz))
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if VERSION >= v"1.7"
@test x ≈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0;;; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0;;; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0;;; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0; 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0; 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0; 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0;;; 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0; 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0; 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0; 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0]
@test y ≈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0]
@test z ≈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0]
end
end
end
@testset "Sparse function coordinates, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), npoint in (1, 5, 10)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", npoint=npoint, grid=grid)
sf_coords = coordinates_data(sf)
@test isa(sf_coords, Devito.DevitoMPIArray)
@test size(sf_coords) == (length(n),npoint)
x = reshape(Float32[1:length(n)*npoint;], length(n), npoint)
copy!(sf_coords, x)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if npoint == 1
@test isempty(parent(sf_coords))
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(sf_coords) ≈ (x[:,1:2])
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(sf_coords) ≈ (x[:,1:5])
end
else
if npoint == 1
@test parent(sf_coords) ≈ x
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(sf_coords) ≈ (x[:,3:end])
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(sf_coords) ≈ (x[:,6:end])
end
end
# round trip
_sf_coords = convert(Array,coordinates_data(sf))
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test _sf_coords ≈ x
end
end
@testset "Sparse time function coordinates, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), npoint in (1, 5, 10)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", npoint=npoint, nt=100, grid=grid)
stf_coords = coordinates_data(stf)
@test isa(stf_coords, Devito.DevitoMPIArray)
@test size(stf_coords) == (length(n),npoint)
x = reshape(Float32[1:length(n)*npoint;], length(n), npoint)
copy!(stf_coords, x)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if npoint == 1
@test isempty(parent(stf_coords))
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(stf_coords) ≈ (x[:,1:2])
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(stf_coords) ≈ (x[:,1:5])
end
else
if npoint == 1
@test parent(stf_coords) ≈ x
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(stf_coords) ≈ (x[:,3:end])
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(stf_coords) ≈ (x[:,6:end])
end
end
# round trip
_stf_coords = convert(Array,coordinates_data(stf))
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test _stf_coords ≈ x
end
end
@testset "Sparse function size npoint=$npoint" for npoint in (1,5)
grid = Grid(shape=(11,12), dtype=Float32)
nt = 100
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", npoint=npoint, grid=grid)
@test size(sf) == (npoint,)
@test size_with_halo(sf) == (npoint,)
end
@testset "Sparse time function size npoint=$npoint" for npoint in (1,5)
grid = Grid(shape=(11,12), dtype=Float32)
nt = 100
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", npoint=npoint, nt=nt, grid=grid)
@test size(stf) == (npoint,nt)
@test size_with_halo(stf) == (npoint,nt)
end
@testset "Sparse function, copy!, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), npoint in (1, 5, 10)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", npoint=npoint, grid=grid)
x = Array{Float32}(undef,0)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
x = Float32[1:npoint;]
end
_x = data(sf)
copy!(_x, x)
x = Float32[1:npoint;]
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if npoint == 1
@test isempty(parent(_x))
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[1:2]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[1:5]
end
else
if npoint == 1
@test parent(_x) ≈ x
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[3:5]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[6:10]
end
end
end
@testset "Sparse time function, copy!, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), npoint in (1, 5, 10)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
nt = 100
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", npoint=npoint, nt=nt, grid=grid)
x = Matrix{Float32}(undef,0,0)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
x = reshape(Float32[1:prod(nt*npoint);], npoint, nt)
end
_x = data(stf)
copy!(_x, x)
x = reshape(Float32[1:prod(nt*npoint);], npoint, nt)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if npoint == 1
@test isempty(parent(_x))
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[1:2,:]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[1:5,:]
end
else
if npoint == 1
@test parent(_x) ≈ x
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[3:5,:]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[6:10,:]
end
end
end
@testset "Sparse function, copy! and convert, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), npoint in (1, 5, 10)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", npoint=npoint, grid=grid)
x = zeros(Float32, npoint)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
x .= Float32[1:npoint;]
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
_x = data(sf)
@test isa(data(sf), Devito.DevitoMPISparseArray)
copy!(_x, x)
x .= Float32[1:npoint;]
__x = convert(Array, _x)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test __x ≈ x
end
end
@testset "Sparse time function, copy! and convert, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), npoint in (1, 5, 10)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
nt = 100
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", npoint=npoint, nt=nt, grid=grid)
x = zeros(Float32, npoint, nt)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
x .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(nt*npoint);], npoint, nt)
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
_x = data(stf)
@test isa(data(stf), Devito.DevitoMPISparseTimeArray)
copy!(_x, x)
x .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(nt*npoint);], npoint, nt)
__x = convert(Array, _x)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test __x ≈ x
end
end
@testset "DevitoMPISparseTimeArray copy! axes check, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", npoint=10, nt=100, grid=grid)
stf_data = data(stf)
@test size(stf_data) == (10,100)
x = rand(100,10)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test_throws ArgumentError copy!(stf_data, x)
end
end
@testset "MPI Getindex for Function n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (5,4), (7,2), (4,5,6), (2,3,4) )
N = length(n)
rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
arr = reshape(1f0*[1:prod(size(grid));], size(grid))
copy!(data(f), arr)
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
for check in 1:nchecks
i = rand((1:n[1]))
j = rand((1:n[2]))
I = (i,j)
if N == 3
k = rand((1:n[3]))
I = (i,j,k)
end
@test data(f)[I...] == arr[I...]
end
if N == 2
@test data(f)[1:div(n[1],2),:] ≈ arr[1:div(n[1],2),:]
else
@test data(f)[1:div(n[1],2),div(n[2],3):2*div(n[2],3),:] ≈ arr[1:div(n[1],2),div(n[2],3):2*div(n[2],3),:]
end
end
@testset "MPI Getindex for TimeFunction n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (5,4), (7,2), (4,5,6), (2,3,4) )
N = length(n)
nt = 5
rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
f = TimeFunction(name="f", grid=grid, save=nt, allowpro=false)
arr = reshape(1f0*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
copy!(data(f), arr)
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
for check in 1:nchecks
i = rand((1:n[1]))
j = rand((1:n[2]))
I = (i,j)
if N == 3
k = rand((1:n[3]))
I = (i,j,k)
end
m = rand((1:nt))
I = (I...,m)
@test data(f)[I...] == arr[I...]
end
if N == 2
@test data(f)[1:div(n[1],2),:,1:div(nt,2)] ≈ arr[1:div(n[1],2),:,1:div(nt,2)]
else
@test data(f)[1:div(n[1],2),div(n[2],3):2*div(n[2],3),:,1:div(nt,2)] ≈ arr[1:div(n[1],2),div(n[2],3):2*div(n[2],3),:,1:div(nt,2)]
end
end
@testset "MPI Getindex for SparseFunction n=$n npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (5,4),(4,5,6) ), npoint in (1,5,10)
N = length(n)
nt = 5
rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
f = SparseFunction(name="f", grid=grid, npoint=npoint)
arr = reshape(1f0*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
copy!(data(f), arr)
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
for check in 1:nchecks
i = rand((1:npoint))
I = (i,)
@test data(f)[I...] == arr[I...]
end
if npoint > 1
@test data(f)[1:div(npoint,2)] ≈ arr[1:div(npoint,2)]
else
@test data(f)[1] == arr[1]
end
end
@testset "MPI Getindex for SparseTimeFunction n=$n npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (5,4),(4,5,6) ), npoint in (1,5,10)
N = length(n)
nt = 5
rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
f = SparseTimeFunction(name="f", grid=grid, nt=nt, npoint=npoint)
arr = reshape(1f0*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
copy!(data(f), arr)
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
for check in 1:nchecks
i = rand((1:npoint))
j = rand((1:nt))
I = (i,j)
@test data(f)[I...] == arr[I...]
end
if npoint > 1
@test data(f)[1:div(npoint,2),2:end-1] ≈ arr[1:div(npoint,2),2:end-1]
else
@test data(f)[1,2:end-1] ≈ arr[1,2:end-1]
end
end
@testset "MPI setindex! for Function n=$n, T=$T" for n in ( (11,10), (5,4), (7,2), (4,5,6), (2,3,4) ), T in (Float32,Float64)
N = length(n)
my_rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
base_array = reshape(one(T)*[1:prod(size(grid));], size(grid))
send_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* n)...)
expected_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* n)...)
if my_rnk == 0
send_arr = base_array
expected_arr = zeros(T, n...)
end
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
local indexes
if N == 2
indexes = [rand((1:n[1]),nchecks) rand((1:n[2]),nchecks) ;]
else
indexes = [rand((1:n[1]),nchecks) rand((1:n[2]),nchecks) rand((1:n[3]),nchecks);]
end
for check in 1:nchecks
data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] = (my_rnk == 0 ? send_arr[indexes[check,:]...] : zero(T))
if my_rnk == 0
expected_arr[indexes[check,:]...] = base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
@test data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] == base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
made_array = convert(Array,data(f))
if my_rnk == 0
@test made_array ≈ expected_arr
end
end
@testset "MPI setindex! for TimeFunction n=$n, T=$T" for n in ( (11,10), (5,4), (7,2), (4,5,6), (2,3,4) ), T in (Float32,Float64)
N = length(n)
time_order = 2
my_rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
f = TimeFunction(name="f", grid=grid, time_order=time_order)
base_array = reshape(one(T)*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
send_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
expected_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
if my_rnk == 0
send_arr = base_array
expected_arr = zeros(T, size(base_array)...)
end
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
local indexes
if N == 2
indexes = [rand((1:n[1]),nchecks) rand((1:n[2]),nchecks) rand((1:time_order+1),nchecks);]
else
indexes = [rand((1:n[1]),nchecks) rand((1:n[2]),nchecks) rand((1:n[3]),nchecks) rand((1:time_order+1),nchecks);]
end
for check in 1:nchecks
data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] = (my_rnk == 0 ? send_arr[indexes[check,:]...] : zero(T) )
if my_rnk == 0
expected_arr[indexes[check,:]...] = base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
@test data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] == base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
made_array = convert(Array,data(f))
if my_rnk == 0
@test made_array ≈ expected_arr
end
end
@testset "MPI settindex! for SparseTimeFunction n=$n, npoint=$npoint, T=$T" for n in ( (5,4),(4,5,6) ), npoint in (1,5,10), T in (Float32,Float64)
N = length(n)
nt = 11
my_rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
f = SparseTimeFunction(name="f", grid=grid, nt=nt, npoint=npoint)
base_array = reshape(one(T)*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
send_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
expected_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
if my_rnk == 0
send_arr = base_array
expected_arr = zeros(T, size(base_array)...)
end
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
indexes = [rand((1:npoint),nchecks) rand((1:nt),nchecks);]
for check in 1:nchecks
data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] = (my_rnk == 0 ? send_arr[indexes[check,:]...] : zero(T) )
if my_rnk == 0
expected_arr[indexes[check,:]...] = base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
@test data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] == base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
made_array = convert(Array,data(f))
if my_rnk == 0
@test made_array ≈ expected_arr
end
end
@testset "MPI settindex! for SparseFunction n=$n, npoint=$npoint, T=$T" for n in ( (5,4),(4,5,6) ), npoint in (1,5,10), T in (Float32,Float64)
N = length(n)
my_rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
f = SparseFunction(name="f", grid=grid, npoint=npoint)
base_array = reshape(one(T)*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
send_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
expected_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
if my_rnk == 0
send_arr = base_array
expected_arr = zeros(T, size(base_array)...)
end
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
indexes = [rand((1:npoint),nchecks);]
for check in 1:nchecks
data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] = (my_rnk == 0 ? send_arr[indexes[check,:]...] : zero(T) )
if my_rnk == 0
expected_arr[indexes[check,:]...] = base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
@test data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] == base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
made_array = convert(Array,data(f))
if my_rnk == 0
@test made_array ≈ expected_arr
end
end
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 31698 | using Devito, MPI, Random, Strided, Test
MPI.Init()
configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
configuration!("language", "openmp")
configuration!("mpi", true)
@testset "DevitoMPIArray, copy!, no halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10))
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data(b)
@test isa(b_data, Devito.DevitoMPIArray{Float32,length(n)})
@test size(b_data) == n
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test = reshape(Float32[1:prod(n);], n)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
_b_data = data(b)
b_data_test = reshape(Float32[1:prod(n);], n)
for rnk in 0:3
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == rnk
if rnk == 0
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[1:6,1:5]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[1:6,1:5]
else
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,1:6,1:5]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,1:6,1:5]
end
@test isa(parent(_b_data), StridedView)
end
if rnk == 1
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[7:11,1:5]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[7:11,1:5]
else
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,7:11,1:5]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,7:11,1:5]
end
@test isa(parent(_b_data), StridedView)
end
if rnk == 2
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[1:6,6:10]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[1:6,6:10]
else
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,1:6,6:10]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,1:6,6:10]
end
@test isa(parent(_b_data), StridedView)
end
if rnk == 3
if length(n) == 2
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[7:11,6:10]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[7:11,6:10]
else
@test parent(_b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,7:11,6:10]
@test parent(b_data) ≈ b_data_test[:,7:11,6:10]
end
@test isa(parent(_b_data), StridedView)
end
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
end
@testset "Convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray then back, no halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data(b)
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(n);], n)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
_b_data = data(b)
b_data_out = convert(Array, _b_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test b_data_out ≈ b_data_test
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
@testset "DevitoMPITimeArray, copy!, data, no halo, n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10))
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=2)
p_data = data(p)
_n = length(n) == 2 ? (11,10,3) : (12,11,10,3)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, _n)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
end
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(_n);], _n)
p_data_local = parent(p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if length(n) == 2
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[1:6,1:5,:]
else
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,1:6,1:5,:]
end
end
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 1
if length(n) == 2
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[7:11,1:5,:]
else
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,7:11,1:5,:]
end
end
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 2
if length(n) == 2
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[1:6,6:10,:]
else
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,1:6,6:10,:]
end
end
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 3
if length(n) == 2
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[7:11,6:10,:]
else
@test p_data_local ≈ p_data_test[:,7:11,6:10,:]
end
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray, then back, extra dimension, n=$n, nextra=$nextra, first=$first" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), nextra in (1,2,5), first in (true,false)
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
extradim = Dimension(name="extra")
space_order = 2
time = stepping_dim(grid)
if first
funcdims = (extradim, dimensions(grid)...)
funcshap = (nextra, n...)
else
funcdims = (dimensions(grid)..., extradim)
funcshap = (n..., nextra)
end
timedims = (funcdims..., time)
timeshap = (funcshap..., 2)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=space_order, dimensions=funcdims, shape=funcshap)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=space_order, dimensions=timedims, shape=timeshap)
b_data = data(b)
p_data = data(p)
@debug "making test data on rank $(MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD))"
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, funcshap)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, timeshap)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(funcshap);], funcshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timeshap);], timeshap)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(funcshap);], funcshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timeshap);], timeshap)
_b_data_test = convert(Array, b_data)
_p_data_test = convert(Array, p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test b_data_test ≈ _b_data_test
@test p_data_test ≈ _p_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray, then back, extra dimensions inhalo, n=$n, nextra=$nextra, first=$first" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), nextra in (1,2,5), first in (false,true)
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
extradim = Dimension(name="extra")
space_order = 2
time = stepping_dim(grid)
padded = (length(n) == 2 ? (19, 18) : (16, 19, 18))
if first
funcdims = (extradim, dimensions(grid)...)
funcshap = (nextra, n...)
arrayshap = (nextra, padded...)
else
funcdims = (dimensions(grid)..., extradim)
funcshap = (n..., nextra)
arrayshap = (padded..., nextra)
end
timedims = (funcdims..., time)
timeshap = (funcshap..., 2)
timearrayshap = (arrayshap..., 2)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=space_order, dimensions=funcdims, shape=funcshap)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=space_order, dimensions=timedims, shape=timeshap)
b_data = data_with_inhalo(b)
p_data = data_with_inhalo(p)
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, arrayshap)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, timearrayshap)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(arrayshap);], arrayshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timearrayshap);], timearrayshap)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(arrayshap);], arrayshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timearrayshap);], timearrayshap)
_b_data_test = convert(Array, b_data)
_p_data_test = convert(Array, p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test b_data_test ≈ _b_data_test
@test p_data_test ≈ _p_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoMPIArray, then back, extra dimensions with halo, n=$n, nextra=$nextra, first=$first" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), nextra in (1,2,5), first in (false,true)
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
extradim = Dimension(name="extra")
space_order = 2
time = stepping_dim(grid)
padded = (length(n) == 2 ? (15, 14) : (16, 15, 14))
if first
funcdims = (extradim, dimensions(grid)...)
funcshap = (nextra, n...)
arrayshap = (nextra, padded...)
else
funcdims = (dimensions(grid)..., extradim)
funcshap = (n..., nextra)
arrayshap = (padded..., nextra)
end
timedims = (funcdims..., time)
timeshap = (funcshap..., 2)
timearrayshap = (arrayshap..., 2)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=space_order, dimensions=funcdims, shape=funcshap)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=space_order, dimensions=timedims, shape=timeshap)
b_data = data_with_halo(b)
@show size(b_data)
p_data = data_with_halo(p)
b_data_test = zeros(Float32, arrayshap)
p_data_test = zeros(Float32, timearrayshap)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(arrayshap);], arrayshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timearrayshap);], timearrayshap)
end
copy!(b_data, b_data_test)
copy!(p_data, p_data_test)
b_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(arrayshap);], arrayshap)
p_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(timearrayshap);], timearrayshap)
_b_data_test = convert(Array, b_data)
_p_data_test = convert(Array, p_data)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test b_data_test ≈ _b_data_test
@test p_data_test ≈ _p_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoSparseMPIArray, then back, extra dimension n=$n, nextra=$nextra, npoint=$npoint, first=$first" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), nextra in (1,2,5), first in (true,false), npoint in (1,2,5)
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
extradim = Dimension(name="extra")
space_order = 2
prec = Dimension(name="prec")
npoint = 8
sparsedims = (extradim, prec)
sparseshape = (nextra, npoint)
if ~first
sparsedims = reverse(sparsedims)
sparseshape = reverse(sparseshape)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", grid=grid, dimensions=sparsedims, shape=sparseshape, npoint=npoint)
else
sf = CoordSlowSparseFunction(name="sf", grid=grid, dimensions=sparsedims, shape=sparseshape, npoint=npoint)
end
sf_data_test = zeros(Float32, sparseshape...)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
sf_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(sparseshape);], sparseshape)
end
copy!( data(sf), sf_data_test)
_sf_data_test = convert(Array, data(sf))
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test sf_data_test ≈ _sf_data_test
end
end
@testset "convert data from rank 0 to DevitoSparseMPITimeArray, then back, extra dimension n=$n, nextra=$nextra, npoint=$npoint, nt=$nt" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), nextra in (1,2,5), npoint in (1,2,5), nt in (1,5,10)
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
extradim = Dimension(name="extra")
space_order = 2
t = time_dim(grid)
prec = Dimension(name="prec")
npoint = 8
sparsedims = (prec, extradim, t)
sparseshape = (npoint, nextra, nt)
sf = SparseTimeFunction(name="sf", grid=grid, dimensions=sparsedims, shape=sparseshape, npoint=npoint, nt=nt)
sf_data_test = zeros(Float32, sparseshape...)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
sf_data_test .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(sparseshape);], sparseshape)
end
copy!( data(sf), sf_data_test)
_sf_data_test = convert(Array, data(sf))
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test sf_data_test ≈ _sf_data_test
end
end
@testset "DevitoMPITimeArray coordinates check" begin
ny,nx = 4,6
grd = Grid(shape=(ny,nx), extent=(ny-1,nx-1), dtype=Float32)
time_order = 1
fx = TimeFunction(name="fx", grid=grd, time_order=time_order, save=time_order+1, allowpro=false)
fy = TimeFunction(name="fy", grid=grd, time_order=time_order, save=time_order+1, allowpro=false)
sx = SparseTimeFunction(name="sx", grid=grd, npoint=ny*nx, nt=time_order+1)
sy = SparseTimeFunction(name="sy", grid=grd, npoint=ny*nx, nt=time_order+1)
cx = [ix-1 for iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx][:]
cy = [iy-1 for iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx][:]
coords = zeros(Float32, 2, ny*nx)
coords[1,:] .= cx
coords[2,:] .= cy
copy!(coordinates_data(sx), coords)
copy!(coordinates_data(sy), coords)
datx = reshape(Float32[ix for iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx, it = 1:time_order+1][:], nx*ny, time_order+1)
daty = reshape(Float32[iy for iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx, it = 1:time_order+1][:], nx*ny, time_order+1)
copy!(data(sx), datx)
copy!(data(sy), daty)
eqx = inject(sx, field=forward(fx), expr=sx)
eqy = inject(sy, field=forward(fy), expr=sy)
op = Operator([eqx, eqy], name="CoordOp")
apply(op)
x = convert(Array, data(fx))
y = convert(Array, data(fy))
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if VERSION >= v"1.7"
@test x ≈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0]
@test y ≈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0]
else
_x = zeros(Float32, ny, nx, 2)
_x[:,:,1] .= [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0]
_x[:,:,2] .= [1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0]
@test x ≈ _x
_y = zeros(Float32, ny, nx, 2)
_y[:,:,1] .= [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0]
_y[:,:,2] .= [1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0]
@test y ≈ _y
end
end
end
@testset "DevitoMPITimeArray coordinates check, 3D" begin
nz,ny,nx = 4,5,6
grd = Grid(shape=(nz,ny,nx), extent=(nz-1,ny-1,nx-1), dtype=Float32)
time_order = 1
fx = TimeFunction(name="fx", grid=grd, time_order=time_order, save=time_order+1, allowpro=false)
fy = TimeFunction(name="fy", grid=grd, time_order=time_order, save=time_order+1, allowpro=false)
fz = TimeFunction(name="fz", grid=grd, time_order=time_order, save=time_order+1, allowpro=false)
sx = SparseTimeFunction(name="sx", grid=grd, npoint=nz*ny*nx, nt=time_order+1)
sy = SparseTimeFunction(name="sy", grid=grd, npoint=nz*ny*nx, nt=time_order+1)
sz = SparseTimeFunction(name="sz", grid=grd, npoint=nz*ny*nx, nt=time_order+1)
cx = [ix-1 for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx][:]
cy = [iy-1 for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx][:]
cz = [iz-1 for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx][:]
coords = zeros(Float32, 3, nz*ny*nx)
coords[1,:] .= cx
coords[2,:] .= cy
coords[3,:] .= cz
copy!(coordinates_data(sx), coords)
copy!(coordinates_data(sy), coords)
copy!(coordinates_data(sz), coords)
datx = reshape(Float32[ix for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx, it = 1:time_order+1][:], nx*ny*nz, time_order+1)
daty = reshape(Float32[iy for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx, it = 1:time_order+1][:], nx*ny*nz, time_order+1)
datz = reshape(Float32[iz for iz = 1:nz, iy = 1:ny, ix=1:nx, it = 1:time_order+1][:], nx*ny*nz, time_order+1)
copy!(data(sx), datx)
copy!(data(sy), daty)
copy!(data(sz), datz)
eqx = inject(sx, field=forward(fx), expr=sx)
eqy = inject(sy, field=forward(fy), expr=sy)
eqz = inject(sz, field=forward(fz), expr=sz)
op = Operator([eqx, eqy, eqz], name="CoordOp")
apply(op)
x = convert(Array, data(fx))
y = convert(Array, data(fy))
z = convert(Array, data(fz))
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if VERSION >= v"1.7"
@test x ≈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0;;; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0;;; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0;;; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0; 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0; 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0; 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0;;; 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0; 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0; 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0; 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0]
@test y ≈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0;;; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0; 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0]
@test z ≈ [0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0; 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0;;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0;;; 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0; 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0; 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0; 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0]
end
end
end
@testset "Sparse function, copy!, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), npoint in (1, 5, 10)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
nt = 100
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", npoint=npoint, grid=grid)
x = Vector{Float32}(undef,0)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
x = Float32[1:npoint;]
end
_x = data(sf)
copy!(_x, x)
x = Float32[1:npoint;]
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if npoint == 1
@test isempty(parent(_x))
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[1:1]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[1:2]
end
elseif MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 1
if npoint == 1
@test isempty(parent(_x))
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[2:2]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[3:4]
end
elseif MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 2
if npoint == 1
@test isempty(parent(_x))
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[3:3]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[5:6]
end
elseif MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 3
if npoint == 1
@test parent(_x) ≈ x
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[4:5]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[7:10]
end
end
end
@testset "Sparse time function, copy!, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), npoint in (1, 5, 10)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
nt = 100
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", npoint=npoint, nt=nt, grid=grid)
x = Matrix{Float32}(undef,0,0)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
x = reshape(Float32[1:prod(nt*npoint);], npoint, nt)
end
_x = data(stf)
copy!(_x, x)
x = reshape(Float32[1:prod(nt*npoint);], npoint, nt)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
if npoint == 1
@test isempty(parent(_x))
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[1:1,:]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[1:2,:]
end
elseif MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 1
if npoint == 1
@test isempty(parent(_x))
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[2:2,:]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[3:4,:]
end
elseif MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 2
if npoint == 1
@test isempty(parent(_x))
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[3:3,:]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[5:6,:]
end
elseif MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 3
if npoint == 1
@test parent(_x) ≈ x
elseif npoint == 5
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[4:5,:]
elseif npoint == 10
@test parent(_x) ≈ x[7:10,:]
end
end
end
@testset "Sparse function, copy! and convert, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), npoint in (1, 5, 10)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
nt = 100
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", npoint=npoint, grid=grid)
x = zeros(Float32, npoint)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
x .= Float32[1:npoint;]
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
_x = data(sf)
@test isa(data(sf), Devito.DevitoMPISparseArray)
copy!(_x, x)
x .= Float32[1:npoint;]
__x = convert(Array, _x)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test __x ≈ x
end
end
@testset "Sparse time function, copy! and convert, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (11,10), (12,11,10) ), npoint in (1, 5, 10)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
nt = 100
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", npoint=npoint, nt=nt, grid=grid)
x = zeros(Float32, npoint, nt)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
x .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(nt*npoint);], npoint, nt)
end
MPI.Barrier(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
_x = data(stf)
@test isa(data(stf), Devito.DevitoMPISparseTimeArray)
copy!(_x, x)
x .= reshape(Float32[1:prod(nt*npoint);], npoint, nt)
__x = convert(Array, _x)
if MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD) == 0
@test __x ≈ x
end
end
@testset "MPI Getindex for Function n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (5,4), (7,2), (4,5,6), (2,3,4) )
N = length(n)
rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
arr = reshape(1f0*[1:prod(size(grid));], size(grid))
copy!(data(f), arr)
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
for check in 1:nchecks
i = rand((1:n[1]))
j = rand((1:n[2]))
I = (i,j)
if N == 3
k = rand((1:n[3]))
I = (i,j,k)
end
@test data(f)[I...] == arr[I...]
end
if N == 2
@test data(f)[1:div(n[1],2),:] ≈ arr[1:div(n[1],2),:]
else
@test data(f)[1:div(n[1],2),div(n[2],3):2*div(n[2],3),:] ≈ arr[1:div(n[1],2),div(n[2],3):2*div(n[2],3),:]
end
end
@testset "MPI Getindex for TimeFunction n=$n" for n in ( (11,10), (5,4), (7,2), (4,5,6), (2,3,4) )
N = length(n)
nt = 5
rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
f = TimeFunction(name="f", grid=grid, save=nt, allowpro=false)
arr = reshape(1f0*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
copy!(data(f), arr)
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
for check in 1:nchecks
i = rand((1:n[1]))
j = rand((1:n[2]))
I = (i,j)
if N == 3
k = rand((1:n[3]))
I = (i,j,k)
end
m = rand((1:nt))
I = (I...,m)
@test data(f)[I...] == arr[I...]
end
if N == 2
@test data(f)[1:div(n[1],2),:,1:div(nt,2)] ≈ arr[1:div(n[1],2),:,1:div(nt,2)]
else
@test data(f)[1:div(n[1],2),div(n[2],3):2*div(n[2],3),:,1:div(nt,2)] ≈ arr[1:div(n[1],2),div(n[2],3):2*div(n[2],3),:,1:div(nt,2)]
end
end
@testset "MPI Getindex for SparseFunction n=$n npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (5,4),(4,5,6) ), npoint in (1,5,10)
N = length(n)
nt = 5
rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
f = SparseFunction(name="f", grid=grid, npoint=npoint)
arr = reshape(1f0*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
copy!(data(f), arr)
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
for check in 1:nchecks
i = rand((1:npoint))
I = (i,)
@test data(f)[I...] == arr[I...]
end
if npoint > 1
@test data(f)[1:div(npoint,2)] ≈ arr[1:div(npoint,2)]
else
@test data(f)[1] == arr[1]
end
end
@testset "MPI Getindex for SparseTimeFunction n=$n npoint=$npoint" for n in ( (5,4),(4,5,6) ), npoint in (1,5,10)
N = length(n)
nt = 5
rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
f = SparseTimeFunction(name="f", grid=grid, nt=nt, npoint=npoint)
arr = reshape(1f0*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
copy!(data(f), arr)
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
for check in 1:nchecks
i = rand((1:npoint))
j = rand((1:nt))
I = (i,j)
@test data(f)[I...] == arr[I...]
end
if npoint > 1
@test data(f)[1:div(npoint,2),2:end-1] ≈ arr[1:div(npoint,2),2:end-1]
else
@test data(f)[1,2:end-1] ≈ arr[1,2:end-1]
end
end
@testset "MPI setindex! for Function n=$n, T=$T" for n in ( (11,10), (5,4), (7,2), (4,5,6), (2,3,4) ), T in (Float32,Float64)
N = length(n)
my_rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
base_array = reshape(one(T)*[1:prod(size(grid));], size(grid))
send_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* n)...)
expected_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* n)...)
if my_rnk == 0
send_arr = base_array
expected_arr = zeros(T, n...)
end
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
local indexes
if N == 2
indexes = [rand((1:n[1]),nchecks) rand((1:n[2]),nchecks) ;]
else
indexes = [rand((1:n[1]),nchecks) rand((1:n[2]),nchecks) rand((1:n[3]),nchecks);]
end
for check in 1:nchecks
data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] = (my_rnk == 0 ? send_arr[indexes[check,:]...] : zero(T))
if my_rnk == 0
expected_arr[indexes[check,:]...] = base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
@test data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] == base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
made_array = convert(Array,data(f))
if my_rnk == 0
@test made_array ≈ expected_arr
end
end
@testset "MPI setindex! for TimeFunction n=$n, T=$T" for n in ( (11,10), (5,4), (7,2), (4,5,6), (2,3,4) ), T in (Float32,Float64)
N = length(n)
time_order = 2
my_rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
f = TimeFunction(name="f", grid=grid, time_order=time_order)
base_array = reshape(one(T)*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
send_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
expected_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
if my_rnk == 0
send_arr = base_array
expected_arr = zeros(T, size(base_array)...)
end
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
local indexes
if N == 2
indexes = [rand((1:n[1]),nchecks) rand((1:n[2]),nchecks) rand((1:time_order+1),nchecks);]
else
indexes = [rand((1:n[1]),nchecks) rand((1:n[2]),nchecks) rand((1:n[3]),nchecks) rand((1:time_order+1),nchecks);]
end
for check in 1:nchecks
data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] = (my_rnk == 0 ? send_arr[indexes[check,:]...] : zero(T) )
if my_rnk == 0
expected_arr[indexes[check,:]...] = base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
@test data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] == base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
made_array = convert(Array,data(f))
if my_rnk == 0
@test made_array ≈ expected_arr
end
end
@testset "MPI settindex! for SparseTimeFunction n=$n, npoint=$npoint, T=$T" for n in ( (5,4),(4,5,6) ), npoint in (1,5,10), T in (Float32,Float64)
N = length(n)
nt = 11
my_rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
f = SparseTimeFunction(name="f", grid=grid, nt=nt, npoint=npoint)
base_array = reshape(one(T)*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
send_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
expected_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
if my_rnk == 0
send_arr = base_array
expected_arr = zeros(T, size(base_array)...)
end
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
indexes = [rand((1:npoint),nchecks) rand((1:nt),nchecks);]
for check in 1:nchecks
data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] = (my_rnk == 0 ? send_arr[indexes[check,:]...] : zero(T) )
if my_rnk == 0
expected_arr[indexes[check,:]...] = base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
@test data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] == base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
made_array = convert(Array,data(f))
if my_rnk == 0
@test made_array ≈ expected_arr
end
end
@testset "MPI settindex! for SparseFunction n=$n, npoint=$npoint, T=$T" for n in ( (5,4),(4,5,6) ), npoint in (1,5,10), T in (Float32,Float64)
N = length(n)
my_rnk = MPI.Comm_rank(MPI.COMM_WORLD)
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
f = SparseFunction(name="f", grid=grid, npoint=npoint)
base_array = reshape(one(T)*[1:prod(size(data(f)));], size(data(f)))
send_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
expected_arr = zeros(T, (0 .* size(data(f)))...)
if my_rnk == 0
send_arr = base_array
expected_arr = zeros(T, size(base_array)...)
end
nchecks = 10
Random.seed!(1234);
indexes = [rand((1:npoint),nchecks);]
for check in 1:nchecks
data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] = (my_rnk == 0 ? send_arr[indexes[check,:]...] : zero(T) )
if my_rnk == 0
expected_arr[indexes[check,:]...] = base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
@test data(f)[indexes[check,:]...] == base_array[indexes[check,:]...]
end
made_array = convert(Array,data(f))
if my_rnk == 0
@test made_array ≈ expected_arr
end
end
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 418 | using Devito
for testscript in ("serialtests.jl", "gencodetests.jl", "csymbolicstests.jl")
include(testscript)
end
# JKW: disabling mpi tests for now, we expect to remove MPI features from Devito.jl in future PR
# run(`$(mpiexec()) -n 2 julia --code-coverage mpitests_2ranks.jl`)
# run(`$(mpiexec()) -n 4 julia --code-coverage mpitests_4ranks.jl`)
if Devito.has_devitopro()
include("devitoprotests.jl")
end
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | code | 43557 | using Devito, Random, PyCall, Strided, Test
# configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
configuration!("log-level", "WARNING")
configuration!("language", "openmp")
configuration!("mpi", false)
# you need to use when testing locally due to the Libdl startup issue for the nv compiler
configuration!("compiler", "gcc")
configuration!("platform", "cpu64")
@testset "configuration" begin
configuration!("log-level", "INFO")
@test configuration("log-level") == "INFO"
configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
c = configuration()
@test c["log-level"] == "DEBUG"
end
@testset "Grid, n=$n, T=$T" for (n,ex,ori) in ( ( (4,5),(40.0,50.0), (10.0,-10.0) ), ( (4,5,6),(40.0,50.0,60.0),(10.0,0.0,-10.0) ) ), T in (Float32, Float64)
grid = Grid(shape = n, extent=ex, origin=ori, dtype = T)
@test size(grid) == n
@test ndims(grid) == length(n)
@test eltype(grid) == T
@test extent(grid) == ex
@test origin(grid) == ori
@test spacing(grid) == ex ./ (n .- 1)
for i in 1:length(n)
@test size(grid,i) == n[i]
end
halo = []
for i in 1:length(n)
push!(halo, [2*i 2*i+1;])
end
@test size_with_halo(grid,halo) == size(grid) .+ (sum.(halo)...,)
end
@testset "DevitoArray creation from PyObject n=$n, T=$T" for n in ((5,6),(5,6,7)), T in (Float32, Float64)
N = length(n)
array = PyObject(ones(T,n...))
devito_array = DevitoArray(array)
@test typeof(devito_array) <: DevitoArray{T,N}
@test devito_array ≈ ones(T, reverse(n)...)
end
@testset "Function, data_with_halo n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data_with_halo(b)
@test ndims(b_data) == length(n)
rand!(b_data)
b_data_test = data_with_halo(b)
@test b_data ≈ b_data_test
end
@testset "Function, grid, n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
@test grid == Devito.grid(b)
@test ndims(grid) == length(n)
end
@testset "Function, halo, n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
so = 2
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=so)
@test ntuple(_->(so,so), length(n)) == halo(b)
end
@testset "Function, ndims, n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
@test length(n) == ndims(b)
end
@testset "Function, data, n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
b_data = data(b)
@test ndims(b_data) == length(n)
copy!(b_data, rand(eltype(grid), size(grid)))
b_data_test = data(b)
@test b_data ≈ b_data_test
end
@testset "Function and TimeFunction, space_order, n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
g = Grid(shape=n)
for so in (1,2,5,8)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=g, space_order=so)
u = Devito.TimeFunction(name="u", grid=g, space_order=so)
@test space_order(f) == so
@test space_order(u) == so
end
end
@testset "Constant" begin
a = Constant(name="a")
@test isconst(a)
@test typeof(value(a)) == Float32
@test value(a) == 0.0
@test value(a) == data(a)
value!(a,2.0)
@test typeof(value(a)) == Float32
@test value(a) == 2.0
@test value(a) == data(a)
value!(a, π)
@test value(a) == convert(Float32,π)
@test typeof(convert(Constant,PyObject(a))) == Constant{Float32}
@test convert(Constant,PyObject(a)) === a
p = Constant(name="p", dtype=Float64, value=π)
@test typeof(value(p)) == Float64
@test value(p) == convert(Float64,π)
@test data(p) == value(p)
@test typeof(convert(Constant,PyObject(p))) == Constant{Float64}
@test convert(Constant,PyObject(p)) === p
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a Constant") convert(Constant,PyObject(Dimension(name="d")))
end
@testset "TimeFunction, data with halo, n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=2)
p_data = data_with_halo(p)
@test ndims(p_data) == length(n)+1
copy!(p_data, rand(eltype(grid), size_with_halo(p)))
p_data_test = data_with_halo(p)
@test p_data ≈ p_data_test
end
@testset "TimeFunction, data, n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, space_order=2)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=2)
p_data = data(p)
@test ndims(p_data) == length(n)+1
copy!(p_data, rand(eltype(grid), size(p)))
p_data_test = data(p)
@test p_data ≈ p_data_test
end
@testset "TimeFunction, grid, n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
p = TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=2)
@test grid == Devito.grid(p)
@test ndims(grid) == length(n)
end
@testset "TimeFunction, halo, n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
so = 2
p = Devito.TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=so)
if length(n) == 2
@test ((so,so),(so,so),(0,0)) == halo(p)
else
@test ((so,so),(so,so),(so,so),(0,0)) == halo(p)
end
end
@testset "TimeFunction, ndims, n=$n" for n in ( (4,5), (4,5,6) )
grid = Grid(shape = n, dtype = Float32)
so = 2
p = Devito.TimeFunction(name="p", grid=grid, time_order=2, space_order=so)
@test length(n)+1 == ndims(p)
end
@testset "SparseFunction Construction, T=$T, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for T in (Float32, Float64), n in ((3,4),(3,4,5)), npoint in (1,5,10)
g = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", grid=g, npoint=npoint)
@test typeof(sf) <: SparseFunction{T,1}
@test sf.o === PyObject(sf)
end
@testset "SparseFunction grid method, T=$T, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for T in (Float32, Float64), n in ((3,4),(3,4,5)), npoint in (1,5,10)
g = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", grid=g, npoint=npoint)
@test grid(sf) == g
end
@testset "SparseFunction size methods, T=$T, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for T in (Float32, Float64), n in ((3,4),(3,4,5)), npoint in (1,5,10)
g = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", grid=g, npoint=npoint)
@test size(sf) == (npoint,)
@test Devito.size_with_inhalo(sf) == (npoint,)
@test size_with_halo(sf) == (npoint,)
end
@testset "Sparse function coordinates, n=$n" for n in ( (10,11), (10,11,12) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", npoint=10, grid=grid)
@test typeof(coordinates(sf)) <: SubFunction{Float32,2}
sf_coords = coordinates_data(sf)
@test isa(sf_coords, Devito.DevitoArray)
@test size(sf_coords) == (length(n),10)
x = rand(length(n),10)
sf_coords .= x
_sf_coords = coordinates_data(sf)
@test _sf_coords ≈ x
end
@testset "SparseFunction from PyObject, T=$T, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for T in (Float32, Float64), n in ((3,4),(3,4,5)), npoint in (1,5,10)
g = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", grid=g, npoint=npoint)
@test SparseFunction(PyObject(sf)) === sf
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", grid=g, npoint=npoint, nt=5)
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.SparseFunction") SparseFunction(PyObject(stf))
end
@testset "Multidimensional SparseFunction, T=$T, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for T in (Float32, Float64), n in ((3,4),(3,4,5)), npoint in (1,5,10)
g = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
recdim = Dimension(name="recdim")
nfdim = 7
fdim = DefaultDimension(name="fdim", default_value=nfdim)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", grid=g, dimensions=(recdim, fdim), npoint=npoint, shape=(npoint, nfdim))
@test dimensions(sf) == (recdim, fdim)
@test size(data(sf)) == (npoint, nfdim)
@test size(coordinates_data(sf)) == (length(n), npoint)
end
@testset "CoordSlowSparseFunction, T=$T, n=$n, npoint=$npoint" for T in (Float32, Float64), n in ((3,4),(3,4,5)), npoint in (1,5,10)
g = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
recdim = Dimension(name="recdim")
nfdim = 7
fdim = DefaultDimension(name="fdim", default_value=nfdim)
sf = CoordSlowSparseFunction(name="sf", grid=g, dimensions=(fdim,recdim), npoint=npoint, shape=(nfdim,npoint))
@test dimensions(sf) == (fdim, recdim)
@test size(data(sf)) == (nfdim, npoint)
@test size(coordinates_data(sf)) == (length(n), npoint)
end
@testset "Sparse time function grid, n=$n, T=$T" for n in ((5,6),(5,6,7)), T in (Float32, Float64)
N = length(n)
grd = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", npoint=1, nt=5, grid=grd)
@test typeof(grid(stf)) <: Grid{T,N}
@test grid(stf) == grd
end
@testset "Sparse time function coordinates, n=$n" for n in ( (10,11), (10,11,12) )
grid = Grid(shape=n, dtype=Float32)
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", npoint=10, nt=100, grid=grid)
@test typeof(coordinates(stf)) <: SubFunction{Float32,2}
stf_coords = coordinates_data(stf)
@test isa(stf_coords, Devito.DevitoArray)
@test size(stf_coords) == (length(n),10)
x = rand(length(n),10)
stf_coords .= x
_stf_coords = coordinates_data(stf)
@test _stf_coords ≈ x
end
@testset "Set Index Writing" begin
grid = Grid(shape=(11,), dtype=Float32)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
d = data(f)
d .= 1.0
op = Operator([Eq(f[1],2.0)],name="indexwrite")
apply(op)
@test data(f)[2] == 2.0
end
@testset "Subdomain" begin
n1,n2 = 5,7
subdom_mid = SubDomain("subdom_mid", [("middle",1,1), ("middle",2,2)] )
subdom_lft = SubDomain("subdom_top", [("middle",0,0), ("left",div(n2,2)+1)] )
subdom_rgt = SubDomain("subdom_bot", [("middle",0,0), ("right",div(n2,2)+1)] )
subdom_top = SubDomain("subdom_lft", [("left",div(n1,2)+1), ("middle",0,0)] )
subdom_bot = SubDomain("subdom_rgt", [("right",div(n1,2)+1), ("middle",0,0)] )
grid = Grid(shape=(n1,n2), dtype=Float32, subdomains=(subdom_mid, subdom_lft, subdom_rgt, subdom_top, subdom_bot))
f0 = Devito.Function(name="f0", grid=grid)
f1 = Devito.Function(name="f1", grid=grid)
f2 = Devito.Function(name="f2", grid=grid)
f3 = Devito.Function(name="f3", grid=grid)
f4 = Devito.Function(name="f4", grid=grid)
f5 = Devito.Function(name="f5", grid=grid)
f6 = Devito.Function(name="f6", grid=grid)
data(f0) .= 1
eqns = []
push!(eqns, Eq(f1,f0,subdomain=subdom_mid))
push!(eqns, Eq(f2,f0,subdomain=subdom_lft))
push!(eqns, Eq(f3,f0,subdomain=subdom_rgt))
push!(eqns, Eq(f4,f0,subdomain=subdom_top))
push!(eqns, Eq(f5,f0,subdomain=subdom_bot))
op = Operator(name="op", eqns)
apply(op)
_mid = zeros(n1,n2)
_lft = zeros(n1,n2)
_rgt = zeros(n1,n2)
_top = zeros(n1,n2)
_bot = zeros(n1,n2)
_mid[2:4,3:5] .= 1
_lft[:,1:4] .= 1
_rgt[:,4:7] .= 1
_top[1:3,:] .= 1
_bot[3:5,:] .= 1
@test data(f1) ≈ _mid
@test data(f2) ≈ _lft
@test data(f3) ≈ _rgt
@test data(f4) ≈ _top
@test data(f5) ≈ _bot
end
@testset "Equation Equality, shape=$shape, T=$T" for shape in ((11,11),(11,11,11)), T in (Float32, Float64)
g = Grid(shape=shape, dtype=T)
f1 = Devito.Function(name="f1", grid=g, dtype=T)
f2 = Devito.Function(name="f2", grid=g, dtype=T)
u1 = TimeFunction(name="u1", grid=g, dtype=T)
u2 = TimeFunction(name="u2", grid=g, dtype=T)
eq1 = Eq(f1,1)
eq2 = Eq(f2,1)
eq3 = Eq(f1,1)
eq4 = Eq(u1,1)
eq5 = Eq(u2,1)
eq6 = Eq(u1,1)
eq7 = Eq(u2,u1+f1)
eq8 = Eq(u2,u1+f1)
@test eq1 == eq3
@test eq2 != eq1
@test eq4 == eq6
@test eq4 != eq5
@test eq1 != eq4
@test eq7 == eq8
end
@testset "Symbolic Min, Max, Size, and Spacing" begin
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
y = SpaceDimension(name="y")
grid = Grid(shape=(6,11), dtype=Float64, dimensions=(x,y))
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=grid)
h = Devito.Function(name="h", grid=grid)
k = Devito.Function(name="k", grid=grid)
op = Operator([Eq(f,symbolic_max(x)),Eq(g,symbolic_min(y)),Eq(h,symbolic_size(x)),Eq(k,spacing(x))],name="SymMinMax")
apply(op)
@test data(f)[1,1] == 5.
@test data(g)[1,1] == 0.
@test data(h)[1,1] == 6.
@test data(k)[1,1] ≈ 1.0/5.0
end
@testset "Min & Max" begin
grid = Grid(shape=(11,11), dtype=Float64)
mx = Devito.Function(name="mx", grid=grid)
mn = Devito.Function(name="mn", grid=grid)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
df = data(f)
df .= -1.0
op = Operator([Eq(mn,Min(f,4)),Eq(mx,Max(f,4))],name="minmax")
apply(op)
@test data(mn)[5,5] == -1.0
@test data(mx)[5,5] == 4
end
@testset "Devito Mathematical Oparations" begin
# positive only block with equivalent functions in base
for F in (:sqrt,)
@eval begin
vals = (1., 2, 10, 100)
gr = Grid(shape=(length(vals),), dtype=Float64)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=gr)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=gr)
op = Operator([Eq(g,Devito.$F(f))],name="MathTest")
data(f) .= vals
apply(op)
for i in 1:length(vals)
@test abs(data(g)[i] - Base.$F(vals[i])) < eps(Float32)
end
end
end
# positive functions needing base pair specified
for (F,B) in ((:ln,:log),(:ceiling,:ceil))
@eval begin
vals = (1., 2, 10, 100)
gr = Grid(shape=(length(vals),), dtype=Float64)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=gr)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=gr)
op = Operator([Eq(g,Devito.$F(f))],name="MathTest")
data(f) .= vals
apply(op)
for i in 1:length(vals)
@test abs(data(g)[i] - Base.$B(vals[i])) < eps(Float32)
end
end
end
# positive and negative
for F in (:cos, :sin, :tan, :sinh, :cosh, :tanh, :exp, :floor)
@eval begin
vals = (-10, -1, 0, 1., 2, pi, 10)
gr = Grid(shape=(length(vals),), dtype=Float64)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=gr)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=gr)
op = Operator([Eq(g,Devito.$F(f))],name="MathTest")
data(f) .= vals
apply(op)
for i in 1:length(vals)
@test abs(data(g)[i] - Base.$F(vals[i])) < eps(Float32)
end
end
end
# functions needing their own equivalent in base to be specified
for (F,B) in ((:Abs,:abs),)
@eval begin
vals = (-10, -1, 0, 1., 2, pi, 10)
gr = Grid(shape=(length(vals),), dtype=Float64)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=gr)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=gr)
op = Operator([Eq(g,Devito.$F(f))],name="MathTest")
data(f) .= vals
apply(op)
for i in 1:length(vals)
@test abs(data(g)[i] - Base.$B(vals[i])) < eps(Float32)
end
end
end
end
@testset "Unitary Minus" begin
grid = Grid(shape=(11,), dtype=Float32)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=grid)
h = Devito.Function(name="h", grid=grid)
x = dimensions(f)[1]
data(f) .= 1.0
op = Operator([Eq(g,-f),Eq(h,-x)],name="unitaryminus")
apply(op)
@show data(f)
@show data(g)
for i in 1:length(data(f))
@test data(g)[i] ≈ -1.0
@test data(h)[i] ≈ 1-i
end
end
@testset "Unitary Plus" begin
grid = Grid(shape=(11,), dtype=Float32)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=grid)
h = Devito.Function(name="h", grid=grid)
x = dimensions(f)[1]
data(f) .= 1.0
op = Operator([Eq(g,+f),Eq(h,+x)],name="unitaryplus")
apply(op)
for i in 1:length(data(f))
@test data(g)[i] ≈ 1.0
@test data(h)[i] ≈ i-1
end
end
@testset "Mod on Dimensions" begin
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
grid = Grid(shape=(5,), dtype=Float64, dimensions=(x,))
g = Devito.Function(name="g1", grid=grid)
eq = Eq(g[x],Mod(x,2))
op = Operator([eq],name="Mod")
apply(op)
for i in 1:5
@test data(g)[i] == (i-1)%2
end
end
@testset "Multiply and Divide" begin
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
grid = Grid(shape=(5,), dtype=Float64, dimensions=(x,))
g1 = Devito.Function(name="g1", grid=grid)
g2 = Devito.Function(name="g2", grid=grid)
f1 = Devito.Function(name="f1", grid=grid)
f2 = Devito.Function(name="f2", grid=grid)
f3 = Devito.Function(name="f3", grid=grid)
f4 = Devito.Function(name="f4", grid=grid)
f5 = Devito.Function(name="f5", grid=grid)
ffuncs = (f1,f2,f3,f4,f5)
scalar = 5
data(g2) .= 5
data(g1) .= 2
muleqns = [Eq(f1,g1*g2),Eq(f2,scalar*g1),Eq(f3,g1*scalar),Eq(f4,g1*symbolic_size(x)),Eq(f5,symbolic_size(x)*g1)]
op = Operator(muleqns,name="Multiplier")
apply(op)
for func in ffuncs
@test data(func)[2] == 10.
end
diveqns = [Eq(f1,g1/g2),Eq(f2,scalar/g1),Eq(f3,g1/scalar),Eq(f4,g1/symbolic_size(x)),Eq(f5,symbolic_size(x)/g1)]
op = Operator(diveqns,name="Divider")
apply(op)
for (func,answer) in zip(ffuncs,(2/5,5/2,2/5,2/5,5/2))
@test data(func)[2] ≈ answer
end
end
@testset "Symbolic Math" begin
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
y = SpaceDimension(name="y")
grd = Grid(shape=(5,5), dimensions=(y,x))
a = Constant(name="a")
b = Constant(name="b")
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grd)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=grd)
@test a != b
@test x != y
@test f != g
@test x+x+y == 2*x+y
@test x*y == y*x
@test x*x == x^2
@test x+x+a == 2*x+a
@test a+a+b == 2*a+b
@test 2*a+b-a == a+b
@test a*b == b*a
@test a*a == a^2
@test f+f+x == 2*f+x
@test 2*f+x-f == f+x
@test f*f == f^2
@test f*g == g*f
@test f+f+a == 2*f+a
@test 2*f+a-f == f+a
@test f+f+g == 2*f+g
@test 2*f+g-f == f+g
@test 0*(1+f+a+x) == 0
@test (1+f+a+x)*0 == 0
end
@testset "Spacing Map" for T in (Float32,Float64)
grid = Grid(shape=(5,6), dtype=T)
smap = spacing_map(grid)
@test typeof(smap) == Dict{PyCall.PyObject, T}
y,x = dimensions(grid)
@test smap[spacing(y)] ≈ 1 / (size(grid)[1] - 1)
@test smap[spacing(x)] ≈ 1 / (size(grid)[2] - 1)
end
@testset "Constants in Operators, T=$T" for T in (Float32,Float64)
a = Constant(name="a", dtype=T, value=1)
b = Constant(name="b", dtype=T, value=2)
grid = Grid(shape=(5,), dtype=T)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid, dtype=T)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=grid, dtype=T)
op1 = Operator([Eq(f,a),Eq(g,f+b)],name="op1")
apply(op1)
for element in data(f)
@test element == 1
end
for element in data(g)
@test element == 3
end
value!(a,0)
value!(b,1)
apply(op1)
for element in data(f)
@test element == 0
end
for element in data(g)
@test element == 1
end
end
@testset "isequal on Devito Objects" begin
a = Constant(name="a", dtype=Float32)
b = Constant(name="b", dtype=Float64)
@test ~isequal(a,b)
a1 = Constant(a.o)
@test isequal(a,a1)
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
y = SpaceDimension(name="y")
g = Grid(shape=(5,4), dtype=Float32, dimensions=(y,x))
@test spacing(x) ∈ keys(spacing_map(g))
@test spacing(y) ∈ keys(spacing_map(g))
y1, x1 = dimensions(g)
@test isequal(x,x1)
@test isequal(y,y1)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=g)
eq = Eq(f,1)
op = Operator(eq)
dict = Dict(f=>true, g=>true, op=>true, eq=>true)
for entry in (f, eq, op, g)
@test dict[entry] = true
end
end
@testset "Math on Dimensions" begin
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
grid = Grid(shape=(5,), dtype=Float64, dimensions=(x,))
g1 = Devito.Function(name="g1", grid=grid)
f1 = Devito.Function(name="f1", grid=grid)
f2 = Devito.Function(name="f2", grid=grid)
f3 = Devito.Function(name="f3", grid=grid)
f4 = Devito.Function(name="f4", grid=grid)
f5 = Devito.Function(name="f5", grid=grid)
f6 = Devito.Function(name="f6", grid=grid)
data(g1) .= 1.0
eq1 = Eq(f1,x+1)
eq2 = Eq(f2,1+x)
eq3 = Eq(f3,x+g1)
eq4 = Eq(f4,g1+x)
eq5 = Eq(f5,x+1.0*g1)
eq6 = Eq(f6,1.0*g1+x)
opl = Operator([eq1,eq3,eq5],name="Left")
opr = Operator([eq2,eq4,eq6],name="Right")
apply(opl)
apply(opr)
for f in (f1,f2,f3,f4,f5,f6)
df = data(f)
for i in 1:length(df)
@test df[i] == i
end
end
end
@testset "Devito Dimension Constructors" begin
attribtes = (:is_Dimension, :is_Space, :is_Time, :is_Default, :is_Custom, :is_Derived, :is_NonlinearDerived, :is_Sub, :is_Conditional, :is_Stepping, :is_Modulo, :is_Incr)
a = Dimension(name="a")
b = SpaceDimension(name="b")
c = TimeDimension(name="c")
d = SteppingDimension(name="d",parent=c)
@test parent(d) == c
e = DefaultDimension(name="e")
f = ConditionalDimension(name="f", parent=c, factor=2)
@test parent(f) == c
for (dim,attribute) in ((_dim,_attribute) for _dim in (a,b,c,d,e,f) for _attribute in attribtes)
@eval begin
@test $attribute($dim) == $dim.o.$attribute
end
end
for _dim in (a,b,c,d,e,f)
@test typeof(dimension(PyObject(_dim))) == typeof(_dim)
@test dimension(PyObject(_dim)) === _dim
end
# tests for ErrorExceptiosn
grd = Grid(shape=(5,4))
@test_throws ErrorException("not implemented") dimension(PyObject(grd))
end
@testset "Devito SubDimensions" begin
d = SpaceDimension(name="d")
dl = SubDimensionLeft(name="dl", parent=d, thickness=2)
dr = SubDimensionRight(name="dr", parent=d, thickness=3)
dm = SubDimensionMiddle(name="dm", parent=d, thickness_left=2, thickness_right=3)
for subdim in (dl,dr,dm)
@test parent(subdim) == d
@test PyObject(subdim) == subdim.o
end
@test (thickness(dl)[1][2], thickness(dl)[2][2]) == (2, nothing)
@test (thickness(dr)[1][2], thickness(dr)[2][2]) == (nothing, 3)
@test (thickness(dm)[1][2], thickness(dr)[2][2]) == (2, 3)
end
@testset "Devito stepping dimension" begin
grid = Grid(shape=(5,5),origin=(0.,0.),extent=(1.,1.))
f = TimeFunction(grid=grid,space_order=8,time_order=2,name="f")
@test stepping_dim(grid) == time_dim(f)
@test stepping_dim(grid) != time_dim(grid)
@test stepping_dim(grid).o.is_Stepping
end
@testset "Sparse Function data with halo npoint=$npoint" for npoint in (1,5)
grid = Grid(shape=(5,5))
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", grid=grid, npoint=npoint)
for i in 1:npoint
data(sf)[i] = Float32(i)
end
for i in 1:npoint
@test data_with_halo(sf)[i] == Float32(i)
end
end
@testset "Sparse Time Function data with halo npoint=$npoint" for npoint in (1,5)
grid = Grid(shape=(5,5))
nt = 10
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", grid=grid, npoint=npoint, nt=nt)
for i in 1:npoint
data(stf)[i,:] .= Float32(i) * [1:nt;]
end
for i in 1:npoint
@test data_with_halo(stf)[i,:] ≈ Float32(i) * [1:nt;]
end
end
@testset "Sparse Time Function Inject and Interpolate" begin
dt = 0.01
nt = 101
time_range = 0.0f0:dt:dt*(nt-1)
grid = Grid(shape=(5,5),origin=(0.,0.),extent=(1.,1.))
p = TimeFunction(grid=grid,space_order=8,time_order=2,name="p")
y,x,t = dimensions(p)
dt = step(time_range)
smap = spacing_map(grid)
smap[spacing(t)] = dt
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=grid, npoint=1, nt=nt)
@test typeof(dimensions(src)[1]) == Dimension
coords = [0; 0.5]
src_coords = coordinates_data(src)
src_coords .= coords
src_data = data(src)
src_data .= reshape(1e3*Base.sin.(time_range .* (3*pi/2)),1,:)
pupdate = Eq(forward(p),1+p)
src_term = inject(src; field=forward(p), expr=src*spacing(t)^2)
rec = SparseTimeFunction(name="rec", grid=grid, npoint=2, nt=nt)
rec_coords = coordinates_data(rec)
rec_coords[:,1] .= coords
rec_coords[:,2] .= reverse(coords)
rec_term = interpolate(rec, expr=p)
op = Operator([pupdate,src_term,rec_term],name="SparseInjectInterp", subs=smap)
apply(op,time_M=nt-1)
@test data(p)[3,1,end-1] ≈ (nt-1) + sum(src_data[1:end-1])*dt^2
@test data(rec)[1,end] ≈ (nt-1) + sum(src_data[1:end-1])*dt^2
@test data(rec)[2,end] ≈ (nt-1)
end
@testset "Sparse Function Inject and Interpolate" begin
grid = Grid(shape=(5,5),origin=(0.,0.),extent=(1.,1.))
f = Devito.Function(grid=grid,space_order=8,time_order=2,name="f")
y,x = dimensions(f)
src = SparseFunction(name="src", grid=grid, npoint=1)
@test typeof(dimensions(src)[1]) == Dimension
coords = [0; 0.5]
src_coords = coordinates_data(src)
src_coords .= coords
src_data = data(src)
src_data .= 1
src_term = inject(src; field=f, expr=src)
rec = SparseFunction(name="rec", grid=grid, npoint=2)
rec_coords = coordinates_data(rec)
rec_coords[:,1] .= coords
rec_coords[:,2] .= reverse(coords)
rec_term = interpolate(rec, expr=f)
op = Operator([src_term,rec_term],name="SparseInjectInterp")
apply(op)
@test data(f)[3,1] == 1.0
# check that this was the only place where f became nonzero
data(f)[3,1] = 0.0
@test data(f) ≈ zeros(Float32,size(f)...)
@test data(rec)[1] == 1
@test data(rec)[2] == 0
end
# dxl/dxr implement Fornberg 1988 table 3, derivative order 1, order of accuracy 2
@testset "Left and Right Derivatives" begin
fornberg = Float64[-3/2, 2.0, -1/2]
n = 5
grid = Grid(shape=(n),extent=(n-1,))
x = dimensions(grid)[1]
fff = Devito.Function(name="fff", grid=grid, space_order=2)
fxl = Devito.Function(name="fxl", grid=grid, space_order=2)
fxr = Devito.Function(name="fxr", grid=grid, space_order=2)
data(fff)[div(n,2)+1] = 1.
eq1 = Eq(fxl, dxl(fff))
eq2 = Eq(fxr, dxr(fff))
op = Operator([eq1,eq2],name="Derivatives")
apply(op)
@test data(fxl)[3:5] ≈ -1 .* fornberg
@test data(fxr)[1:3] ≈ +1 .* reverse(fornberg)
end
@testset "Derivative Operator and Mixed Derivatives" begin
grid = Grid(shape=(12,16))
f = Devito.Function(grid=grid, name="f", space_order=8)
y, x = dimensions(f)
g1 = Devito.Function(grid=grid, name="g1", space_order=8)
g2 = Devito.Function(grid=grid, name="g2", space_order=8)
h1 = Devito.Function(grid=grid, name="h1", space_order=8)
h2 = Devito.Function(grid=grid, name="h2", space_order=8)
j1 = Devito.Function(grid=grid, name="j1", space_order=8)
j2 = Devito.Function(grid=grid, name="j2", space_order=8)
k1 = Devito.Function(grid=grid, name="k1", space_order=8)
k2 = Devito.Function(grid=grid, name="k2", space_order=8)
data(f) .= rand(Float32, size(f)...)
eq1a = Eq(g1, dx2(f))
eq1b = Eq(g2, Derivative(f, (x,2)))
eq2a = Eq(h1, dy2(f))
eq2b = Eq(h2, Derivative(f, (y,2)))
eq3a = Eq(j1, dxdy(f))
eq3b = Eq(j2, Derivative(f, y, x))
eq4a = Eq(k1, dy(dx2(f)))
eq4b = Eq(k2, Derivative(f, x, y, deriv_order=(2,1)))
derivop = Operator([eq1a, eq1b, eq2a, eq2b, eq3a, eq3b, eq4a, eq4b], name="derivOp")
apply(derivop)
@test sum(abs.(data(g1))) > 0
@test sum(abs.(data(h1))) > 0
@test sum(abs.(data(j1))) > 0
@test sum(abs.(data(k1))) > 0
@test data(g1) ≈ data(g2)
@test data(h1) ≈ data(h2)
@test data(j1) ≈ data(j2)
@test data(k1) ≈ data(k2)
end
@testset "Derivatives on Constants" begin
for x in (Constant(name="a", value=2), Constant(name="b", dtype=Float64, value=2), 1, -1.0, π)
@test dx(x) == 0
@test dxl(x) == 0
@test dxr(x) == 0
@test dy(x) == 0
@test dyl(x) == 0
@test dyr(x) == 0
@test dz(x) == 0
@test dzl(x) == 0
@test dzr(x) == 0
@test dx2(x) == 0
@test dy2(x) == 0
@test Derivative(x) == 0
@test dx(dx(x)+1) == 0
@test dxl(dxl(x)+1) == 0
@test dxr(dxr(x)+1) == 0
@test dy(dy(x)+1) == 0
@test dyl(dyl(x)+1) == 0
@test dyr(dyr(x)+1) == 0
@test dz(dz(x)+1) == 0
@test dzl(dzl(x)+1) == 0
@test dzr(dzr(x)+1) == 0
@test dx2(dx2(x)+1) == 0
@test dy2(dy2(x)+1) == 0
end
end
@testset "Derivatives on dimensions not in a function, T=$T" for T in (Float32,Float64)
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
grid = Grid(shape=(5,), dimensions=(x,), dtype=T)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid, dtype=T)
u = Devito.TimeFunction(name="u", grid=grid, dtype=T)
a = Constant(name="a", dtype=T, value=2)
b = Constant(name="b", dtype=T, value=2)
for func in (f,u)
@test dy(func) == 0
@test dyl(func) == 0
@test dyr(func) == 0
@test dz(func) == 0
@test dzl(func) == 0
@test dzr(func) == 0
@test dy(b*func+a-1) == 0
@test dyl(b*func+a-1) == 0
@test dyr(b*func+a-1) == 0
@test dz(b*func+a-1) == 0
@test dzl(b*func+a-1) == 0
@test dzr(b*func+a-1) == 0
end
end
@testset "Conditional Dimension Subsampling" begin
size, factr = 17, 4
i = Devito.SpaceDimension(name="i")
grd = Grid(shape=(size,),dimensions=(i,))
ci = ConditionalDimension(name="ci", parent=i, factor=factr)
@test parent(ci) == i
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=grd, shape=(size,), dimensions=(i,))
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grd, shape=(div(size,factr),), dimensions=(ci,))
op = Operator([Eq(g, i), Eq(f, g)],name="Conditional")
apply(op)
for j in 1:div(size,factr)
@test data(f)[j] == data(g)[(j-1)*factr+1]
end
end
@testset "Conditional Dimension Honor Condition" begin
# configuration!("log-level", "DEBUG")
# configuration!("opt", "noop")
# configuration!("jit-backdoor", false)
# configuration!("jit-backdoor", true)
# @show configuration()
x = Devito.SpaceDimension(name="x")
y = Devito.SpaceDimension(name="y")
grd = Grid(shape=(5,5),dimensions=(y,x),extent=(4,4))
f1 = Devito.Function(name="f1", grid=grd, space_order=0, is_transient=true)
f2 = Devito.Function(name="f2", grid=grd, space_order=0, is_transient=true)
f3 = Devito.Function(name="f3", grid=grd, space_order=0, is_transient=true)
g = Devito.Function(name="g", grid=grd, space_order=0, is_transient=true)
data(f1) .= 1.0
data(f2) .= 1.0
data(g)[:,3:end] .= 1.0
ci1 = ConditionalDimension(name="ci1", parent=y, condition=And(Ne(g, 0), Lt(y, 2)))
ci2 = ConditionalDimension(name="ci2", parent=y, condition=And(Ne(g, 0), Le(y, 2)))
# Note, the order of dimensions feeding into parent seems to matter.
# If the grid dimensions were (x,y)
# the above conditional dimension would cause a compilation error on the operator at runtime.
# write(stdout,"\n")
# @show data(f1)
# @show data(f2)
# @show data(f3)
# @show data(g)
eq1 = Eq(f1, f1+g, implicit_dims=ci1)
eq2 = Eq(f2, f2+g, implicit_dims=ci2)
eq3 = Eq(f3, f2-f1)
op = Operator([eq1,eq2,eq3], name="Implicit")
# apply(op, nthreads=2)
apply(op)
# write(stdout,"\n")
# @show data(f1)
# @show data(f2)
# @show data(f3)
# @show data(g)
# write(stdout,"\n")
# @show view(DevitoArray{Float32,2}(f1.o."_data_allocated"), localindices(f1)...)
@test data(f1)[1,1] == 1.0
@test data(f1)[1,3] == 2.0
@test data(f1)[1,5] == 2.0
@test data(f1)[2,2] == 1.0
@test data(f1)[2,3] == 2.0
@test data(f1)[3,3] == 1.0
@test data(f1)[5,1] == 1.0
@test data(f1)[5,3] == 1.0
@test data(f1)[5,5] == 1.0
@test data(f3)[1,1] == 0.0
@test data(f3)[3,1] == 0.0
@test data(f3)[3,2] == 0.0
@test data(f3)[3,3] == 1.0
@test data(f3)[3,4] == 1.0
@test data(f3)[3,5] == 1.0
@test data(f3)[2,3] == 0.0
@test data(f3)[2,4] == 0.0
@test data(f3)[2,5] == 0.0
@test data(f3)[4,3] == 0.0
@test data(f3)[4,4] == 0.0
@test data(f3)[4,5] == 0.0
end
@testset "Retrieve time_dim" begin
g = Grid(shape=(5,5))
@test time_dim(g) == dimension(g.o.time_dim)
t = TimeDimension(name="t")
f = TimeFunction(name="f",time_dim=t,grid=g)
@test time_dim(f) == t
@test time_dim(f) == dimensions(f)[end]
end
@testset "Dimension ordering in Function and Time Function Constuction, n=$n" for n in ((5,6),(4,5,6))
g = Grid(shape=n)
dims = dimensions(g)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=g, dimensions=dims)
@test dimensions(f) == dims
t = stepping_dim(g)
u = TimeFunction(name="u", grid=g, dimensions=(dims...,t))
@test typeof(dimensions(u)[end]) == Devito.SteppingDimension
@test dimensions(u) == (dims...,t)
end
@testset "Dimension ordering in SparseTimeFunction construction, n=$n" for n in ((5,6),(4,5,6))
g = Grid(shape=n)
p = Dimension(name="p")
t = time_dim(g)
dims = (p,t)
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", dimensions=dims, npoint=5, nt=4, grid=g)
@test dimensions(stf) == dims
end
@testset "Time Derivatives" begin
grd = Grid(shape=(5,5))
t = TimeDimension(name="t")
f1 = TimeFunction(name="f1",grid=grd,time_order=2,time_dim=t)
f2 = TimeFunction(name="f2",grid=grd,time_order=2,time_dim=t)
f3 = TimeFunction(name="f3",grid=grd,time_order=2,time_dim=t)
data(f1)[:,:,1] .= 0
data(f1)[:,:,2] .= 1
data(f1)[:,:,3] .= 4
smap = spacing_map(grd)
t_spacing = 0.5
smap[spacing(t)] = t_spacing
op = Operator([Eq(f2,dt(f1)),Eq(f3,dt2(f1))],name="DerivTest",subs=smap)
apply(op)
@test data(f2)[3,3,2] == (data(f1)[3,3,3] - data(f1)[3,3,2])/t_spacing
@test data(f3)[3,3,2] == (data(f1)[3,3,3] - 2*data(f1)[3,3,2] + data(f1)[3,3,1] )/t_spacing^2
end
@testset "nsimplify" begin
@test nsimplify(0) == 0
@test nsimplify(-1) == -1
@test nsimplify(1) == 1
@test nsimplify(π; tolerance=0.1) == nsimplify(22/7)
@test nsimplify(π) != nsimplify(π; tolerance=0.1)
g = Grid(shape=(5,))
x = dimensions(g)[1]
@test nsimplify(x+1) == x+1
@test nsimplify(1+x) == x+1
end
@testset "solve" begin
g = Grid(shape=(11,11))
u = TimeFunction(grid=g, name="u", time_order=2, space_order=8)
v = TimeFunction(grid=g, name="v", time_order=2, space_order=8)
for k in 1:size(data(u))[3], j in 1:size(data(u))[2], i in 1:size(data(u))[1]
data(u)[i,j,k] = k*0.02 + i*i*0.01 - j*j*0.03
end
data(v) .= data(u)
y,x,t = dimensions(u)
pde = dt2(u) - (dx(dx(u)) + dy(dy(u))) - dy(dx(u))
solved = Eq(forward(u),solve(pde, forward(u)))
eq = Eq(forward(v), (2 * v - backward(v)) + spacing(t)^2 * ( dx(dx(v)) - dy(dx(v)) + dy(dy(v))))
smap = spacing_map(g)
smap[spacing(t)] = 0.001
op = Operator([solved,eq],subs=smap,name="solve")
apply(op,time_M=5)
@test data(v) ≈ data(u)
end
@testset "name" begin
a = Constant(name="a")
@test name(a) == "a"
x = SpaceDimension(name="x")
@test name(x) == "x"
t = TimeDimension(name="t")
@test name(t) == "t"
t1 = ConditionalDimension(name="t1", parent=t, factor=2)
@test name(t1) == "t1"
time = SteppingDimension(name="time", parent=t)
@test name(time) == "time"
grid = Grid(shape=(5,))
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
@test name(f) == "f"
u = Devito.TimeFunction(name="u", grid=grid)
@test name(u) == "u"
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", npoint=1, grid=grid)
@test name(sf) == "sf"
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", npoint=1, nt=10, grid=grid)
@test name(stf) == "stf"
op = Operator(Eq(f,1), name="op")
@test name(op) == "op"
end
# jkw: had to switch to py"repr" to get string representation of PyObject
# something must have changes somewhere as we can no longer directly compare like `g == evaluate(h)``
@testset "subs" begin
grid = Grid(shape=(5,5,5))
dims = dimensions(grid)
for staggered in ((dims[1],),(dims[2],),(dims[3],),dims[1:2],dims[2:3],(dims[1],dims[3]),dims)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid, staggered=staggered)
for d in staggered
stagdict1 = Dict()
stagdict2 = Dict()
stagdict1[d] = d-spacing(d)/2
stagdict2[d] = d-spacing(d)
h = f
g = f
h = subs(h,stagdict1)
g = .5 * (g + subs(g,stagdict2))
sg = py"repr"(g)
sh = py"repr"(evaluate(h))
@show sg, sh, sg == sh
@test sg == sh
end
end
end
@testset "ccode" begin
grd = Grid(shape=(5,5))
f = Devito.Function(grid=grd, name="f")
op = Operator(Eq(f,1),name="ccode")
@test ccode(op) === nothing
ccode(op; filename="/tmp/ccode.cc")
code = open(f->read(f, String),"/tmp/ccode.cc")
@test typeof(code) == String
@test code != ""
end
@testset "Operator default naming" begin
grid1 = Devito.Grid(shape=(2,2), origin=(0,0), extent=(1,1), dtype=Float32)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid1, space_order=4)
op = Operator([Eq(f,1)]; name="foo")
@test name(op) == "foo"
op = Operator([Eq(f,1)])
@test name(op) == "Kernel"
op = Operator(Eq(f,1))
@test name(op) == "Kernel"
op = Operator( (Eq(f,1), Eq(f,1)))
@test name(op) == "Kernel"
op = Operator( [Eq(f,1), Eq(f,1)])
@test name(op) == "Kernel"
op = Operator(Eq(f,1), opt="advanced")
@test name(op) == "Kernel"
op = Operator( (Eq(f,1), Eq(f,1)), opt="advanced")
@test name(op) == "Kernel"
op = Operator( [Eq(f,1), Eq(f,1)], opt="advanced")
@test name(op) == "Kernel"
end
@testset "operator PyObject convert" begin
grid = Grid(shape=(3,4))
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grid)
op = Operator(Eq(f,1), name="ConvertOp")
@test typeof(convert(Operator, PyObject(op))) == Operator
@test convert(Operator, PyObject(op)) === op
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not an operator") convert(Operator, PyObject(f))
end
@testset "in_range throws out of range error" begin
@test_throws ErrorException("Outside Valid Ranges") Devito.in_range(10, ([1:5],[6:9]))
end
@testset "Serial inner halo methods, n=$n, space_order=$space_order" for n in ((3,4),(3,4,5)), space_order in (1,2,4)
grd = Grid(shape=n)
N = length(n)
time_order = 2
nt = 11
npoint=6
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=grd, space_order=space_order)
u = TimeFunction(name="u", grid=grd, space_order=space_order, time_order=2)
sf = SparseFunction(name="sf", grid=grd, npoint=npoint)
stf = SparseTimeFunction(name="stf", grid=grd, npoint=npoint, nt=nt)
for func in (f,u,sf,stf)
data(func) .= 1.0
end
halo_n = (2*space_order) .+ n
@test size(data_with_inhalo(f)) == halo_n
@test size(data_with_inhalo(u)) == (halo_n...,time_order+1)
@test size(data_with_inhalo(sf)) == (npoint,)
@test size(data_with_inhalo(stf)) == (npoint,nt)
haloed_f = zeros(Float32, halo_n...)
haloed_u = zeros(Float32, halo_n...,time_order+1)
if N == 2
haloed_f[1+space_order:end-space_order,1+space_order:end-space_order] .= 1.0
haloed_u[1+space_order:end-space_order,1+space_order:end-space_order,:] .= 1.0
else
haloed_f[1+space_order:end-space_order,1+space_order:end-space_order,1+space_order:end-space_order] .= 1.0
haloed_u[1+space_order:end-space_order,1+space_order:end-space_order,1+space_order:end-space_order,:] .= 1.0
end
@test data_with_inhalo(f) ≈ haloed_f
@test data_with_inhalo(u) ≈ haloed_u
@test data_with_inhalo(sf) ≈ ones(Float32, npoint)
@test data_with_inhalo(stf) ≈ ones(Float32, npoint, nt)
end
@testset "Buffer construction and use, buffer size = $value" for value in (1,2,4)
b = Buffer(value)
@test typeof(b) == Buffer
shp = (5,6)
grd = Grid(shape=shp)
u = TimeFunction(name="u", grid=grd, save=b)
@test size(u) == (shp...,value)
end
@testset "Generate Function from PyObject, n=$n" for n in ((3,4),(3,4,5))
g = Grid(shape=n)
f1 = Devito.Function(name="f1", grid=g)
f2 = Devito.Function(PyObject(f1))
@test isequal(f1, f2)
# try to make Functions from non-function objects
u = TimeFunction(name="u", grid=g)
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.Function") Devito.Function(PyObject(u))
c = Constant(name="c")
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.Function") Devito.Function(PyObject(c))
s = SparseFunction(name="s", grid=g, npoint=5)
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.Function") Devito.Function(PyObject(s))
st = SparseTimeFunction(name="st", grid=g, npoint=5, nt=10)
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.Function") Devito.Function(PyObject(st))
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.Function") Devito.Function(PyObject(1))
end
@testset "Generate SparseTimeFunction from PyObject, n=$n" for n in ((3,4),(3,4,5))
g = Grid(shape=n)
s1 = SparseTimeFunction(name="s1", grid=g, nt=10, npoint=5)
s2 = SparseTimeFunction(PyObject(s1))
@test isequal(s1, s2)
# try to make Functions from non-function objects
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=g)
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.SparseTimeFunction") SparseTimeFunction(PyObject(f))
u = TimeFunction(name="u", grid=g)
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.SparseTimeFunction") SparseTimeFunction(PyObject(u))
c = Constant(name="c")
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.SparseTimeFunction") SparseTimeFunction(PyObject(c))
s = SparseFunction(name="s", grid=g, npoint=5)
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.SparseTimeFunction") SparseTimeFunction(PyObject(s))
@test_throws ErrorException("PyObject is not a devito.SparseTimeFunction") SparseTimeFunction(PyObject(1))
end
@testset "Indexed Data n=$n, T=$T, space_order=$so" for n in ((3,4), (3,4,5)), T in (Float32, Float64), so in (4,8)
g = Grid(shape=n, dtype=T)
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=g, space_order=so)
fi = indexed(f)
@test typeof(fi) <: Devito.IndexedData
fi_index = fi[(n .- 1 )...]
@show fi_index
x = dimensions(g)[end]
fd_index = fi[(n[1:end-1] .- 2)..., x]
@test typeof(fi_index) <: Devito.Indexed
@test typeof(fd_index) <: Devito.Indexed
op = Operator([Eq(fi_index, 1), Eq(fd_index, 2)])
apply(op)
@test data(f)[(n .- 1 )...] == 1
data(f)[(n .- 1 )...] = 0
@test data(f)[(n[1:end-1] .- 2)...,:] ≈ 2 .* ones(T, n[end])
data(f)[(n[1:end-1] .- 2)...,:] .= 0
@test data(f) ≈ zeros(T, n...)
end
@testset "Function Inc, shape=$n" for n in ((4,5),(6,7,8),)
grid = Grid(shape=n)
A = Devito.Function(name="A", grid=grid)
v = Devito.Function(name="v", grid=grid, shape=size(grid)[1:end-1], dimensions=dimensions(grid)[1:end-1])
b = Devito.Function(name="b", grid=grid, shape=(size(grid)[end],), dimensions=(dimensions(grid)[end],))
data(v) .= 1.0
data(A) .= reshape([1:prod(size(grid));],size(grid)...)
op = Operator([Inc(b, A*v)], name="inctest")
apply(op)
@test data(b)[:] ≈ sum(data(A), dims=Tuple([1:length(n)-1;]))[:]
end
nothing
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | docs | 1302 | # Devito.jl contributor guidelines
## Issue reporting
If you have found a bug in Devito.jl or have any suggestions for changes to
Devito.jl functionality, please consider filing an issue using the GitHub
isssue tracker. Please do not forget to search for an existing issue
which may already cover your suggestion.
## Contributing
We try to follow GitHub flow (https://guides.github.com/introduction/flow/) for
making changes to Devito.jl.
Contributors retain copyright on their contributions, and the MIT license
(https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT) applies to the contribution.
The basic steps to making a contribution are as follows, and assume some knowledge of
git:
1. fork the Devito.jl repository
2. create an appropriately titled branch for your contribution
3. if applicable, add a unit-test to ensure the functionality of your contribution
(see the `test` subfolder).
4. run `]test Devito` in the `test` folder
5. make a pull-request
6. have fun
## Coding conventions
We try to follow the same coding conventions as https://github.com/JuliaLang/julia.
This primarily means using 4 spaces to indent (no tabs). In addition, we make a
best attempt to follow the guidelines in the style guide chapter of the julia
manual: https://docs.julialang.org/en/v1/manual/style-guide/
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | docs | 1392 |
# Devito.jl
| **Documentation** | **Action Statuses** |
|:---:|:---:|
| [![][docs-dev-img]][docs-dev-url] [![][docs-stable-img]][docs-stable-url] | [![][doc-build-status-img]][doc-build-status-url] [![][build-status-img]][build-status-url] [![][code-coverage-img]][code-coverage-results] |
Devito.jl is a Julia API supporting a sub-set of [devitoproject.org](https://www.devitoproject.org/). It provides support for Devito `Grid`'s, `Function`'s, `TimeFunction`'s, `SparseTimeFunction`'s, `SubDomain`'s, `Dimension`'s, etc... for both their serial and domain decomposed MPI variants.
[docs-dev-img]: https://img.shields.io/badge/docs-dev-blue.svg
[docs-dev-url]: https://chevronetc.github.io/Devito.jl/dev/
[docs-stable-img]: https://img.shields.io/badge/docs-stable-blue.svg
[docs-stable-url]: https://ChevronETC.github.io/Devito.jl/stable
[doc-build-status-img]: https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl/workflows/Documentation/badge.svg
[doc-build-status-url]: https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl/actions?query=workflow%3ADocumentation
[build-status-img]: https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl/workflows/Tests/badge.svg
[build-status-url]: https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl/actions?query=workflow%3A"Tests"
[code-coverage-img]: https://codecov.io/gh/ChevronETC/Devito.jl/branch/master/graph/badge.svg
[code-coverage-results]: https://codecov.io/gh/ChevronETC/Devito.jl
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | docs | 1150 | # Benchmarking
We use [PkgBenchmark.jl](http://github.com/juliaCI/PkgBenchmark.jl) which can be
installed using `Pkg.add("PkgBenchmark")`. To run the benchmarks:
```julia
using PkgBenchmark
results=benchmarkpkg("Devito")
export_markdown("results.md", results)
```
In order to compare the benchmarks against a different version:
```julia
results=judge("Devito", "e1d4076")
export_markdown("results.md", results)
```
where `e1d4076` is a Git SHA or the name of a Git branch. To run a specific
benchmark:
```julia
benchmarks=include("benchmarks.jl")
run(benchmarks["Partition of unity"]["construct"])
```
You can profile a benchmark. For example:
```julia
benchmarks=include("benchmarks.jl")
using Profile
@profile run(benchmarks["Partition of unity"]["construct"])
```
Use `Profile.print()` and `using ProfileView; ProfileView.view()` to inspect the
profile. Note that `ProfileView.view()` requires
[ProfileView.jl](http://github.com/timholy/ProfileView.jl).
For more information, please see the documentation for
[PkgBenchmark.jl](http://github.com/juliaCI/PkgBenchmark.jl) and
[BenchmarkTools.jl](https://github.com/JuliaCI/BenchmarkTools.jl).
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | docs | 6447 | # Devito.jl
This is a Julia API for Devito. it provides a Julia API's for a sub-set of Devito,
supporting `Grid`'s, `Function`'s, `TimeFunction`'s and `SparseTimeFunction`'s for both their
serial and domain decomposed MPI variants.
## Construction of a Devito stencil
The procedure for constructing a stencil operator consists of five parts:
1. Construction of a Grid object containing grid size and spacing information on which the stencil will operate
2. Construction of TimeFunction or Function objects that hold the actual arrays on which the stencil will operate
3. Construction of SparseTimeFunction objects that hold source and receiver data for injection and retrieval during the stencil operation
4. Construction of Eqn objects (equation objects) that specify the equations that the stencil operator will carry out
5. Construction of the operator object which generates the low level C code fo rthe stencil operator
Following this the operator may be executed. An example of these five steps is detailed below
1\. Definition of the Grid object
The `Grid` object is specified by initializing extent, spacing, and origin tuples in the constructor. Dimension objects contain the
abstract spacing variables used by SymPy in specifying abstract equations in the stencil definition
```julia
dt=1.
shpe=(20,20)
spacing=(5.,5.)
origin=(0.,0.)
extent=(shpe.-1).*spacing
spacet=Constant(name="h_t", dt)
t=TimeDimension(name="t",spacing=spacet)
spacex=Constant(name="h_x", spacing[1])
x=SpaceDimension(name="x",spacing=spacex)
spacez=Constant(name="h_z", spacing[2])
z=SpaceDimension(name="z",spacing=spacez)
grid=Grid(extent=extent, shape=shpe, origin=origin, dimensions=(x,z), time_dimension=t)
```
Note that unlike with the Devito Python implementation, which is column-major, all tuples involving dimensions are passed in row-major ordering. This row-major ordering convention is consistent throughout Devito.jl
2\. Construction of time and space functions
Parameters on the grid are specified using Function objects, while time dependent fields are specified using TimeFunction objects,
as in this 2D elastic example:
```julia
so=4
bx=Devito.Function(name= "bx" ,grid=grid, staggered=x, space_order=so)
bz=Devito.Function(name= "bz" ,grid=grid, staggered=z, space_order=so)
c11=Devito.Function(name="c11",grid=grid, space_order=so)
c33=Devito.Function(name="c33",grid=grid, space_order=so)
c55=Devito.Function(name="c55",grid=grid, staggered=(x,z), space_order=so)
c13=Devito.Function(name="c13",grid=grid, space_order=so)
data(bx).=mp[:,:,1]
data(bz).=mp[:,:,2]
data(c11).=mp[:,:,3]
data(c33).=mu[:,:,2]
data(c55).=mp[:,:,4]
data(c13).=mp[:,:,5]
vx=TimeFunction(name="vx", grid=grid,space_order=so, staggered=x, time_order=1)
vz=TimeFunction(name="vz", grid=grid,space_order=so, staggered=z, time_order=1)
tauxx=TimeFunction(name="tauxx",grid=grid,space_order=so, time_order=1)
tauzz=TimeFunction(name="tauzz",grid=grid,space_order=so, time_order=1)
tauxz=TimeFunction(name="tauxz",grid=grid,space_order=so, staggered=(x,z), time_order=1)
```
In this example, the `data()` function returns a view to the Function's internal data, which is then initialized from an externally defined arrays mp and mu.
3\. Construction of SparseTimeFunctions
`SparseTimeFunctions` are used to inject source and retrieve receiver information during the stencil operations
```julia
src = SparseTimeFunction(name="src", grid=grid, npoint=1, nt=nt)
src_coords = coordinates(src)
src_coords .= [625.0; 5.0]
src_data = data(src)
src_data.= ricker(nt,dt,f0)
src_term = inject(src; field=forward(tauxx), expr=src)
```
In this example, the source is created with an external function `ricker()`, which is then used to initialize the SparseTimeFunction data that will be injected into the
time function `forward(tauxx)`
4\. Construction of stencil equations
Stencil equations are created using the Eqn constructor
```julia
eqvx = Eq(forward(vx), vx + dt*bx*dx(tauxx) + dt*bx*dz(tauxz, x0=z) - dt*damp*vx)
eqvz = Eq(forward(vz), vz + dt*bz*dx(tauxz, x0=x) + dt*bz*dz(tauzz) - dt*damp*vz)
```
In this particular fragment from an elastic 2D example, damp is an externally defined array for damping at the boundaries, vx and vz are particle velocities, and the tau variables are the stresses
5\. Construction of the operator
Construction of the operator requires a list containing all objects created using the `inject()`, `interpolate()`, and `Eq()` functions:
```julia
op=Operator(op_list, subs=spacing_map(grid))
apply(op)
```
where op_list contains the objects comprising the stencil.
## Data access
Devito.jl provides a Julia array interface for convenient and fast (copy-free) access to
the Devito numpy arrays. For example,
```julia
using Devito
configuration!("language", "openmpi")
configuration!("mpi", false)
configuration() # show the Devito configuration
g = Grid(shape=(10,20,30))
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=g, space_order=8)
d = data(f)
d_with_halo = data_with_halo(f)
d_with_inhalo = data_with_inhalo(f)
```
In the above code listing:
* `d` is a view of the underlying numpy array that excludes Devito's exterior and interior halo padding
* `d_with_halo` is a view that includes Devito's exterior halo padding, but excludes its interior halo padding
* `d_with_inhalo` is a view that includes Divito's exterior and interior halo padding
If we are running with MPI turned on, then the `data`, `data_with_halo` and `data_with_inhalo` methods return
a view to an MPI domain distributed array. This array can be gathered to the rank 0 MPI rank with the convert
method:
```julia
using Devito
configuration!("language", "openmpi")
configuration!("mpi", true)
g = Grid(shape=(10,20,30))
f = Devito.Function(name="f", grid=g, space_order=8)
d = data(f)
p = parent(d) # array local to this MPI rank
_d = convert(Array, d) # _d is an Array on MPI rank 0 gathered from `d` which is decomposed accross all MPI ranks
```
Please see the `demo` folder in this package for more details.
In general, the wrapping of Devito functionality uses the same function and argument names as in the original Python implementation, with
python class members being accessed in Julia through functions having the same name as the member, and taking the class object as the first argument.
For more details, please refer to the Devito website https://github.com/devitocodes/devito.
| Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.13.4 | 74a131037d93a10cd857d958e635c3b6b70d8238 | docs | 77 | # Reference
```@autodocs
Modules = [Devito]
Order = [:function, :type]
``` | Devito | https://github.com/ChevronETC/Devito.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 486 | using Documenter, DynamicGrids, CUDAKernels
CI = get(ENV, "CI", nothing) == "true" || get(ENV, "GITHUB_TOKEN", nothing) !== nothing
makedocs(
modules = [DynamicGrids],
sitename = "DynamicGrids.jl",
checkdocs = :all,
strict = true,
format = Documenter.HTML(
prettyurls = CI,
),
pages = [
"DynamicGrids" => "index.md",
# "Examples" => "examples.md",
],
)
deploydocs(
repo = "github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git",
)
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 3744 | module DynamicGrids
# Use the README as the module docs
@doc let
path = joinpath(dirname(@__DIR__), "README.md")
include_dependency(path)
read(path, String)
end DynamicGrids
using Adapt,
Colors,
ConstructionBase,
Crayons,
DimensionalData,
FreeTypeAbstraction,
FileIO,
LinearAlgebra,
KernelAbstractions,
OffsetArrays,
REPL,
Reexport,
Requires,
Setfield,
StaticArrays,
Test,
UnicodeGraphics
@reexport using ModelParameters
import ModelParameters.Flatten
using DimensionalData.LookupArrays, DimensionalData.Dimensions
const DG = DynamicGrids
const DD = DimensionalData
using Base: tail, @propagate_inbounds
import Base: show, getindex, setindex!, lastindex, size, length, push!, append!,
broadcast, broadcast!, similar, eltype, iterate
export sim!, resume!, step!, savegif, isinferred
export rules
export inbounds, isinbounds
export gridsize, currentframe, currenttime, currenttimestep, timestep
export add!, sub!, min!, max!, and!, or!, xor!
export Extent, StaticExtent
export Rule, NeighborhoodRule, CellRule, SetCellRule, SetNeighborhoodRule, SetGridRule
export Cell, Neighbors, SetNeighbors, SetCell, Convolution, SetGrid, Life, CopyTo
export RuleWrapper, Chain, RunIf, RunAt
export AbstractRuleset, Ruleset, StaticRuleset
export AbstractSimData
export Processor, SingleCPU, ThreadedCPU, CPUGPU
export PerformanceOpt, NoOpt, SparseOpt
export BoundaryCondition, Remove, Wrap
export ParameterSource, Aux, Grid, Delay, Lag, Frame
export Output, ArrayOutput, ResultOutput, TransformedOutput
export GraphicOutput, REPLOutput
export ImageOutput, GifOutput
export Renderer, Image, Layout, SparseOptInspector
export TextConfig
export ObjectScheme, Greyscale, Grayscale
export CharStyle, Block, Braile
# From Neighborhoods module
export Neighborhood, Window, AbstractKernelNeighborhood, Kernel,
Moore, VonNeumann, Positional, LayeredPositional
export neighbors, neighborhood, kernel, kernelproduct, offsets, positions, radius, distances
const DEFAULT_KEY = :_default_
const EXPERIMENTAL = """
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions,
and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
"""
include("Neighborhoods/Neighborhoods.jl")
using .Neighborhoods
import .Neighborhoods: neighbors, neighborhood, kernel, kernelproduct, offsets, positions,
radius, distances, readwindow, setwindow, unsafe_readwindow,
updatewindow, unsafe_updatewindow
include("interface.jl")
include("flags.jl")
include("rules.jl")
include("settings.jl")
include("rulesets.jl")
include("extent.jl")
include("grid.jl")
include("simulationdata.jl")
include("parametersources.jl")
include("gpu.jl")
include("atomic.jl")
include("chain.jl")
include("condition.jl")
include("outputs/interface.jl")
include("outputs/output.jl")
include("outputs/graphic.jl")
include("outputs/schemes.jl")
include("outputs/textconfig.jl")
include("outputs/render.jl")
include("outputs/image.jl")
include("outputs/array.jl")
include("outputs/transformed.jl")
include("outputs/repl.jl")
include("outputs/gif.jl")
include("framework.jl")
include("modifyrule.jl")
include("sequencerules.jl")
include("generated.jl")
include("maprules.jl")
include("boundaries.jl")
include("sparseopt.jl")
include("utils.jl")
include("copyto.jl")
include("life.jl")
include("adapt.jl")
include("show.jl")
function __init__()
global terminal
terminal = REPL.Terminals.TTYTerminal(get(ENV, "TERM", Base.Sys.iswindows() ? "" : "dumb"), stdin, stdout, stderr)
@require CUDAKernels = "72cfdca4-0801-4ab0-bf6a-d52aa10adc57" include("cuda.jl")
end
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 1247 | # Adapt method for DynamicGrids objects
function Adapt.adapt_structure(to, x::AbstractSimData)
@set! x.grids = map(g -> Adapt.adapt(to, g), x.grids)
@set! x.extent = Adapt.adapt(to, x.extent)
return x
end
function Adapt.adapt_structure(to, x::GridData)
@set! x.source = Adapt.adapt(to, x.source)
@set! x.source = Adapt.adapt(to, x.source)
@set! x.mask = Adapt.adapt(to, x.mask)
@set! x.dest = Adapt.adapt(to, x.dest)
@set! x.optdata = Adapt.adapt(to, x.optdata)
return x
end
function Adapt.adapt_structure(to, x::AbstractExtent)
@set! x.init = _adapt_x(to, init(x))
@set! x.mask = _adapt_x(to, mask(x))
@set! x.aux = _adapt_x(to, aux(x))
return x
end
_adapt_x(to, A::AbstractArray) = Adapt.adapt(to, A)
_adapt_x(to, nt::NamedTuple) = map(A -> Adapt.adapt(to, A), nt)
_adapt_x(to, nt::Nothing) = nothing
# Adapt output frames to GPU
# TODO: this may be incorrect use of Adapt.jl, as the Output
# object is not entirely adopted for GPU use, the CuArray
# frames are still held in a regular Array.
function Adapt.adapt_structure(to, o::Output)
frames = map(o.frames) do f
_adapt_x(to, f)
end
@set! o.extent = adapt(to, o.extent)
@set! o.frames = frames
return o
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 1075 | # Atomic opterations
const atomic_ops = ((:add!, :+), (:sub!, :-), (:min!, :min), (:max!, :max),
(:and!, :&), (:or!, :|), (:xor!, :xor))
# Methods for writing to a WritableGridData grid from . These are
# associative and commutative so that write order does not affect the result.
for (f, op) in atomic_ops
@eval begin
@propagate_inbounds ($f)(d::AbstractSimData, x, I...) = ($f)(first(d), x, I...)
@propagate_inbounds ($f)(d::WritableGridData{<:Any,R}, x, I...) where R = ($f)(d, proc(d), x, I...)
@propagate_inbounds function ($f)(d::WritableGridData{<:Any,R}, ::Processor, x, I...) where R
@boundscheck checkbounds(dest(d), I...)
@inbounds _setoptindex!(d, x, I...)
@inbounds dest(d)[I...] = ($op)(dest(d)[I...], x)
end
@propagate_inbounds function ($f)(
d::WritableGridData{<:Any,R}, proc::Union{ThreadedCPU,CPUGPU}, x, I...
) where R
lock(proc)
($f)(d, SingleCPU(), x, I...)
unlock(proc)
end
end
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 4136 | # See interface docs
@inline inbounds(data::Union{GridData,AbstractSimData}, I::Tuple) = inbounds(data, I...)
@inline inbounds(data::Union{GridData,AbstractSimData}, I...) =
_inbounds(boundary(data), gridsize(data), I...)
@inline function _inbounds(boundary::BoundaryCondition, size::Tuple, i1, i2)
a, inbounds_a = _inbounds(boundary, size[1], i1)
b, inbounds_b = _inbounds(boundary, size[2], i2)
(a, b), inbounds_a & inbounds_b
end
@inline _inbounds(::Remove, size::Number, i::Number) = i, _isinbounds(size, i)
@inline function _inbounds(::Wrap, size::Number, i::Number)
if i < oneunit(i)
size + rem(i, size), true
elseif i > size
rem(i, size), true
else
i, true
end
end
# See interface docs
@inline isinbounds(data::Union{GridData,AbstractSimData}, I::Tuple) = isinbounds(data, I...)
@inline isinbounds(data::Union{GridData,AbstractSimData}, I...) = _isinbounds(gridsize(data), I...)
@inline _isinbounds(size::Tuple, I...) = all(map(_isinbounds, size, I))
@inline _isinbounds(size, i) = i >= one(i) && i <= size
# _updateboundary
# Reset or wrap boundary where required. This allows us to ignore
# bounds checks on neighborhoods and still use a wraparound grid.
_updateboundary!(grids::Tuple) = map(_updateboundary!, grids)
function _updateboundary!(g::GridData{<:Any,R}) where R
R < 1 && return g
return _updateboundary!(g, boundary(g))
end
function _updateboundary!(g::GridData{S,R}, ::Remove) where {S<:Tuple{L},R} where {L}
src = parent(source(g))
@inbounds src[1:R] .= Ref(padval(g))
@inbounds src[L+R+1:L+2R] .= Ref(padval(g))
return g
end
function _updateboundary!(g::GridData{S,R}, ::Remove) where {S<:Tuple{Y,X},R} where {Y,X}
src = parent(source(g))
# Left
@inbounds src[1:Y, 1:R] .= Ref(padval(g))
# Right
@inbounds src[1:Y, X+R+1:X+2R] .= Ref(padval(g))
# Top middle
@inbounds src[1:R, R+1:X+R] .= Ref(padval(g))
# Bottom middle
@inbounds src[Y+R+1:Y+2R, R+1:X+R] .= Ref(padval(g))
return g
end
function _updateboundary!(g::GridData{S,R}, ::Wrap) where {S<:Tuple{L},R} where {L}
src = parent(source(g))
startpad = 1:R
endpad = L+R+1:L+2R
startvals = R+1:2R+1
endvals = L:L+R
@inbounds copyto!(src, CartesianIndices((startpad,)), src, CartesianIndices((endvals,)))
@inbounds copyto!(src, CartesianIndices((endpad,)), src, CartesianIndices((startvals,)))
return g
end
function _updateboundary!(g::GridData{S,R}, ::Wrap) where {S<:Tuple{Y,X},R} where {Y,X}
src = parent(source(g))
nrows, ncols = gridsize(g)
startpadrow = startpadcol = 1:R
endpadrow = nrows+R+1:nrows+2R
endpadcol = ncols+R+1:ncols+2R
startrow = startcol = 1+R:2R
endrow = nrows+1:nrows+R
endcol = ncols+1:ncols+R
rows = 1+R:nrows+R
cols = 1+R:ncols+R
# Sides ---
# Left
@inbounds copyto!(src, CartesianIndices((rows, startpadcol)),
src, CartesianIndices((rows, endcol)))
# Right
@inbounds copyto!(src, CartesianIndices((rows, endpadcol)),
src, CartesianIndices((rows, startcol)))
# Top
@inbounds copyto!(src, CartesianIndices((startpadrow, cols)),
src, CartesianIndices((endrow, cols)))
# Bottom
@inbounds copyto!(src, CartesianIndices((endpadrow, cols)),
src, CartesianIndices((startrow, cols)))
# Corners ---
# Top Left
@inbounds copyto!(src, CartesianIndices((startpadrow, startpadcol)),
src, CartesianIndices((endrow, endcol)))
# Top Right
@inbounds copyto!(src, CartesianIndices((startpadrow, endpadcol)),
src, CartesianIndices((endrow, startcol)))
# Botom Left
@inbounds copyto!(src, CartesianIndices((endpadrow, startpadcol)),
src, CartesianIndices((startrow, endcol)))
# Botom Right
@inbounds copyto!(src, CartesianIndices((endpadrow, endpadcol)),
src, CartesianIndices((startrow, startcol)))
_wrapopt!(g)
return g
end
_wrapopt!(g) = _wrapopt!(g, opt(g))
_wrapopt!(g, ::PerformanceOpt) = g
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 4571 | """
Chain(rules...)
Chain(rules::Tuple)
`Chain`s allow chaining rules together to be completed in a single processing step,
without intermediate reads or writes from grids.
They are potentially compiled together into a single function call, especially if you
use `@inline` on all `applyrule` methods. `Chain` can hold either all [`CellRule`](@ref)
or [`NeighborhoodRule`](@ref) followed by [`CellRule`](@ref).
[`SetRule`](@ref) can't be used in `Chain`, as it doesn't have a return value.
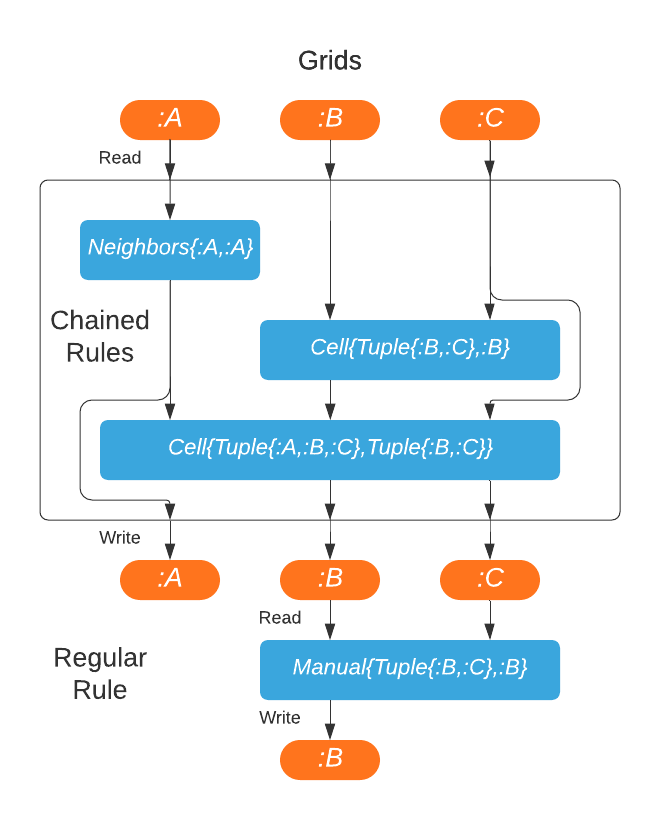
"""
struct Chain{R,W,T<:Union{Tuple{},Tuple{Union{<:NeighborhoodRule,<:CellRule},Vararg{<:CellRule}}}} <: RuleWrapper{R,W}
rules::T
end
Chain(rules...) = Chain(rules)
Chain(rules::Tuple) = begin
rkeys = Tuple{union(map(k -> _asiterable(_readkeys(k)), rules)...)...}
wkeys = Tuple{union(map(k -> _asiterable(_writekeys(k)), rules)...)...}
Chain{rkeys,wkeys,typeof(rules)}(rules)
end
# Getter
rules(chain::Chain) = chain.rules
# Only the first rule in a chain can be a NeighborhoodRule
radius(chain::Chain) = radius(chain[1])
neighborhoodkey(chain::Chain) = neighborhoodkey(chain[1])
neighborhood(chain::Chain) = neighborhood(chain[1])
neighbors(chain::Chain) = neighbors(chain[1])
@inline function setwindow(chain::Chain{R,W}, win) where {R,W}
rules = (setwindow(chain[1], win), tail(chain.rules)...)
Chain{R,W,typeof(rules)}(rules)
end
function Base.tail(chain::Chain{R,W}) where {R,W}
chaintail = tail(rules(chain))
Chain{R,W,typeof(chaintail)}(chaintail)
end
Base.getindex(chain::Chain, i) = getindex(rules(chain), i)
Base.iterate(chain::Chain) = iterate(rules(chain))
Base.length(chain::Chain) = length(rules(chain))
Base.firstindex(chain::Chain) = firstindex(rules(chain))
Base.lastindex(chain::Chain) = lastindex(rules(chain))
ruletype(chain::Chain) = ruletype(first(chain))
@generated function applyrule(data::AbstractSimData, chain1::Chain{R,W,T}, state1, index) where {R,W,T}
expr = Expr(:block)
nrules = length(T.parameters)
for i in 1:nrules
# Variables are numbered to make debugging type stability easier
state = Symbol("state$i")
nextstate = Symbol("state$(i+1)")
rule = Symbol("rule$i")
read = Symbol("read$i")
write = Symbol("write$i")
chain = Symbol("chain$i")
nextchain = Symbol("chain$(i+1)")
rule_expr = quote
$rule = $chain[1]
# Get the state needed by this rule
$read = _filter_readstate($rule, $state)
# Run the rule
$write = applyrule(data, $rule, $read, index)
# Create new state with the result and state from other rules
$nextstate = _update_chainstate($rule, $state, $write)
$nextchain = tail($chain)
end
push!(expr.args, rule_expr)
end
laststate = Symbol("state$(nrules+1)")
push!(expr.args, :(_filter_writestate(chain1, $laststate)))
expr
end
function modifyrule(chain::Chain{R,W}, simdata) where {R,W}
Chain{R,W}(_modifyrules(rules(chain), simdata))
end
# Get the state to pass to the specific rule as a `NamedTuple` or single value
@generated function _filter_readstate(::Rule{R,W}, state::NamedTuple) where {R<:Tuple,W}
expr = Expr(:tuple)
keys = Tuple(R.parameters)
for k in keys
push!(expr.args, :(state[$(QuoteNode(k))]))
end
:(NamedTuple{$keys}($expr))
end
@inline _filter_readstate(::Rule{R,W}, state::NamedTuple) where {R,W} = state[R]
# Get the state to write for the specific rule
@generated function _filter_writestate(::Rule{R,W}, state::NamedTuple) where {R<:Tuple,W<:Tuple}
expr = Expr(:tuple)
keys = Tuple(W.parameters)
for k in keys
push!(expr.args, :(state[$(QuoteNode(k))]))
end
expr
end
# Merge new state with previous state.
# Returns a new `NamedTuple` with all keys having the most recent state
@generated function _update_chainstate(rule::Rule{R,W}, state::NamedTuple{K,V}, writestate
) where {R,W,K,V}
expr = Expr(:tuple)
writekeys = W isa Symbol ? (W,) : W.parameters
keys = (union(K, writekeys)...,)
for (i, k) in enumerate(keys)
if k in writekeys
for (j, wkey) in enumerate(writekeys)
if k == wkey
push!(expr.args, :(writestate[$j]))
end
end
else
push!(expr.args, :(state[$i]))
end
end
:(NamedTuple{$keys}($expr))
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 3784 | """
RunIf(f, rule)
`RunIf`s allows wrapping a rule in a condition, passed the `SimData` object and the cell state and index.
```julia
RunIf(dispersal) do data, state, I
state >= oneunit(state)
end
`` `
"""
struct RunIf{R,W,F,T<:Rule{R,W}} <: RuleWrapper{R,W}
f::F
rule::T
end
rule(runif::RunIf) = runif.rule
# Forward ruletype, radius and neighborhoodkey to the contained rule
ruletype(runif::RunIf) = ruletype(rule(runif))
radius(runif::RunIf) = radius(rule(runif))
neighborhoodkey(runif::RunIf) = neighborhoodkey(rule(runif))
neighborhood(runif::RunIf) = neighborhood(rule(runif))
neighbors(runif::RunIf) = neighbors(rule(runif))
@inline function setwindow(runif::RunIf{R,W}, win) where {R,W}
f = runif.f
r = setwindow(rule(runif), win)
RunIf{R,W,typeof(f),typeof(r)}(f, r)
end
# We have to hook into cell_kernel! to handle the option of no return value
@inline function cell_kernel!(
simdata, ruletype::Val{<:Rule}, condition::RunIf, rkeys, wkeys, I...
)
readval = _readcell(simdata, rkeys, I...)
if condition.f(simdata, readval, I)
writeval = applyrule(simdata, rule(condition), readval, I)
_writecell!(simdata, ruletype, wkeys, writeval, I...)
else
# Otherwise copy source to dest without change
_writecell!(simdata, ruletype, wkeys, _readcell(simdata, wkeys, I...), I...)
end
return nothing
end
# We have to hook into cell_kernel! to handle the option of no return value
@inline function cell_kernel!(
simdata, ::Type{<:SetRule}, condition::RunIf, rkeys, wkeys, I...
)
readval = _readcell(simdata, rkeys, I...)
if condition.f(data, readval, I)
applyrule!(simdata, rule(condition), readval, I)
end
return nothing
end
"""
RunAt(rules...)
RunAt(rules::Tuple)
`RunAt`s allow running a `Rule` or multiple `Rule`s at a lower frequeny
than the main simulation, using a `range` matching the main `tspan` but with a larger
span, or specific events - by using a vector of arbitrary times in `tspan`.
"""
struct RunAt{R,W,Ru<:Tuple,Ti<:AbstractVector} <: RuleWrapper{R,W}
rules::Ru
times::Ti
end
RunAt(rules...; times) = RunAt(rules, times)
RunAt(rules::Tuple; times) = RunAt(rules, times)
function RunAt(rules::Tuple, times)
rkeys = Tuple{union(map(k -> _asiterable(_readkeys(k)), rules)...)...}
wkeys = Tuple{union(map(k -> _asiterable(_writekeys(k)), rules)...)...}
RunAt{rkeys,wkeys,typeof(rules),typeof(times)}(rules, times)
end
rules(runat::RunAt) = runat.rules
# Only the first rule in runat can be a NeighborhoodRule, but this seems annoying...
radius(runat::RunAt) = radius(first(rules(runat)))
# Forward ruletype to the contained rule
ruletype(runat::RunAt) = ruletype(first(rules(runat)))
neighborhoodkey(runat::RunAt) = neighborhoodkey(first(rules(runat)))
neighborhood(runat::RunAt) = neighborhood(neighborhood(rules(runat)))
neighbors(runat::RunAt) = neighbors(rules(runat))
function sequencerules!(simdata::AbstractSimData, rules::Tuple{<:RunAt,Vararg})
runat = rules[1]
if currenttime(simdata) in runat.times
# Run the sequenced rule
simdata = sequencerules!(simdata, DynamicGrids.rules(runat))
end
# Run the rest of the rules recursively
sequencerules!(simdata, tail(rules))
end
function Base.tail(runat::RunAt{R,W}) where {R,W}
rulestail = tail(rules(runat))
RunAt{R,W,typeof(rulestail),typeof(runat.times)}(rulestail, runat.times)
end
Base.getindex(runat::RunAt, i) = getindex(rules(runat), i)
Base.iterate(runat::RunAt) = iterate(rules(runat))
Base.iterate(runat::RunAt, nothing) = iterate(rules(runat), nothing)
Base.length(runat::RunAt) = length(rules(runat))
Base.firstindex(runat::RunAt) = firstindex(rules(runat))
Base.lastindex(runat::RunAt) = lastindex(rules(runat))
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 818 | """
CopyTo <: CellRule
CopyTo{W}(from)
CopyTo{W}(; from)
A simple rule that copies aux array slices to a grid over time.
This can be used for comparing simulation dynamics to aux data dynamics.
"""
struct CopyTo{W,F} <: CellRule{Tuple{},W}
"An Aux or Grid key for data source or a single value"
from::F
end
CopyTo(from) = CopyTo{DEFAULT_KEY}(from)
CopyTo(; from) = CopyTo{DEFAULT_KEY}(from)
CopyTo{W}(from) where W = CopyTo{W,typeof(from)}(from)
CopyTo{W}(; from) where W = CopyTo{W,typeof(from)}(from)
ConstructionBase.constructorof(::Type{<:CopyTo{W}}) where W = CopyTo{W}
DynamicGrids.applyrule(data, rule::CopyTo, state, I) = get(data, rule.from, I)
DynamicGrids.applyrule(data, rule::CopyTo{W}, state, I) where W <: Tuple =
ntuple(i -> get(data, rule.from, I), length(_asiterable(W)))
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 981 | using .CUDAKernels, .CUDAKernels.CUDA
import ModelParameters.Flatten
export CuGPU
"""
CuGPU <: GPU
CuGPU()
CuGPU{threads_per_block}()
```julia
ruleset = Ruleset(rule; proc=CuGPU())
# or
output = sim!(output, rule; proc=CuGPU())
```
"""
struct CuGPU{X} <: GPU end
CuGPU() = CuGPU{32}()
# CUDA setup
kernel_setup(::CuGPU{N}) where N = CUDAKernels.CUDADevice(), (N, N)
# _proc_setup
# Convert all arrays in SimData to CuArrays
@noinline function _proc_setup(::CuGPU, simdata::AbstractSimData)
Adapt.adapt(CuArray, simdata)
end
_copyto_output!(outgrid, grid::GridData, proc::GPU) = copyto!(outgrid, gridview(grid))
# Thread-safe CUDA atomic ops
for (f, op) in atomic_ops
atomic_f = Symbol(:atomic_, f)
@eval begin
function ($f)(d::WritableGridData{<:Any,R}, ::CuGPU, x, I...) where R
A = parent(dest(d))
i = Base._to_linear_index(A, (I .+ R)...)
(CUDA.$atomic_f)(pointer(A, i), x)
end
end
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 3855 | """
AbstractExtent
Abstract supertype for `Extent` objects, that hold all variables related
to space and time in a simulation. Usually the field of an output.
"""
abstract type AbstractExtent{I,M,A,PV} end
init(e::AbstractExtent) = e.init
mask(e::AbstractExtent) = e.mask
aux(e::AbstractExtent) = e.aux
@inline aux(e::AbstractExtent, key) = aux(aux(e), key)
@noinline aux(::Nothing, key) =
throw(ArgumentError("No aux data available. Pass a NamedTuple to the `aux=` keyword of the Output"))
padval(e::AbstractExtent) = e.padval
tspan(e::AbstractExtent) = e.tspan # Never type-stable, only access in `modifyrule` methods
gridsize(extent::AbstractExtent) = gridsize(init(extent))
Base.ndims(e::AbstractExtent{<:AbstractArray}) = ndims(init(e))
Base.ndims(e::AbstractExtent{<:NamedTuple}) = ndims(first(init(e)))
Base.size(e::AbstractExtent{<:AbstractArray}) = size(init(e))
Base.size(e::AbstractExtent{<:NamedTuple}) = size(first(init(e)))
(::Type{T})(e::AbstractExtent) where T<:AbstractExtent = T(init(e), mask(e), aux(e), padval(e), tspan(e))
const EXTENT_KEYWORDS = """
- `init`: initialisation `Array`/`NamedTuple` for grid/s.
- `mask`: `BitArray` for defining cells that will/will not be run.
- `aux`: NamedTuple of arbitrary input data. Use `aux(data, Aux(:key))` to access from
a `Rule` in a type-stable way.
- `padval`: padding value for grids with neighborhood rules. The default is
`zero(eltype(init))`.
- `tspan`: Time span range. Never type-stable, only access this in `modifyrule` methods
"""
"""
Extent <: AbstractExtent
Extent(init, mask, aux, padval, tspan)
Extent(; init, tspan, mask=nothing, aux=nothing, padval=zero(eltype(init)), kw...)
Container for extensive variables: spatial and timeseries data.
These are kept separate from rules to allow application
of rules to alternate spatial and temporal contexts.
Extent is not usually constructed directly by users, but it can be passed
to `Output` constructors instead of `init`, `mask`, `aux` and `tspan`.
# Arguments/Keywords
$EXTENT_KEYWORDS
"""
mutable struct Extent{I<:Union{AbstractArray,NamedTuple},
M<:Union{AbstractArray,Nothing},
A<:Union{NamedTuple,Nothing},
PV} <: AbstractExtent{I,M,A,PV}
init::I
mask::M
aux::A
padval::PV
tspan::AbstractRange
function Extent(init::I, mask::M, aux::A, padval::PV, tspan::T) where {I,M,A,PV,T}
# Check grid sizes match
gridsize = if init isa NamedTuple
size_ = size(first(init))
if !all(map(i -> size(i) == size_, init))
throw(ArgumentError("`init` grid sizes do not match"))
end
size_
else
size(init)
end
if (mask !== nothing) && (size(mask) != gridsize)
throw(ArgumentError("`mask` size do not match `init`"))
end
new{I,M,A,PV}(init, mask, aux, padval, tspan)
end
end
Extent(; init, mask=nothing, aux=nothing, padval=_padval(init), tspan, kw...) =
Extent(init, mask, aux, padval, tspan)
Extent(init::Union{AbstractArray,NamedTuple}; kw...) = Extent(; init, kw...)
settspan!(e::Extent, tspan) = e.tspan = tspan
_padval(init::NamedTuple) = map(_padval, init)
_padval(init::AbstractArray{T}) where T = zero(T)
# An immutable `Extent` object, for internal use.
struct StaticExtent{I<:Union{AbstractArray,NamedTuple},
M<:Union{AbstractArray,Nothing},
A<:Union{NamedTuple,Nothing},
PV,T} <: AbstractExtent{I,M,A,PV}
init::I
mask::M
aux::A
padval::PV
tspan::T
end
StaticExtent(; init, mask=nothing, aux=nothing, padval=_padval(init), tspan, kw...) =
StaticExtent(init, mask, aux, padval, tspan)
StaticExtent(init::Union{AbstractArray,NamedTuple}; kw...) = Extent(; init, kw...)
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 2515 | """
PerformanceOpt
Abstract supertype for performance optimisation flags.
"""
abstract type PerformanceOpt end
"""
NoOpt <: PerformanceOpt
NoOpt()
Flag to run a simulation without performance optimisations besides basic high performance
programming. Still fast, but not intelligent about the work that it does: all cells are run
for all rules.
`NoOpt` is the default `opt` method.
"""
struct NoOpt <: PerformanceOpt end
"""
Processor
Abstract supertype for selecting a hardware processor, such as ia CPU or GPU.
"""
abstract type Processor end
"""
CPU <: Processor
Abstract supertype for CPU processors.
"""
abstract type CPU <: Processor end
"""
SingleCPU <: CPU
SingleCPU()
[`Processor`](@ref) flag that specifies to use a single thread on a single CPU.
Specifiy with:
```julia
ruleset = Ruleset(rule; proc=SingleCPU())
# or
output = sim!(output, rule; proc=SingleCPU())
```
"""
struct SingleCPU <: CPU end
"""
ThreadedCPU <: CPU
ThreadedCPU()
[`Processor`](@ref) flag that specifies to use a `Threads.nthreads()` CPUs.
Specifiy with:
```julia
ruleset = Ruleset(rule; proc=ThreadedCPU())
# or
output = sim!(output, rule; proc=ThreadedCPU())
```
"""
struct ThreadedCPU{L} <: CPU
spinlock::L
end
ThreadedCPU() = ThreadedCPU(Base.Threads.SpinLock())
Base.Threads.lock(opt::ThreadedCPU) = lock(opt.spinlock)
Base.Threads.unlock(opt::ThreadedCPU) = unlock(opt.spinlock)
"""
BoundaryCondition
Abstract supertype for flags that specify the boundary conditions used in the simulation,
used in [`inbounds`](@ref) and to update [`NeighborhoodRule`](@ref) grid padding.
These determine what happens when a neighborhood or jump extends outside of the grid.
"""
abstract type BoundaryCondition end
"""
Wrap <: BoundaryCondition
Wrap()
[`BoundaryCondition`](@ref) flag to wrap cordinates that boundary boundaries back to the
opposite side of the grid.
Specifiy with:
```julia
ruleset = Ruleset(rule; boundary=Wrap())
# or
output = sim!(output, rule; boundary=Wrap())
```
"""
struct Wrap <: BoundaryCondition end
"""
Remove <: BoundaryCondition
Remove()
[`BoundaryCondition`](@ref) flag that specifies to assign `padval` to cells that overflow
grid boundaries. `padval` defaults to `zero(eltype(grid))` but can be assigned as a keyword
argument to an [`Output`](@ref).
Specifiy with:
```julia
ruleset = Ruleset(rule; boundary=Remove())
# or
output = sim!(output, rule; boundary=Remove())
```
"""
struct Remove <: BoundaryCondition end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 9310 |
"""
sim!(output, rules::Rule...; kw...)
sim!(output, rules::Tuple{<:Rule,Vararg}; kw...)
sim!(output, [ruleset::Ruleset=ruleset(output)]; kw...)
Runs the simulation rules over the `output` `tspan`,
writing the destination array to `output` for each time-step.
# Arguments
- `output`: An [`Output`](@ref) to store grids or display them on the screen.
- `ruleset`: A [`Ruleset`](@ref) containing one or more [`Rule`](@ref)s. If the output
has a `Ruleset` attached, it will be used.
# Keywords
Theses are the taken from the `output` argument by default:
- `init`: optional array or NamedTuple of arrays.
- `mask`: a `Bool` array matching the init array size. `false` cells do not run.
- `aux`: a `NamedTuple` of auxilary data to be used by rules.
- `tspan`: a tuple holding the start and end of the timespan the simulaiton will run for.
- `fps`: the frames per second to display. Will be taken from the output if not passed in.
Theses are the taken from the `ruleset` argument by default:
- `proc`: a [`Processor`](@ref) to specificy the hardware to run simulations on,
like [`SingleCPU`](@ref), [`ThreadedCPU`](@ref) or [`CuGPU`](@ref) when
KernelAbstractions.jl and a CUDA gpu is available.
- `opt`: a [`PerformanceOpt`](@ref) to specificy optimisations like
[`SparseOpt`](@ref) or [`NoOpt`](@ref). Defaults to `NoOpt()`.
- `boundary`: what to do with boundary of grid edges. Options are [`Remove`](@ref) or [`Wrap`](@ref), defaulting to `Remove()`.
- `cellsize`: the size of cells, which may be accessed by rules.
- `timestep`: fixed timestep where this is required for some rules.
eg. `Month(1)` or `1u"s"`.
Other:
- `simdata`: a [`SimData`](@ref) object. Keeping it between simulations can reduce memory
allocation a little, when that is important.
"""
function sim!(output::Output, ruleset=ruleset(output);
init=init(output),
mask=mask(output),
tspan=tspan(output),
aux=aux(output),
fps=fps(output),
boundary=boundary(ruleset),
proc=proc(ruleset),
opt=opt(ruleset),
cellsize=cellsize(ruleset),
timestep=timestep(ruleset),
simdata=nothing,
)
isrunning(output) && error("Either a simulation is already running in this output, or an error occurred")
setrunning!(output, true) || error("Could not start the simulation with this output")
gridsize(init) == gridsize(DG.init(output)) || throw(ArgumentError("init size does not match output init"))
# Rebuild Extent to allow kwarg alterations
extent = Extent(; init=_asnamedtuple(init), mask=mask, aux=aux, tspan=tspan)
simruleset = Ruleset(rules(ruleset);
boundary=boundary, proc=proc, opt=opt, cellsize=cellsize, timestep=timestep,
)
# Some rules are only valid for a set time-step size.
step(simruleset) !== nothing && step(simruleset) != step(tspan) &&
throw(ArgumentError("tspan step $(step(tspan)) must equal rule step $(step(simruleset))"))
# Set up output
settspan!(output, tspan)
# Create or update the combined data object for the simulation
simdata = initdata!(simdata, output, extent, simruleset)
init_output_grids!(output, init)
# Set run speed for GraphicOutputs
setfps!(output, fps)
# Run any initialisation the output needs to do
initialise!(output, simdata)
# Show the first grid
showframe(output, simdata)
# Let the init grid be displayed for as long as a normal grid
maybesleep(output, 1)
# Run the simulation over simdata and a unitrange we keep
# the original ruleset to allow interactive updates to rules.
# We pass throught the original ruleset as a handle for e.g.
# control sliders to update the rules.
return runsim!(output, simdata, ruleset, 1:lastindex(tspan))
end
sim!(output::Output, rules::Tuple; kw...) = sim!(output, rules...; kw...)
sim!(output::Output, rules::Rule...; kw...) = sim!(output, Ruleset(rules...); kw...)
"""
resume!(output::GraphicOutput, ruleset::Ruleset=ruleset(output); tstop, kw...)
Restart the simulation from where you stopped last time. For arguments see [`sim!`](@ref).
The keyword arg `tstop` can be used to extend the length of the simulation.
# Arguments
- `output`: An [`Output`](@ref) to store grids or display them on the screen.
- `ruleset`: A [`Ruleset`](@ref) containing one ore more [`Rule`](@ref)s.
These will each be run in sequence.
# Keywords (optional)
- `tstop`: the new stop time for the simulation. Taken from the output length by default.
- `fps`: the frames per second to display. Taken from the output by default.
- `simdata`: a [`SimData`](@ref) object. Keeping it between simulations can improve performance
when that is important
"""
function resume!(output::GraphicOutput, ruleset::Ruleset=ruleset(output);
tstop=last(tspan(output)),
fps=fps(output),
simdata=nothing,
)
# Check status and arguments
isrunning(output) && error("A simulation is already running in this output")
# Calculate new timespan
new_tspan = first(tspan(output)):step(tspan(output)):tstop
frame = stoppedframe(output)
fspan = frame:lastindex(new_tspan)
settspan!(output, new_tspan)
# Use the last frame of the existing simulation as the init frame
if frame <= length(output)
init = output[frame]
else
init = output[1]
end
setfps!(output, fps)
extent = Extent(; init=_asnamedtuple(init), mask=mask(output), aux=aux(output), tspan=new_tspan)
simdata = initdata!(simdata, output, extent, ruleset)
initialise!(output, simdata)
setrunning!(output, true) || error("Could not start the simulation with this output")
return runsim!(output, simdata, ruleset, fspan)
end
# Simulation runner. Runs a simulation synchonously or asynchonously
# depending on the return value of `isasync(output)` - which may be a
# fixed trait or a field value depending on the output type.
# This allows interfaces with interactive components to update during the simulations.
function runsim!(output, simdata, ruleset, fspan)
if isasync(output)
@async simloop!(output, simdata, ruleset, fspan)
else
simloop!(output, simdata, ruleset, fspan)
end
end
# Loop over the frames in `fspan`, running the ruleset and displaying the output.
# Operations on outputs and rulesets are allways mutable and in-place.
# Operations on [`Rule`](@ref)s and [`SimData`](@ref) objects are in a
# functional style, as they are used in inner loops where immutability improves
# performance.
function simloop!(output::Output, simdata, ruleset, fspan)
# Set the frame timestamp for fps calculation
settimestamp!(output, first(fspan))
# Initialise types etc
simdata = _updatetime(simdata, 1) |> _proc_setup
# Loop over the simulation
for f in fspan[2:end]
# Update the current simulation frame and time
simdata = _updatetime(simdata, f)
# Update any Delay parameters
drules = _setdelays(rules(ruleset), simdata)
# Run a timestep
simdata = _step!(simdata, drules)
# Save/do something with the the current grid
storeframe!(output, simdata)
# Let output UI things happen
isasync(output) && yield()
# Stick to the FPS
maybesleep(output, f)
# Exit gracefully
if !isrunning(output) || f == last(fspan)
showframe(output, simdata)
setstoppedframe!(output, f)
finalise!(output, simdata)
break
end
end
setrunning!(output, false)
return output
end
_step!(sd::AbstractSimData, rules) = _updaterules(rules, sd) |> sequencerules!
"""
step!(sd::AbstractSimData)
Allows stepping a simulation one frame at a time, for a more manual approach
to simulation that `sim!`. This may be useful if other processes need to be run
between steps, or the simulation is of variable length. `step!` also removes the use
of `Output`s, meaning storing of grid data must be handled manually, if that is
required. Of course, an output can also be updated manually, using:
```julia
DynmicGrids.storeframe!(output, simdata)
```
Instead of an `Output`, the internal [`SimData`](@ref) objects are used directly,
and can be defined using a [`Extent`](@ref) object and a [`Ruleset`](@ref).
# Example
```julia
using DynmicGrids, Plots
ruleset = Ruleset(Life(); proc=ThreadedCPU())
extent = Extent(; init=(a=A, b=B), aux=aux, tspan=tspan)
simdata = SimData(extent, ruleset)
# Run a single step, which returns an updated `SimData` object
simdata = step!(simdata)
# Get a view of the grid without padding
grid = DynmicGrids.gridview(simdata[:a])
heatmap(grid)
```
This example returns a `GridData` object for the `:a` grid, which is `<: AbstractAray`.
"""
step!(sd::AbstractSimData; rules=rules(sd)) = step!(sd::AbstractSimData, rules)
step!(sd::AbstractSimData, r1::Rule, rs::Rule...) = step!(sd::AbstractSimData, (r1, rs...))
function step!(sd::AbstractSimData, rules::Tuple)
_updatetime(sd, currentframe(sd) + 1) |>
_proc_setup |>
sd -> _step!(sd, rules)
end
# _proc_setup
# Allows different processors to modify the simdata object
# GPU needs this to convert arrays to CuArray
_proc_setup(simdata::AbstractSimData) = _proc_setup(proc(simdata), simdata)
_proc_setup(proc, simdata) = simdata
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 7977 |
# Low-level generated functions for working with grids
# _initialise_windows => NTuple{N,SMatrix}
# Generate an SArray from the main array
@generated function _initialise_windows(src::AbstractArray{T}, ::Val{R}, i, j) where {T,R}
B = 2R; S = 2R + 1; L = S^2
columns = []
# This column is never used, so fill with zeros
zerocol = Expr[]
for r in 1:2B
push!(zerocol, :(zero(T)))
end
push!(columns, zerocol)
for c in 0:S-2
newcol = Expr[]
for r in 0:2B-1
push!(newcol, :(@inbounds src[i + $r, j + $c]))
end
push!(columns, newcol)
end
newwindows = Expr(:tuple)
for b in 1:B
winvals = Expr(:tuple)
for c in 1:S, r in b:b+B
exp = columns[c][r]
push!(winvals.args, exp)
end
push!(newwindows.args, :(SArray{Tuple{$S,$S},$T,2,$L}($winvals)))
end
return quote
return $newwindows
end
end
# _slide_windows => NTuple{N,SMatrix}
# Generate a tuple of SArrays from the main array and the previous SArrays
@generated function _slide_windows(
windows::Tuple, src::AbstractArray{T}, ::Val{R}, i, j
) where {T,R}
B = 2R; S = 2R + 1; L = S^2
newvals = Expr[]
for n in 0:2B-1
push!(newvals, :(@inbounds src[i + $n, j + 2R]))
end
newwindows = Expr(:tuple)
for b in 1:B
winvals = Expr(:tuple)
for n in S+1:L
push!(winvals.args, :(@inbounds windows[$b][$n]))
end
for n in b:b+B
push!(winvals.args, newvals[n])
end
push!(newwindows.args, :(SArray{Tuple{$S,$S},$T,2,$L}($winvals)))
end
return quote
return $newwindows
end
end
# _readcell
# Returns a single value or NamedTuple of values.
# This occurs for every cell for every rule, so has to be very fast.
@generated function _readcell(data, ::K, I...) where K<:Tuple
expr = Expr(:tuple)
keys = map(_unwrap, Tuple(K.parameters))
for (i, k) in enumerate(keys)
push!(expr.args, :(@inbounds source(data[$(QuoteNode(k))])[I...]))
end
return quote
keys = $keys
vals = $expr
NamedTuple{keys,typeof(vals)}(vals)
end
end
@inline function _readcell(data::AbstractSimData, ::Val{K}, I...) where K
@inbounds source(data[K])[I...]
end
# _writecell! => nothing
# Write values to grid/s at index `I`.
# This occurs for every cell for every rule, so has to be very fast.
@generated function _writecell!(data, ::Val{<:CellRule}, wkeys::K, vals::Union{Tuple,NamedTuple}, I...) where K<:Tuple
expr = Expr(:block)
keys = map(_unwrap, Tuple(K.parameters))
for (i, k) in enumerate(keys)
# MUST write to source(grid) - CellRule doesn't switch grids
push!(expr.args, :(@inbounds source(data[$(QuoteNode(k))])[I...] = vals[$i]))
end
push!(expr.args, :(nothing))
return expr
end
@inline function _writecell!(data, ::Val{<:CellRule}, wkeys::Val{K}, val, I...) where K
# MUST write to source(grid) - CellRule doesn't switch grids
@inbounds source(data[K])[I...] = val
return nothing
end
@generated function _writecell!(data, ::Val, wkeys::K, vals::Union{Tuple,NamedTuple}, I...) where K<:Tuple
expr = Expr(:block)
keys = map(_unwrap, Tuple(K.parameters))
for (i, k) in enumerate(keys)
# MUST write to dest(grid) here, not grid K
# setindex! has overrides for the grid
push!(expr.args, :(@inbounds dest(data[$(QuoteNode(k))])[I...] = vals[$i]))
end
push!(expr.args, :(nothing))
return expr
end
@inline function _writecell!(data, ::Val, wkeys::Val{K}, val, I...) where K
# MUST write to dest(grid) here, not grid K
# setindex! has overrides for the grid
@inbounds dest(data[K])[I...] = val
return nothing
end
# _getreadgrids => Union{ReadableGridData,Tuple{ReadableGridData,Vararg}}
# Retrieves `GridData` from a `SimData` object to match the requirements of a `Rule`.
# Returns a `Tuple` holding the key or `Tuple` of keys, and grid or `Tuple` of grids.
@generated function _getreadgrids(::Rule{R,W}, data::AbstractSimData) where {R<:Tuple,W}
Expr(:tuple,
Expr(:tuple, (:(Val{$(QuoteNode(key))}()) for key in R.parameters)...),
Expr(:tuple, (:(data[$(QuoteNode(key))]) for key in R.parameters)...),
)
end
@generated function _getreadgrids(::Rule{R,W}, data::AbstractSimData) where {R,W}
:((Val{$(QuoteNode(R))}(), data[$(QuoteNode(R))]))
end
# _getwritegrids => Union{WritableGridData,Tuple{WritableGridData,Vararg}}
# Retrieves `GridData` from a `SimData` object to match the requirements of a `Rule`.
# Returns a `Tuple` holding the key or `Tuple` of keys, and grid or `Tuple` of grids.
@generated function _getwritegrids(::Rule{R,W}, data::AbstractSimData) where {R,W<:Tuple}
Expr(:tuple,
Expr(:tuple, (:(Val{$(QuoteNode(key))}()) for key in W.parameters)...),
Expr(:tuple, (:(WritableGridData(data[$(QuoteNode(key))])) for key in W.parameters)...),
)
end
@generated function _getwritegrids(::Rule{R,W}, data::AbstractSimData) where {R,W}
:((Val{$(QuoteNode(W))}(), WritableGridData(data[$(QuoteNode(W))])))
end
# _combinegrids => AbstractSimData
# Combine grids into a new NamedTuple of grids depending
# on the read and write keys required by a rule.
@inline function _combinegrids(data::AbstractSimData, wkeys, wgrids)
allkeys = map(Val, keys(data))
allgrids = values(data)
_combinegrids(data, allkeys, allgrids, wkeys, wgrids)
end
@inline function _combinegrids(data::AbstractSimData, rkeys, rgrids, wkeys, wgrids)
@set data.grids = _combinegrids(rkeys, rgrids, wkeys, wgrids)
end
@inline function _combinegrids(rkey, rgrids, wkey, wgrids)
_combinegrids((rkey,), (rgrids,), (wkey,), (wgrids,))
end
@inline function _combinegrids(rkey, rgrids, wkeys::Tuple, wgrids::Tuple)
_combinegrids((rkey,), (rgrids,), wkeys, wgrids)
end
@inline function _combinegrids(rkeys::Tuple, rgrids::Tuple, wkey, wgrids)
_combinegrids(rkeys, rgrids, (wkey,), (wgrids,))
end
@generated function _combinegrids(rkeys::Tuple, rgrids::Tuple, wkeys::Tuple, wgrids::Tuple)
rkeys = _vals2syms(rkeys)
wkeys = _vals2syms(wkeys)
keysexp = Expr(:tuple, QuoteNode.(wkeys)...)
dataexp = Expr(:tuple, :(wgrids...))
for (i, key) in enumerate(rkeys)
if !(key in wkeys)
push!(dataexp.args, :(rgrids[$i]))
push!(keysexp.args, QuoteNode(key))
end
end
return quote
keys = $keysexp
vals = $dataexp
NamedTuple{keys,typeof(vals)}(vals)
end
end
# _replacegrids => AbstractSimData
# Replace grids in a NamedTuple with new grids where required.
function _replacegrids(data::AbstractSimData, newkeys, newgrids)
@set data.grids = _replacegrids(grids(data), newkeys, newgrids)
end
@generated function _replacegrids(allgrids::NamedTuple, newkeys::Tuple, newgrids::Tuple)
newkeys = map(_unwrap, newkeys.parameters)
allkeys = allgrids.parameters[1]
expr = Expr(:tuple)
for key in allkeys
if key in newkeys
i = findfirst(k -> k == key, newkeys)
push!(expr.args, :(newgrids[$i]))
else
push!(expr.args, :(allgrids.$key))
end
end
return quote
vals = $expr
NamedTuple{$allkeys,typeof(vals)}(vals)
end
end
@generated function _replacegrids(allgrids::NamedTuple, newkey::Val, newgrid::GridData)
newkey = _unwrap(newkey)
allkeys = allgrids.parameters[1]
expr = Expr(:tuple)
for key in allkeys
if key == newkey
push!(expr.args, :(newgrid))
else
push!(expr.args, :(allgrids.$key))
end
end
return quote
vals = $expr
NamedTuple{$allkeys,typeof(vals)}(vals)
end
end
# _vals2syms => Union{Symbol,Tuple}
# Get symbols from a Val or Tuple type
@inline _vals2syms(x::Type{<:Tuple}) = map(v -> _vals2syms(v), x.parameters)
@inline _vals2syms(::Type{<:Val{X}}) where X = X
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 1636 | """
GPU <: Processor
Abstract supertype for GPU processors.
"""
abstract type GPU <: Processor end
"""
CPUGPU <: GPU
CPUGPU()
Uses the CUDA GPU code on CPU using KernelAbstractions, to test it.
"""
struct CPUGPU{L} <: GPU
spinlock::L
end
CPUGPU() = CPUGPU(Base.Threads.SpinLock())
Base.Threads.lock(opt::CPUGPU) = lock(opt.spinlock)
Base.Threads.unlock(opt::CPUGPU) = unlock(opt.spinlock)
kernel_setup(::CPUGPU) = KernelAbstractions.CPU(), 1
function maprule!(
data::AbstractSimData, proc::GPU, opt, ruletype::Val{<:Rule}, rule, rkeys, wkeys
)
kernel! = ka_rule_kernel!(kernel_setup(proc)...)
kernel!(data, ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys; ndrange=gridsize(data)) |> wait
return nothing
end
# ka_rule_kernel!
# Runs cell_kernel! on GPU after retrieving the global index
# and setting the neighborhood buffer to a SArray window retrieved
# from the first (neighborhood) grid
@kernel function ka_rule_kernel!(data, ruletype::Val{<:NeighborhoodRule}, rule, rkeys, wkeys)
I = @index(Global, NTuple)
neighborhood_kernel!(data, _firstgrid(data, rkeys), ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys, I...)
nothing
end
@kernel function ka_rule_kernel!(data, ruletype::Val, rule, rkeys, wkeys)
I = @index(Global, NTuple)
cell_kernel!(data, ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys, I...)
nothing
end
### Indexing. UNSAFE / LOCKS required
# This is not safe for general use.
# It can be used where only identical transformations of a cell
# can happen from any other cell, such as setting all 1s to 2.
@propagate_inbounds function _setindex!(d::WritableGridData, opt::GPU, x, I...)
dest(d)[I...] = x
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 9344 | """
GridData <: StaticArray
Simulation data specific to a single grid.
These behave like arrays, but contain both source and
destination arrays as simulations need separate read and
write steps to maintain independence between cells.
`GridData` objects also contain other data and settings needed
for optimisations.
# Type parameters
- `S`: grid size type tuple
- `R`: grid padding radius
- `T`: grid data type
"""
abstract type GridData{S,R,T,N} <: StaticArray{S,T,N} end
function (::Type{G})(d::GridData{S,R,T,N}) where {G<:GridData,S,R,T,N}
args = source(d), dest(d), mask(d), proc(d), opt(d), boundary(d), padval(d), optdata(d)
G{S,R,T,N,map(typeof, args)...}(args...)
end
function ConstructionBase.constructorof(::Type{T}) where T<:GridData{S,R} where {S,R}
T.name.wrapper{S,R}
end
# Getters
radius(d::GridData{<:Any,R}) where R = R
mask(d::GridData) = d.mask
proc(d::GridData) = d.proc
opt(d::GridData) = d.opt
optdata(d::GridData) = d.optdata
boundary(d::GridData) = d.boundary
padval(d::GridData) = d.padval
source(d::GridData) = d.source
dest(d::GridData) = d.dest
# Get the size of the grid
gridsize(d::GridData) = size(d)
gridsize(A::AbstractArray) = size(A)
gridsize(nt::NamedTuple) = gridsize(first(nt))
gridsize(nt::NamedTuple{(),Tuple{}}) = 0, 0
# Get a view of the grid, without padding
gridview(d::GridData) = sourceview(d)
# Get a view of the grid source, without padding
sourceview(d::GridData) = _padless_view(source(d), axes(d), radius(d))
# Get a view of the grid dest, without padding
destview(d::GridData) = _padless_view(dest(d), axes(d), radius(d))
_padless_view(A::OffsetArray, axes, radius) = _padless_view(parent(A), axes, radius)
function _padless_view(A::AbstractArray, axes, radius)
ranges = map(axes) do axis
axis .+ radius
end
return view(A, ranges...)
end
# Get an a view of the source, preferring the underlying array if it is not a padded OffsetArray
source_array_or_view(d::GridData) = source(d) isa OffsetArray ? sourceview(d) : source(d)
# Get an a view of the dest, preferring the underlying array if it is not a padded OffsetArray
dest_array_or_view(d::GridData) = dest(d) isa OffsetArray ? destview(d) : dest(d)
# Base methods
function Base.copy!(grid::GridData{<:Any,R}, A::AbstractArray) where R
pad_axes = map(ax -> ax .+ R, axes(A))
copyto!(parent(source(grid)), CartesianIndices(pad_axes), A, CartesianIndices(A))
return _update_optdata!(grid)
end
function Base.copy!(A::AbstractArray, grid::GridData{<:Any,R}) where R
pad_axes = map(ax -> ax .+ R, axes(A))
copyto!(A, CartesianIndices(A), parent(source(grid)), CartesianIndices(pad_axes))
return A
end
function Base.copy!(A::AbstractDimArray{T,N}, grid::GridData{<:Any,R}) where {T,N,R}
copy!(parent(A), grid)
return A
end
function Base.copy!(grid::GridData{<:Any,R}, A::AbstractDimArray{T,N}) where {R,T,N}
copy!(grid, parent(A))
return grid
end
function Base.copy!(dst::GridData{<:Any,RD}, src::GridData{<:Any,RS}) where {RD,RS}
dst_axes = map(s -> RD:s + RD, size(dst))
src_axes = map(s -> RS:s + RS, size(src))
copyto!(parent(source(dst)), CartesianIndices(dst_axes),
parent(source(src)), CartesianIndices(src_axes)
)
return dst
end
@propagate_inbounds Base.getindex(d::GridData{s}, I...) where s = getindex(source(d), I...)
@propagate_inbounds function Base.getindex(d::GridData{s}, i1::Int, I::Int...) where s
getindex(source(d), i1, I...)
end
# Local utility methods
# _addpadding => OffsetArray{T,N}
# Find the maximum radius required by all rules
# Add padding around the original init array, offset into the negative
# So that the first real cell is still 1, 1
function _addpadding(init::AbstractArray{T,1}, r, padval) where T
l = length(init)
paddedsize = l + 2r
paddedaxis = -r + 1:l + r
sourceparent = fill(convert(T, padval), paddedsize)
source = OffsetArray(sourceparent, paddedaxis)
# Copy the init array to the middle section of the source array
for i in 1:l
@inbounds source[i] = init[i]
end
return source
end
function _addpadding(init::AbstractArray{T,2}, r, padval) where T
h, w = size(init)
paddedsize = h + 4r, w + 2r
paddedaxes = -r + 1:h + 3r, -r + 1:w + r
pv = convert(eltype(init), padval)
sourceparent = similar(init, typeof(pv), paddedsize...)
sourceparent .= Ref(pv)
# Copy the init array to the middle section of the source array
_padless_view(sourceparent, axes(init), r) .= init
source = OffsetArray(sourceparent, paddedaxes...)
return source
end
# _swapsource => ReadableGridData
# Swap source and dest arrays of a grid
_swapsource(d::Tuple) = map(_swapsource, d)
function _swapsource(grid::GridData)
src = grid.source
dst = grid.dest
@set! grid.dest = src
@set! grid.source = dst
_swapoptdata(opt(grid), grid)
end
_swapoptdata(opt::PerformanceOpt, grid::GridData) = grid
_build_optdata(opt::PerformanceOpt, init, r) = nothing
_update_optdata!(grid::GridData) = _update_optdata!(grid, opt(grid))
_update_optdata!(grid, opt) = grid
# _indtoblock
# Convert regular index to block index
@inline _indtoblock(x::Int, blocksize::Int) = (x - 1) ÷ blocksize + 1
# _blocktoind
# Convert block index to regular index
@inline _blocktoind(x::Int, blocksize::Int) = (x - 1) * blocksize + 1
"""
ReadableGridData <: GridData
ReadableGridData(grid::GridData)
ReadableGridData{S,R}(init::AbstractArray, mask, opt, boundary, padval)
[`GridData`](@ref) object passed to rules for reading only.
Reads are always from the `source` array.
"""
struct ReadableGridData{
S<:Tuple,R,T,N,Sc,D,M,P<:Processor,Op<:PerformanceOpt,Bo,PV,OD
} <: GridData{S,R,T,N}
source::Sc
dest::D
mask::M
proc::P
opt::Op
boundary::Bo
padval::PV
optdata::OD
end
function ReadableGridData{S,R}(
source::Sc, dest::D, mask::M, proc::P, opt::Op, boundary::Bo,
padval::PV, optdata::OD
) where {S,R,Sc<:AbstractArray{T,N},D,M,P,Op,Bo,PV,OD} where {T,N}
ReadableGridData{S,R,T,N,Sc,D,M,P,Op,Bo,PV,OD}(
source, dest, mask, proc, opt, boundary, padval, optdata
)
end
@inline function ReadableGridData{S,R}(
init::AbstractArray, mask, proc, opt, boundary, padval
) where {S,R}
# If the grid radius is larger than zero we pad it as an OffsetArray
if R > 0
source = _addpadding(init, R, padval)
dest = _addpadding(init, R, padval)
else
source = deepcopy(init)
dest = deepcopy(init)
end
optdata = _build_optdata(opt, source, R)
grid = ReadableGridData{S,R}(
source, dest, mask, proc, opt, boundary, padval, optdata
)
return _update_optdata!(grid)
end
function Base.parent(d::ReadableGridData{S,<:Any,T,N}) where {S,T,N}
SizedArray{S,T,N}(source_array_or_view(d))
end
"""
WritableGridData <: GridData
WritableGridData(grid::GridData)
[`GridData`](@ref) object passed to rules as write grids, and can be written
to directly as an array, or preferably using `add!` etc. All writes handle
updates to `SparseOpt()` and writing to the correct source/dest array.
Reads are always from the `source` array, while writes are always to the
`dest` array. This is because rules application must not be sequential
between cells - the order of cells the rule is applied to does not matter.
This means that using e.g. `+=` is not supported. Instead use `add!`.
"""
struct WritableGridData{
S<:Tuple,R,T,N,Sc<:AbstractArray{T,N},D<:AbstractArray{T,N},
M,P<:Processor,Op<:PerformanceOpt,Bo,PV,OD
} <: GridData{S,R,T,N}
source::Sc
dest::D
mask::M
proc::P
opt::Op
boundary::Bo
padval::PV
optdata::OD
end
function WritableGridData{S,R}(
source::Sc, dest::D, mask::M, proc::P, opt::Op,
boundary::Bo, padval::PV, optdata::OD
) where {S,R,Sc<:AbstractArray{T,N},D<:AbstractArray{T,N},M,P,Op,Bo,PV,OD} where {T,N}
WritableGridData{S,R,T,N,Sc,D,M,P,Op,Bo,PV,OD}(
source, dest, mask, proc, opt, boundary, padval, optdata
)
end
Base.parent(d::WritableGridData{S}) where {S} = SizedArray{S}(destview(d))
### UNSAFE / LOCKS required
# Base.setindex!
# This is not safe for general use.
# It can be used where only identical transformations of a cell
# can happen from any other cell, such as setting all 1s to 2.
@propagate_inbounds function Base.setindex!(d::WritableGridData, x, I...)
_setindex!(d, proc(d), x, I...)
end
@propagate_inbounds function Base.setindex!(d::WritableGridData, x, i1::Int, I::Int...)
_setindex!(d, proc(d), x, i1, I...)
end
@propagate_inbounds function _setindex!(d::WritableGridData, proc::SingleCPU, x, I...)
@boundscheck checkbounds(dest(d), I...)
@inbounds _setoptindex!(d, x, I...)
@inbounds dest(d)[I...] = x
end
@propagate_inbounds function _setindex!(d::WritableGridData, proc::ThreadedCPU, x, I...)
# Dest status is not threadsafe, even if the
# setindex itself is safe. So we LOCK
lock(proc)
@inbounds _setoptindex!(d, x, I...)
unlock(proc)
@inbounds dest(d)[I...] = x
end
# _setoptindex!
# Do anything the optimisation needs on `setindex`
_setoptindex!(d::WritableGridData{<:Any,R}, x, I...) where R = _setoptindex!(d, opt(d), x, I...)
_setoptindex!(d::WritableGridData{<:Any,R}, opt::PerformanceOpt, x, I...) where R = nothing
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 6617 | """
applyrule(data::AbstractSimData, rule::Rule{R,W}, state, index::Tuple{Int,Int}) -> cell value(s)
Apply a rule to the cell state and return values to write to the grid(s).
This is called in `maprule!` methods during the simulation,
not by the user. Custom `Rule` implementations must define this method.
## Arguments
- `data` : [`AbstractSimData`](@ref)
- `rule` : [`Rule`](@ref)
- `state`: the value(s) of the current cell
- `index`: a (row, column) tuple of Int for the current cell coordinates
Returns the value(s) to be written to the current cell(s) of
the grids specified by the `W` type parameter.
"""
function applyrule end
"""
applyrule!(data::AbstractSimData, rule::{R,W}, state, index::Tuple{Int,Int}) -> Nothing
Apply a rule to the cell state and manually write to the grid data array.
Used in all rules inheriting from [`SetCellRule`](@ref).
This is called in internal `maprule!` methods during the simulation, not by
the user. Custom [`SetCellRule`](@ref) implementations must define this method.
Only grids specified with the `W` type parameter will be writable from `data`.
## Arguments
- `data` : [`AbstractSimData`](@ref)
- `rule` : [`Rule`](@ref)
- `state`: the value(s) of the current cell
- `index`: a (row, column) tuple of Int for the current cell coordinates - `t`: the current time step
"""
function applyrule! end
"""
modifyrule(rule::Rule, data::AbstractSimData) -> Rule
Precalculates rule fields at each timestep. Define this method if a [`Rule`](@ref)
has fields that need to be updated over time.
`Rule`s are immutable (it's faster and works on GPU), so `modifyrule` is
expected to return a new rule object with changes applied to it. Setfield.jl or
Acessors.jl may help with updating the immutable struct.
The default behaviour is to return the existing rule without change. Updated rules
are discarded after use, and the `rule` argument is always the original object passed in.
# Example
We define a rule with a parameter that is the total sum of the grids current,
and update it for each time-step using `modifyrule`.
This could be used to simulate top-down control e.g. a market mechanism in a
geographic model that includes agricultural economics.
```jldoctest
using DynamicGrids, Setfield
struct MySummedRule{R,W,T} <: CellRule{R,W}
gridsum::T
end
function modifyrule(rule::MySummedRule{R,W}, data::AbstractSimData) where {R,W}
Setfield.@set rule.gridsum = sum(data[R])
end
# output
modifyrule (generic function with 1 method)
```
"""
function modifyrule end
"""
add!(data::WritableGridData, x, I...)
Add the value `x` to a grid cell.
## Example useage
```jldoctest
using DynamicGrids
rule = SetCell{:a}() do data, a, cellindex
dest, is_inbounds = inbounds(data, (jump .+ cellindex)...)
# Update spotted cell if it's on the grid
is_inbounds && add!(data[:a], state, dest...)
end
# output
SetCell{:a,:a}(
f = var"#1#2"
)
```
"""
function add! end
"""
sub!(data::WritableGridData, x, I...)
Subtract the value `x` from a grid cell. See `add!` for example usage.
"""
function sub! end
"""
min!(data::WritableGridData, x, I...)
Set a gride cell to the minimum of `x` and the current value. See `add!` for example usage.
"""
function min! end
"""
max!(data::WritableGridData, x, I...)
Set a gride cell to the maximum of `x` and the current value. See `add!` for example usage.
"""
function max! end
"""
and!(data::WritableGridData, x, I...)
and!(A::AbstractArray, x, I...)
Set the grid cell `c` to `c & x`. See `add!` for example usage.
"""
function and! end
"""
or!(data::WritableGridData, x, I...)
or!(A::AbstractArray, x, I...)
Set the grid cell `c` to `c | x`. See `add!` for example usage.
"""
function or! end
"""
xor!(data::WritableGridData, x, I...)
xor!(A::AbstractArray, x, I...)
Set the grid cell `c` to `xor(c, x)`. See `add!` for example usage.
"""
function xor! end
"""
inbounds(data::AbstractSimData, I::Tuple) -> Tuple{NTuple{2,Int}, Bool}
inbounds(data::AbstractSimData, I...) -> Tuple{NTuple{2,Int}, Bool}
Check grid boundaries for a coordinate before writing in [`SetCellRule`](@ref).
Returns a `Tuple` containing a coordinates `Tuple` and a `Bool` - `true`
if the cell is inside the grid bounds, `false` if not.
[`BoundaryCondition`](@ref) of type [`Remove`](@ref) returns the coordinate and `false`
to skip coordinates that boundary outside of the grid.
[`Wrap`](@ref) returns a tuple with the current position or it's
wrapped equivalent, and `true` as it is allways in-bounds.
"""
function inbounds end
"""
isinbounds(data, I::Tuple) -> Bool
isinbounds(data, I...) -> Bool
Check that a coordinate is within the grid, usually in [`SetCellRule`](@ref).
Unlike [`inbounds`](@ref), [`BoundaryCondition`](@ref) status is ignored.
"""
function isinbounds end
"""
init(obj) -> Union{AbstractArray,NamedTUple}
Retrieve the mask from an [`Output`](@ref), [`Extent`](@ref) or [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object.
"""
function init end
"""
mask(obj) -> AbstractArray
Retrieve the mask from an [`Output`](@ref), [`Extent`](@ref) or [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object.
"""
function mask end
"""
aux(obj, [key])
Retrieve auxilary data `NamedTuple` from an [`Output`](@ref),
[`Extent`](@ref) or [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object.
Given `key` specific data will be returned. `key` should be a
`Val{:symbol}` for type stability and zero-cost access inside rules.
`Symbol` will also work, but may be slow.
"""
function aux end
"""
tspan(obj) -> AbstractRange
Retrieve the time-span `AbstractRange` from an [`Output`](@ref),
[`Extent`](@ref) or [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object.
"""
function tspan end
"""
timestep(obj)
Retrieve the timestep size from an [`Output`](@ref),
[`Extent`](@ref), [`Ruleset`](@ref) or [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object.
This will be in whatever type/units you specify in `tspan`.
"""
function timestep end
"""
currentframe(simdata::AbstractSimData) -> Int
Retrieve the current simulation frame a [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object.
"""
function currentframe end
"""
currenttime(simdata::AbstractSimData)
Retrieve the current simulation time from a [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object.
This will be in whatever type/units you specify in `tspan`.
"""
function currenttime end
"""
currenttimestep(simdata::AbstractSimData)
Retrieve the current timestep from a [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object.
This may be different from the `timestep`. If the timestep is `Month`,
`currenttimestep` will return `Seconds` for the length of the specific month.
"""
function currenttimestep end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 2721 | """
Life <: NeighborhoodRule
Life(neighborhood, born=3, survive=(2, 3))
Rule for game-of-life style cellular automata. This is a demonstration of
Cellular Automata more than a seriously optimised game of life rule.
Cells becomes active if it is empty and the number of neightbors is a number in
the `born`, and remains active the cell is active and the number of neightbors is
in `survive`.
## Examples (gleaned from CellularAutomata.jl)
```julia
using DynamicGrids, Distributions
# Use `Binomial` to tweak the density random true values
init = Bool.(rand(Binomial(1, 0.5), 70, 70))
output = REPLOutput(init; tspan=1:100, fps=25, color=:red)
# Morley
sim!(output, Ruleset(Life(born=[3, 6, 8], survive=[2, 4, 5])))
# 2x2
sim!(output, Ruleset(Life(born=[3, 6], survive=[1, 2, 5])))
# Dimoeba
init = rand(Bool, 400, 300)
init[:, 100:200] .= 0
output = REPLOutput(init; tspan=1:100, fps=25, color=:blue, style=Braile())
sim!(output, Life(born=(3, 5, 6, 7, 8), survive=(5, 6, 7, 8)))
## No death
sim!(output, Life(born=(3,), survive=(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8)))
## 34 life
sim!(output, Life(born=(3, 4), survive=(3, 4)))
# Replicator
init = fill(true, 300,300)
init[:, 100:200] .= false
init[10, :] .= 0
output = REPLOutput(init; tspan=1:100, fps=25, color=:yellow)
sim!(output, Life(born=(1, 3, 5, 7), survive=(1, 3, 5, 7)))
nothing
# output
```

"""
struct Life{R,W,N,B,S,L} <: NeighborhoodRule{R,W}
"A Neighborhood, usually Moore(1)"
neighborhood::N
"Int, Array, Tuple or Iterable of values that match sum(neighbors) when cell is empty"
born::B
"Int, Array, Tuple or Iterable of values that match sum(neighbors) when cell is full"
survive::S
lookup::L
end
function Life{R,W}(
neighborhood::N, born::B, survive::S, lookup_
) where {R,W,N<:Neighborhood{<:Any,<:Any,L},B,S} where L
lookup = ntuple(i -> (i - 1) in born, L+1), ntuple(i -> (i - 1) in survive, L+1)
Life{R,W,N,B,S,typeof(lookup)}(neighborhood, born, survive, lookup)
end
function Life{R,W}(neighborhood, born, survive) where {R,W}
Life{R,W}(neighborhood, born, survive, nothing)
end
function Life{R,W}(;
neighborhood=Moore(1),
born=Param(3, bounds=(0, 8)),
survive=(Param(2, bounds=(0, 8)), Param(3, bounds=(0, 8))),
) where {R,W}
Life{R,W}(neighborhood, born, survive, nothing)
end
function setwindow(r::Life{R,W,N,B,S,LU}, buffer) where {R,W,N,B,S,LU}
hood = setwindow(r.neighborhood, buffer)
Life{R,W,typeof(hood),B,S,LU}(hood, r.born, r.survive, r.lookup)
end
function applyrule(data, rule::Life, state, I)
rule.lookup[state + 1][sum(neighbors(rule)) + 1]
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 8238 |
# Map a rule over the grids it reads from, updating the grids it writes to.
# This is broken into setup methods and application methods,
# for dispatch and to introduce a function barrier for type stability.
maprule!(data::AbstractSimData, rule) = maprule!(data, Val{ruletype(rule)}(), rule)
function maprule!(data::AbstractSimData, ruletype::Val{<:CellRule}, rule)
rkeys, _ = _getreadgrids(rule, data)
wkeys, _ = _getwritegrids(rule, data)
maprule!(RuleData(data), ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys)
return data
end
function maprule!(data::AbstractSimData, ruletype::Val{<:NeighborhoodRule}, rule)
rkeys, rgrids = _getreadgrids(rule, data)
wkeys, wgrids = _getwritegrids(rule, data)
# NeighborhoodRule will read from surrounding cells
# so may incorporate cells from the masked area
_maybemask!(rgrids)
# Copy or zero out boundary where needed
_updateboundary!(rgrids)
_cleardest!(data[neighborhoodkey(rule)])
maprule!(RuleData(data), ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys)
# Swap the dest/source of grids that were written to
# and combine the written grids with the original simdata
return _replacegrids(data, wkeys, _swapsource(_to_readonly(wgrids)))
end
function maprule!(data::AbstractSimData, ruletype::Val{<:SetRule}, rule)
rkeys, _ = _getreadgrids(rule, data)
wkeys, wgrids = _getwritegrids(rule, data)
map(_astuple(wkeys, wgrids)) do g
copyto!(parent(dest(g)), parent(source(g)))
end
ruledata = RuleData(_combinegrids(data, wkeys, wgrids))
maprule!(ruledata, ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys)
return _replacegrids(data, wkeys, _swapsource(_to_readonly(wgrids)))
end
function maprule!(data::AbstractSimData, ruletype::Val{<:SetGridRule}, rule)
rkeys, rgrids = _getreadgrids(rule, data)
wkeys, wgrids = _getwritegrids(rule, data)
_maybemask!(rgrids) # TODO... mask wgrids?
ruledata = RuleData(_combinegrids(data, wkeys, wgrids))
# Run the rule
applyrule!(ruledata, rule)
return data
end
function maprule!(data::AbstractSimData, ruletype::Val, rule, rkeys, wkeys)
maprule!(data, proc(data), opt(data), ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys)
end
# Most Rules
# 2 dimensional, with processor selection and optimisations in `optmap`
function maprule!(data::AbstractSimData{<:Tuple{Y,X}}, proc::CPU, opt, ruletype::Val, rule, rkeys, wkeys) where {Y,X}
let data=data, proc=proc, opt=opt, rule=rule,
rkeys=rkeys, wkeys=wkeys, ruletype=ruletype
optmap(data, proc, opt, ruletype, rkeys) do I
cell_kernel!(data, ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys, I...)
end
end
end
# Arbitrary dimensions, no proc/opt selection beyond CPU/GPU
function maprule!(data::AbstractSimData, proc::CPU, opt, ruletype::Val, rule, rkeys, wkeys)
let data=data, proc=proc, opt=opt, rule=rule,
rkeys=rkeys, wkeys=wkeys, ruletype=ruletype
for I in CartesianIndices(first(grids(data)))
cell_kernel!(data, ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys, Tuple(I)...)
end
end
end
# Neighborhood rules
# 2 dimensional, with processor selection and optimisations
function maprule!(
data::AbstractSimData{<:Tuple{Y,X}}, proc::CPU, opt, ruletype::Val{<:NeighborhoodRule},
rule, rkeys, wkeys
) where {Y,X}
hoodgrid = _firstgrid(data, rkeys)
let data=data, hoodgrid=hoodgrid, proc=proc, opt=opt, ruletyp=ruletype, rule=rule, rkeys=rkeys, wkeys=wkeys
B = 2radius(hoodgrid)
# UNSAFE: we must avoid sharing status blocks, it could cause race conditions
# when setting status from different threads. So we split the grid in 2 interleaved
# sets of rows, so that we never run adjacent rows simultaneously
procmap(proc, 1:2:_indtoblock(Y, B)) do bi
row_kernel!(data, hoodgrid, proc, opt, ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys, bi)
end
procmap(proc, 2:2:_indtoblock(Y, B)) do bi
row_kernel!(data, hoodgrid, proc, opt, ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys, bi)
end
end
return nothing
end
# Arbitrary dimensions, no proc/opt selection beyond CPU/GPU
function maprule!(
data::AbstractSimData, proc::CPU, opt, ruletype::Val{<:NeighborhoodRule}, rule, rkeys, wkeys
)
hoodgrid = _firstgrid(data, rkeys)
for I in CartesianIndices(hoodgrid)
neighborhood_kernel!(data, hoodgrid, ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys, Tuple(I)...)
end
return nothing
end
### Rules that don't need a neighborhood window ####################
# optmap
# Map kernel over the grid, specialising on PerformanceOpt.
# Run kernel over the whole grid, cell by cell:
function optmap(
f, simdata::AbstractSimData{S}, proc, ::NoOpt, ::Val{<:Rule}, rkeys
) where S<:Tuple{Y,X} where {Y,X}
procmap(proc, 1:X) do j
for i in 1:Y
f((i, j)) # Run rule for each row in column j
end
end
end
# Use @simd for CellRule
function optmap(
f, simdata::AbstractSimData{S}, proc, ::NoOpt, ::Val{<:CellRule}, rkeys
) where S<:Tuple{Y,X} where {Y,X}
procmap(proc, 1:X) do j
@simd for i in 1:Y
f((i, j)) # Run rule for each row in column j
end
end
end
# procmap
# Map kernel over the grid, specialising on Processor
# Looping over cells or blocks on CPU
@inline procmap(f, proc::SingleCPU, range) =
for n in range
f(n) # Run rule over each column
end
@inline procmap(f, proc::ThreadedCPU, range) =
Threads.@threads for n in range
f(n) # Run rule over each column, threaded
end
# cell_kernel!
# runs a rule for the current cell
@inline function cell_kernel!(simdata, ruletype::Val{<:Rule}, rule, rkeys, wkeys, I...)
readval = _readcell(simdata, rkeys, I...)
writeval = applyrule(simdata, rule, readval, I)
_writecell!(simdata, ruletype, wkeys, writeval, I...)
writeval
end
@inline function cell_kernel!(simdata, ::Val{<:SetRule}, rule, rkeys, wkeys, I...)
readval = _readcell(simdata, rkeys, I...)
applyrule!(simdata, rule, readval, I)
nothing
end
# neighborhood_kernel!
# Runs a rule for the current cell/neighborhood, when there is no
# row-based optimisation
@inline function neighborhood_kernel!(
data, hoodgrid, ruletype::Val{<:NeighborhoodRule}, rule, rkeys, wkeys, I...
)
rule1 = unsafe_updatewindow(rule, source(hoodgrid), I...)
cell_kernel!(data, ruletype, rule1, rkeys, wkeys, I...)
end
# row_kernel!
# Run a NeighborhoodRule rule row by row. When we move along a row by one cell, we
# access only a single new column of data with the height of 4R, and move the existing
# data in the neighborhood windows array across by one column. This saves on reads
# from the main array.
function row_kernel!(
simdata::AbstractSimData, grid::GridData{<:Tuple{Y,X},R}, proc, opt::NoOpt,
ruletype::Val, rule::Rule, rkeys, wkeys, bi
) where {Y,X,R}
B = 2R
i = _blocktoind(bi, B)
i > Y && return nothing
# Loop along the block ROW.
src = parent(source(grid))
windows = _initialise_windows(src, Val{R}(), i, 1)
blocklen = min(Y, i + B - 1) - i + 1
for j = 1:X
windows = _slide_windows(windows, src, Val{R}(), i, j)
# Loop over the COLUMN of windows covering the block
for b in 1:blocklen
@inbounds rule1 = setwindow(rule, windows[b])
cell_kernel!(simdata, ruletype, rule1, rkeys, wkeys, i + b - 1, j)
end
end
return nothing
end
#### Utils
_to_readonly(data::Tuple) = map(ReadableGridData, data)
_to_readonly(data::WritableGridData) = ReadableGridData(data)
# _maybemask!
# mask the source grid
_maybemask!(wgrids::Union{Tuple,NamedTuple}) = map(_maybemask!, wgrids)
_maybemask!(wgrid::GridData) = _maybemask!(wgrid, proc(wgrid), mask(wgrid))
_maybemask!(wgrid::GridData, proc, mask::Nothing) = nothing
function _maybemask!(
wgrid::GridData{<:Tuple{Y,X}}, proc::CPU, mask::AbstractArray
) where {Y,X}
procmap(proc, 1:X) do j
@simd for i in 1:Y
source(wgrid)[i, j] *= mask[i, j]
end
end
end
function _maybemask!(
wgrid::GridData{<:Tuple{Y,X}}, proc, mask::AbstractArray
) where {Y,X}
sourceview(wgrid) .*= mask
end
# _cleardest!
# only needed with optimisations
_cleardest!(grid) = _cleardest!(grid, opt(grid))
_cleardest!(grid, opt) = nothing
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 780 |
# _updaterules
# Update the StaticRuleset in the SimData object with
# a (potentially) modifed version of the original rules tuple.
# This must be passed in to allow async updating from a live
# interface while the simulation runs.
function _updaterules(rules::Tuple, sd::AbstractSimData)
newrs = ModelParameters.setparent(
ruleset(sd),
_modifyrules(_proc_setup(proc(sd), ModelParameters.stripparams(rules)), sd)
)
@set sd.ruleset = newrs
end
# _modifyrules
# Run `modifyrule` for each rule, recursively.
_modifyrules(rules::Tuple, simdata) =
(modifyrule(rules[1], simdata), _modifyrules(tail(rules), simdata)...)
_modifyrules(rules::Tuple{}, simdata) = ()
# The default `modifyrule` returns the rule unchanged.
modifyrule(rule, simdata) = rule
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 11857 | """
ParameterSource
Abstract supertypes for parameter source wrappers such as [`Aux`](@ref),
[`Grid`](@ref) and [`Delay`](@ref). These allow flexibility in that parameters
can be retreived from various data sources not specified when the rule is written.
"""
abstract type ParameterSource end
"""
get(data::AbstractSimData, source::ParameterSource, I...)
get(data::AbstractSimData, source::ParameterSource, I::Union{Tuple,CartesianIndex})
Allows parameters to be taken from a single value or a [`ParameterSource`](@ref)
such as another [`Grid`](@ref), an [`Aux`](@ref) array, or a [`Delay`](@ref).
Other `source` objects are used as-is without indexing with `I`.
"""
@propagate_inbounds Base.get(data::AbstractSimData, val, I...) = val
@propagate_inbounds Base.get(data::AbstractSimData, key::ParameterSource, I...) =
get(data, key, I)
@propagate_inbounds Base.get(data::AbstractSimData, key::ParameterSource, I::CartesianIndex) =
get(data, key, Tuple(I))
"""
Aux <: ParameterSource
Aux{K}()
Aux(K::Symbol)
Use auxilary array with key `K` as a parameter source.
Implemented in rules with:
```julia
get(data, rule.myparam, I)
```
When an `Aux` param is specified at rule construction with:
```julia
rule = SomeRule(; myparam=Aux{:myaux})
output = ArrayOutput(init; aux=(myaux=myauxarray,))
```
If the array is a DimensionalData.jl `DimArray` with a `Ti` (time)
dimension, the correct interval will be selected automatically,
precalculated for each timestep so it has no significant overhead.
Currently this is cycled by default. Note that cycling may be incorrect
when the simulation timestep (e.g. `Week`) does not fit
equally into the length of the time dimension (e.g. `Year`).
This will reuire a `Cyclic` index mode in DimensionalData.jl in future
to correct this problem.
"""
struct Aux{K} <: ParameterSource end
Aux(key::Symbol) = Aux{key}()
_unwrap(::Aux{X}) where X = X
_unwrap(::Type{<:Aux{X}}) where X = X
@inline aux(nt::NamedTuple, ::Aux{Key}) where Key = nt[Key]
@propagate_inbounds function Base.get(data::AbstractSimData, key::Aux, I::Tuple)
_getaux(data, key, I)
end
# _getaux
# Get the value of an auxilliary array at index I and/or the synchonised time-step
@propagate_inbounds function _getaux(
data::AbstractSimData, key::Union{Aux,Symbol}, I::Tuple
)
_getaux(aux(data, key), data, key, I)
end
# For an Array just return the value for the index
@propagate_inbounds function _getaux(
A::AbstractArray, data::AbstractSimData, key::Union{Aux,Symbol}, I::Tuple
)
A[I...]
end
# For a DimArray with a time dimension we return the value at the
# current auxframe, also using the index `I` if aux is multidimensional.
@propagate_inbounds function _getaux(
A::AbstractDimArray{<:Any,1}, data::AbstractSimData, key::Union{Aux,Symbol}, I::Tuple
)
hasdim(A, TimeDim) ? A[auxframe(data, key)] : A[I...]
end
@propagate_inbounds function _getaux(
A::AbstractDimArray, data::AbstractSimData, key::Union{Aux,Symbol}, I::Tuple
)
if hasdim(A, TimeDim)
last(dims(A)) isa TimeDim || throw(ArgumentError("The time dimensions in aux data must be the last dimension"))
A[I..., auxframe(data, key)]
else
A[I...]
end
end
# boundscheck_aux
# Bounds check the aux arrays ahead of time
function boundscheck_aux(data::AbstractSimData, key::Aux)
boundscheck_aux(data, aux(data), key)
end
function boundscheck_aux(data::AbstractSimData, A::Nothing, key::Aux{Key}) where Key
_auxmissingerror(Key, a)
end
function boundscheck_aux(data::AbstractSimData, aux::NamedTuple, key::Aux{Key}) where Key
boundscheck_aux(data, aux[_unwrap(key)], key)
end
function boundscheck_aux(data::AbstractSimData, A::AbstractArray, key::Aux{Key}) where Key
size(A) === size(data) || _auxsizeerror(Key, size(A), size(data))
end
function boundscheck_aux(data::AbstractSimData, A::AbstractDimArray{<:Any,1}, key::Aux{Key}) where Key
hasdim(A, TimeDim) || size(data) === size(A) || _auxsizeerror(Key, size(A), size(data))
end
function boundscheck_aux(data::AbstractSimData, A::AbstractDimArray, key::Aux{Key}) where Key
if hasdim(A, TimeDim)
asize = size(otherdims(A, TimeDim))
asize == size(data) || _auxsizeerror(Key, asize, size(data))
else
size(A) == size(data) || _auxsizeerror(Key, size(A), size(data))
end
end
# _calc_auxframe
# Calculate the frame to use in the aux data for this timestep.
# This uses the index of any AbstractDimArray, which must be a
# matching type to the simulation tspan.
# This is called from _updatetime in simulationdata.jl
_calc_auxframe(data::AbstractSimData) = _calc_auxframe(aux(data), data)
function _calc_auxframe(aux::NamedTuple, data::AbstractSimData)
map(A -> _calc_auxframe(A, data), aux)
end
function _calc_auxframe(A::AbstractDimArray, data)
hasdim(A, TimeDim) || return nothing
curtime = currenttime(data)
firstauxtime = first(dims(A, TimeDim))
auxstep = step(dims(A, TimeDim))
# Use julias range objects to calculate the distance between the
# current time and the start of the aux
i = if curtime >= firstauxtime
length(firstauxtime:auxstep:curtime)
else
1 - length(firstauxtime-timestep(data):-auxstep:curtime)
end
# TODO use a cyclic mode DimensionalArray
# and handle the mismatch of e.g. weeks and years
return _cyclic_index(i, size(A, Ti))
end
_calc_auxframe(aux, data) = nothing
# _cyclic_index
# Cycle an index over the length of the aux data.
function _cyclic_index(i::Integer, len::Integer)
return if i > len
rem(i + len - 1, len) + 1
elseif i <= 0
i + (i ÷ len -1) * -len
else
i
end
end
"""
Grid <: ParameterSource
Grid{K}()
Grid(K::Symbol)
Use grid with key `K` as a parameter source.
Implemented in rules with:
```julia
get(data, rule.myparam, I)
```
And specified at rule construction with:
```julia
SomeRule(; myparam=Grid(:somegrid))
```
"""
struct Grid{K} <: ParameterSource end
Grid(key::Symbol) = Grid{key}()
_unwrap(::Grid{X}) where X = X
_unwrap(::Type{<:Grid{X}}) where X = X
@propagate_inbounds Base.get(data::AbstractSimData, key::Grid{K}, I::Tuple) where K =
data[K][I...]
"""
AbstractDelay <: ParameterSource
Abstract supertype for [`ParameterSource`](@ref)s that use data from a grid
with a time delay.
$EXPERIMENTAL
"""
abstract type AbstractDelay{K} <: ParameterSource end
@inline frame(delay::AbstractDelay) = delay.frame
@propagate_inbounds function Base.get(
data::AbstractSimData, delay::AbstractDelay{K}, I::Tuple
) where K
_getdelay(frames(data)[frame(delay, data)], delay, I)
end
# The output may store a single Array or a NamedTuplea.
@propagate_inbounds function _getdelay(frame::AbstractArray, ::AbstractDelay, I::Tuple)
frame[I...]
end
@propagate_inbounds function _getdelay(
frame::NamedTuple, delay::AbstractDelay{K}, I::Tuple
) where K
_getdelay(frame[K], delay, I)
end
"""
Delay <: AbstractDelay
Delay{K}(steps)
`Delay` allows using a [`Grid`](@ref) from previous timesteps as a parameter source as
a field in any `Rule` that uses `get` to retrieve it's parameters.
It must be coupled with an output that stores all frames, so that `@assert
DynamicGrids.isstored(output) == true`. With [`GraphicOutput`](@ref)s this may be
acheived by using the keyword argument `store=true` when constructing the output object.
# Type Parameters
- `K::Symbol`: matching the name of a grid in `init`.
# Arguments
- `steps`: As a user supplied parameter, this is a multiple of the step size of the output
`tspan`. This is automatically replaced with an integer for each step. Used within the
code in a rule, it must be an `Int` number of frames, for performance.
# Example
```julia
SomeRule(;
someparam=Delay(:grid_a, Month(3))
otherparam=1.075
)
```
$EXPERIMENTAL
"""
struct Delay{K,S} <: AbstractDelay{K}
steps::S
end
Delay{K}(steps::S) where {K,S} = Delay{K,S}(steps)
ConstructionBase.constructorof(::Delay{K}) where K = Delay{K}
steps(delay::Delay) = delay.steps
# _to_frame
# Replace the delay step size with an integer for fast indexing
# checking that the delay matches the simulation step size.
# Delays at the start just use the init frame.
function _to_frame(delay::Delay{K}, data::AbstractSimData) where K
nsteps = steps(delay) / step(tspan(data))
isteps = trunc(Int, nsteps)
nsteps == isteps || _delaysteperror(delay, step(tspan(data)))
frame = max(currentframe(data) - isteps, 1)
Frame{K}(frame)
end
"""
Lag <: AbstractDelay
Lag{K}(frames::Int)
`Lag` allows using a [`Grid`](@ref) from a specific previous frame from within a rule,
using `get`. It is similar to [`Delay`](@ref), but an integer amount of frames should be
used, instead of a quantity related to the simulation `tspan`. The lower bound is the first
frame.
# Type Parameter
- `K::Symbol`: matching the name of a grid in `init`.
# Argument
- `frames::Int`: number of frames to lag by, 1 or larger.
# Example
```julia
SomeRule(;
someparam=Lag(:grid_a, Month(3))
otherparam=1.075
)
```
$EXPERIMENTAL
"""
struct Lag{K} <: AbstractDelay{K}
nframes::Int
end
# convert the Lag to a Frame object
# Lags at the start just use the init frame.
function _to_frame(ps::Lag{K}, data::AbstractSimData) where K
Frame{K}(frame(ps, data))
end
@inline frame(ps::Lag, data) = max(1, currentframe(data) - ps.nframes)
"""
Frame <: AbstractDelay
Frame{K}(frame)
`Frame` allows using a [`Grid`](@ref) from a specific previous timestep from within
a rule, using `get`. It should only be used within rule code, not as a parameter.
# Type Parameter
- `K::Symbol`: matching the name of a grid in `init`.
# Argument
- `frame::Int`: the exact frame number to use.
$EXPERIMENTAL
"""
struct Frame{K} <: AbstractDelay{K}
frame::Int
Frame{K}(frame::Int) where K = new{K}(frame)
end
ConstructionBase.constructorof(::Frame{K}) where K = Frame{K}
@inline frame(ps::Frame) = ps.frame
@inline frame(ps::Frame, data) = frame(ps)
# Delay utils
# Types to ignore when flattening rules to <: AbstractDelay
const DELAY_IGNORE = Union{Function,SArray,AbstractDict,Number}
@inline function hasdelay(rules::Tuple)
# Check for Delay as parameter or used in rule code
length(_getdelays(rules)) > 0 || any(map(needsdelay, rules))
end
# needsdelay
# Speficy that a rule needs a delay frames present
# to run. This will throw an early error if the Output
# does not store frames, instead of an indexing error during
# the simulation.
needsdelay(rule::Rule) = false
# _getdelays
# Get all the delays found in fields of the rules tuple
_getdelays(rules::Tuple) = Flatten.flatten(rules, AbstractDelay, DELAY_IGNORE)
# _setdelays
# Update any AbstractDelay anywhere in the rules Tuple.
# These are converted to Frame objects so the calculation
# happens only once for each timestep, instead of for each cell.
function _setdelays(rules::Tuple, data::AbstractSimData)
delays = _getdelays(rules)
if length(delays) > 0
newdelays = map(d -> _to_frame(d, data), delays)
_setdelays(rules, newdelays)
else
rules
end
end
_setdelays(rules::Tuple, delays::Tuple) =
Flatten.reconstruct(rules, delays, AbstractDelay, DELAY_IGNORE)
# Errors
@noinline _notstorederror() =
throw(ArgumentError("Output does not store frames, which is needed for a Delay. Use ArrayOutput or any GraphicOutput with `store=true` keyword"))
@noinline _delaysteperror(delay::Delay{K}, simstep) where K =
throw(ArgumentError("Delay $K size $(steps(delay)) is not a multiple of simulations step $simstep"))
@noinline _auxmissingerror(key, aux) = error("Aux data $key is not present in aux")
@noinline _auxsizeerror(key, asize, gsize) =
error("Aux data $key is size $asize does not match grid size $gsize")
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 21610 |
"""
Rule
A `Rule` object contains the information required to apply an
`applyrule` method to every cell of every timestep of a simulation.
The [`applyrule`](@ref) method follows the form:
```julia
@inline applyrule(data::AbstractSimData, rule::MyRule, state, I::Tuple{Int,Int}) = ...
```
Where `I` is the cell index, and `state` is a single value, or a `NamedTuple`
if multiple grids are requested. the [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object can be used to access
current timestep and other simulation data and metadata.
Rules can be updated from the original rule before each timestep, in [`modifyrule`](@ref).
Here a paremeter depends on the sum of a grid:
```jldoctest
using DynamicGrids, Setfield
struct MySummedRule{R,W,T} <: CellRule{R,W}
gridsum::T
end
function modifyrule(rule::MySummedRule{R,W}, data::AbstractSimData) where {R,W}
Setfield.@set rule.gridsum = sum(data[R])
end
# output
modifyrule (generic function with 1 method)
```
Rules can also be run in sequence, as a `Tuple` or in a [`Ruleset`](@ref)s.
DynamicGrids guarantees that:
- `modifyrule` is run once for every rule for every timestep.
The result is passed to `applyrule`, but not retained after that.
- `applyrule` is run once for every rule, for every cell, for every timestep, unless an
optimisation like [`SparseOpt`](@ref) is used to skip empty cells.
- the output of running a rule for any cell does not affect the input of the
same rule running anywhere else in the grid.
- rules later in the sequence are passed grid state updated by the earlier rules.
- masked areas, and wrapped or removed `boundary` regions are updated between rules when
they have changed.
## Multiple grids
The keys of the init `NamedTuple` will be match the grid keys used in `R` and `W` for each
rule, which is a type like `Tuple{:key1,:key1}`. Note that the names are user-specified,
and should never be fixed by a `Rule`.
Read grid names are retrieved from the type here as `R1` and `R2`, while write grids are
`W1` and `W2`.
```jldoctest
using DynamicGrids
struct MyMultiSetRule{R,W} <: SetCellRule{R,W} end
function applyrule(
data::AbstractSimData, rule::MyMultiSetRule{Tuple{R1,R2},Tuple{W1,W2}}, (r1, r2), I
) where {R1,R2,W1,W2}
add!(data[W1], 1, I)
add!(data[W2], 1, I)
end
# output
applyrule (generic function with 1 method)
```
The return value of an `applyrule` is written to the current cell in the specified `W`
write grid/s. `Rule`s writing to multiple grids simply return a `Tuple` in the order
specified by the `W` type params.
## Rule Performance
Rules may run many millions of times during a simulation. They need to be fast.
Some basic guidlines for writing rules are:
- Never allocate memory in a `Rule` if you can help it.
- Type stability is essential. [`isinferred`](@ref) is useful to check
if your rule is type-stable.
- Using the `@inline` macro on `applyrule` can help force inlining your
code into the simulation.
- Reading and writing from multiple grids is expensive due to additional load
on fast cahce memory. Try to limit the number of grids you use.
- Use a graphical profiler, like ProfileView.jl, to check your rules overall
performance when run with `sim!`.
"""
abstract type Rule{R,W} end
# Rules are also traits - because we use wrapper rules
ruletype(::Rule) = Rule
#= Default constructors for all Rules.
Sets both the read and write grids to `:_default`.
This strategy relies on a one-to-one relationship between fields
and type parameters, besides the initial `R` and `W` params. =#
# No {R,W} with args or kw
function (::Type{T})(args...; kw...) where T<:Rule
T{DEFAULT_KEY,DEFAULT_KEY}(args...; kw...)
end
# {R,W} with args
function (::Type{T})(args...) where T<:Rule{R,W} where {R,W}
# _checkfields(T, args)
T{map(typeof, args)...}(args...)
end
# Only R specified
function (::Type{T})(args...; kw...) where T<:Rule{R} where R
T{R}(args...; kw...)
end
@generated function Base.keys(rule::Rule{R,W}) where {R,W}
Expr(:tuple, QuoteNode.(union(_asiterable(W), _asiterable(R)))...)
end
@inline _writekeys(::Rule{R,W}) where {R,W} = W
@generated function _writekeys(::Rule{R,W}) where {R,W<:Tuple}
Expr(:tuple, QuoteNode.(W.parameters)...)
end
@inline _readkeys(::Rule{R,W}) where {R,W} = R
@generated function _readkeys(::Rule{R,W}) where {R<:Tuple,W}
Expr(:tuple, QuoteNode.(R.parameters)...)
end
# Define the constructor for generic rule reconstruction in Flatten.jl and Setfield.jl
function ConstructionBase.constructorof(::Type{T}) where T<:Rule{R,W} where {R,W}
T.name.wrapper{R,W}
end
# Find the largest radius present in the passed in rules.
function radius(rules::Tuple{Vararg{<:Rule}})
allkeys = Tuple(union(map(keys, rules)...))
maxradii = Tuple(radius(rules, key) for key in allkeys)
return NamedTuple{allkeys}(maxradii)
end
radius(rules::Tuple{}) = NamedTuple{(),Tuple{}}(())
# Get radius of specific key from all rules
radius(rules::Tuple{Vararg{<:Rule}}, key::Symbol) =
reduce(max, radius(ru) for ru in rules if key in keys(ru); init=0)
radius(rule::Rule, args...) = 0
"""
RuleWrapper <: Rule
A `Rule` that wraps other rules, altering their behaviour or how they are run.
"""
abstract type RuleWrapper{R,W} <: Rule{R,W} end
"""
Cellrule <: Rule
A `Rule` that only writes and uses a state from single cell of the read grids,
and has its return value written back to the same cell(s).
This limitation can be useful for performance optimisation,
such as wrapping rules in [`Chain`](@ref) so that no writes occur between rules.
`CellRule` is defined with :
```jldoctest yourcellrule
using DynamicGrids
struct MyCellRule{R,W} <: CellRule{R,W} end
# output
```
And applied as:
```jldoctest yourcellrule
function applyrule(data, rule::MyCellRule, state, I)
state * 2
end
# output
applyrule (generic function with 1 method)
```
As the index `I` is provided in `applyrule`, you can use it to look up [`Aux`](@ref) data.
"""
abstract type CellRule{R,W} <: Rule{R,W} end
ruletype(::CellRule) = CellRule
"""
Call <: CellRule
Cell(f)
Cell{R,W}(f)
A [`CellRule`](@ref) that applies a function `f` to the `R` grid value,
or `Tuple` of values, and returns the `W` grid value or `Tuple` of values.
Especially convenient with `do` notation.
## Example
Double the cell value in grid `:a`:
```jldoctest Cell
using DynamicGrids
simplerule = Cell{:a}() do data, a, I
2a
end
# output
Cell{:a,:a}(
f = var"#1#2"
)
```
`data` is an [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object, `a` is the cell value, and `I`
is a `Tuple` holding the cell index.
If you need to use multiple grids (a and b), use the `R`
and `W` type parameters. If you want to use external variables,
wrap the whole thing in a `let` block, for performance. This
rule sets the new value of `b` to the value of `a` to `b` times scalar `y`:
```jldoctest Cell
y = 0.7
rule = let y = y
rule = Cell{Tuple{:a,:b},:b}() do data, (a, b), I
a + b * y
end
end
# output
Cell{Tuple{:a, :b},:b}(
f = var"#3#4"{Float64}
)
```
"""
struct Cell{R,W,F} <: CellRule{R,W}
"Function to apply to the R grid values"
f::F
end
Cell{R,W}(; kw...) where {R,W} = _nofunctionerror(Cell)
@inline function applyrule(data, rule::Cell, read, I)
let data=data, rule=rule, read=read, I=I
rule.f(data, read, I)
end
end
"""
SetRule <: Rule
Abstract supertype for rules that manually write to the grid in some way.
These must define methods of [`applyrule!`](@ref).
"""
abstract type SetRule{R,W} <: Rule{R,W} end
ruletype(::SetRule) = SetRule
"""
SetCellRule <: Rule
Abstract supertype for rules that can manually write to any cells of the
grid that they need to.
For example, `SetCellRule` is applied with like this, here simply adding 1 to the current cell:
```jldoctest SetCellRule
using DynamicGrids
struct MySetCellRule{R,W} <: SetCellRule{R,W} end
function applyrule!(data::AbstractSimData, rule::MySetCellRule{R,W}, state, I) where {R,W}
# Add 1 to the cell 10 up and 10 accross
I, isinbounds = inbounds(I .+ 10)
isinbounds && add!(data[W], 1, I...)
return nothing
end
# output
applyrule! (generic function with 1 method)
```
Note the `!` bang - this method alters the state of `data`.
To update the grid, you can use atomic operators [`add!`](@ref), [`sub!`](@ref),
[`min!`](@ref), [`max!`](@ref), and [`and!`](@ref), [`or!`](@ref) for `Bool`.
These methods safely combined writes from all grid cells - directly using `setindex!`
would cause bugs.
It there are multiple write grids, you will need to get the grid keys from
type parameters, here `W1` and `W2`:
```jldoctest SetCellRule
function applyrule(data, rule::MySetCellRule{R,Tuple{W1,W2}}, state, I) where {R,W1,W2}
add!(data[W1], 1, I...)
add!(data[W2], 2, I...)
return nothing
end
# output
applyrule (generic function with 1 method)
```
DynamicGrids guarantees that:
- values written to anywhere on the grid do not affect other cells in
the same rule at the same timestep.
- values written to anywhere on the grid are available to the next rule in the
sequence, or in the next timestep if there are no remaining rules.
- if atomic operators like `add!` and `sub!` are always used to write to the grid,
race conditions will not occur on any hardware.
"""
abstract type SetCellRule{R,W} <: SetRule{R,W} end
ruletype(::SetCellRule) = SetCellRule
"""
SetCell <: SetCellRule
SetCell(f)
SetCell{R,W}(f)
A [`SetCellRule`](@ref) to manually write to the array where you need to.
`f` is passed a [`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object, the grid state or `Tuple` of grid
states for the cell and a `Tuple{Int,Int}` index of the current cell.
To update the grid, you can use: [`add!`](@ref), [`sub!`](@ref) for `Number`,
and [`and!`](@ref), [`or!`](@ref) for `Bool`. These methods safely combined
writes from all grid cells - directly using `setindex!` would cause bugs.
## Example
Choose a destination cell and if it is in the grid, update it based on the
state of both grids:
```jldoctest SetCell
using DynamicGrids
rule = SetCell{Tuple{:a,:b},:b}() do data, (a, b), I
dest = your_dest_pos_func(I)
if isinbounds(data, dest)
destval = your_dest_val_func(a, b)
add!(data[:b], destval, dest...)
end
end
# output
SetCell{Tuple{:a, :b},:b}(
f = var"#1#2"
)
```
"""
struct SetCell{R,W,F} <: SetCellRule{R,W}
"Function to apply to data, index and read grid values"
f::F
end
SetCell{R,W}(; kw...) where {R,W} = _nofunctionerror(Set)
@inline function applyrule!(data, rule::SetCell, read, I)
let data=data, rule=rule, read=read, I=I
rule.f(data, read, I)
end
end
"""
NeighborhoodRule <: Rule
A Rule that only accesses a neighborhood centered around the current cell.
`NeighborhoodRule` is applied with the method:
```julia
applyrule(data::AbstractSimData, rule::MyNeighborhoodRule, state, I::Tuple{Int,Int})
```
`NeighborhoodRule` must have a `neighborhood` method or field, that holds
a [`Neighborhood`](@ref) object. `neighbors(rule)` returns an iterator
over the surrounding cell pattern defined by the `Neighborhood`.
For each cell in the grids the neighborhood buffer will be updated
for use in the `applyrule` method, managed to minimise array reads.
This allows memory optimisations and the use of high-perforance routines on the
neighborhood buffer. It also means that and no bounds checking is required in
neighborhood code.
For neighborhood rules with multiple read grids, the first is always
the one used for the neighborhood, the others are passed in as additional
state for the cell. Any grids can be written to, but only for the current cell.
"""
abstract type NeighborhoodRule{R,W} <: Rule{R,W} end
ruletype(::NeighborhoodRule) = NeighborhoodRule
neighbors(rule::NeighborhoodRule) = neighbors(neighborhood(rule))
neighborhood(rule::NeighborhoodRule) = rule.neighborhood
offsets(rule::NeighborhoodRule) = offsets(neighborhood(rule))
kernel(rule::NeighborhoodRule) = kernel(neighborhood(rule))
kernelproduct(rule::NeighborhoodRule) = kernelproduct(neighborhood(rule))
positions(rule::NeighborhoodRule, args...) = positions(neighborhood(rule), args...)
neighborhoodkey(rule::NeighborhoodRule{R,W}) where {R,W} = R
# The first argument is for the neighborhood grid
neighborhoodkey(rule::NeighborhoodRule{<:Tuple{R1,Vararg},W}) where {R1,W} = R1
radius(rule::NeighborhoodRule, args...) = radius(neighborhood(rule))
@inline function setwindow(rule, window)
@set rule.neighborhood = setwindow(neighborhood(rule), window)
end
@inline function unsafe_updatewindow(rule::NeighborhoodRule, A::AbstractArray, I...)
setwindow(rule, unsafe_readwindow(neighborhood(rule), A, I...))
end
@inline function unsafe_readwindow(rule::Rule, A::AbstractArray, I...)
unsafe_readwindow(neighborhood(rule), A, I)
end
"""
Neighbors <: NeighborhoodRule
Neighbors(f, neighborhood=Moor(1))
Neighbors{R,W}(f, neighborhood=Moore())
A [`NeighborhoodRule`](@ref) that receives a [`Neighborhood`](@ref) object
for the first `R` grid, followed by the cell value/s for the required grids,
as with [`Cell`](@ref).
Returned value(s) are written to the `W` grid/s.
As with all [`NeighborhoodRule`](@ref), you do not have to check bounds at
grid edges, that is handled for you internally.
Using [`SparseOpt`](@ref) may improve neighborhood performance
when a specific value (often zero) is common and can be safely ignored.
## Example
Runs a game of life glider on grid `:a`:
```jldoctest
using DynamicGrids
const sum_states = (0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0),
(0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
life = Neighbors{:a}(Moore(1)) do data, hood, a, I
sum_states[a + 1][sum(hood) + 1]
end
init = Bool[
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
]
output = REPLOutput((; a=init); fps=25, tspan=1:50)
sim!(output, Life{:a}(); boundary=Wrap())
output[end][:a]
# output
5×15 Matrix{Bool}:
0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
```
"""
struct Neighbors{R,W,F,N} <: NeighborhoodRule{R,W}
"Function to apply to the neighborhood and R grid values"
f::F
"Defines the neighborhood of cells around the central cell"
neighborhood::N
end
Neighbors{R,W}(; kw...) where {R,W} = _nofunctionerror(Neighbors)
Neighbors{R,W}(f; neighborhood=Moore(1)) where {R,W} =
Neighbors{R,W}(f, neighborhood)
@inline function applyrule(data, rule::Neighbors, read, I)
let rule=rule, hood=neighborhood(rule), read=read, I=I
rule.f(data, hood, read, I)
end
end
"""
Convolution <: NeighborhoodRule
Convolution(kernel::AbstractArray)
Convolution{R,W}(kernel::AbstractArray)
A [`NeighborhoodRule`](@ref) that runs a convolution kernel over the grid.
`kernel` must be a square matrix.
## Performance
Small radius convolutions in DynamicGrids.jl will be comparable or even faster than using
DSP.jl or ImageConvolutions.jl. As the radius increases these packages will be a lot faster.
But `Convolution` is convenient to chain into a simulation, and combined with some other
rules. It should perform reasonably well with all but very large kernels.
Values are not normalised, so make sure the kernel sums to `1` if you need that.
## Example
A streaking convolution that looks a bit like sand blowing.
Swap out the matrix values to change the pattern.
```julia
using DynamicGrids, DynamicGridsGtk
streak = Convolution([0.0 0.01 0.48;
0.0 0.5 0.01;
0.0 0.0 0.0])
output = GtkOutput(rand(500, 500); tspan = 1:1000, fps=100)
sim!(output, streak; boundary=Wrap())
```
"""
struct Convolution{R,W,N} <: NeighborhoodRule{R,W}
"The neighborhood of cells around the central cell"
neighborhood::N
end
Convolution{R,W}(A::AbstractArray) where {R,W} = Convolution{R,W}(Kernel(SMatrix{size(A)...}(A)))
Convolution{R,W}(; neighborhood) where {R,W} = Convolution{R,W}(neighborhood)
@inline applyrule(data, rule::Convolution, read, I) = kernelproduct(neighborhood(rule))
"""
SetNeighborhoodRule <: SetRule
A [`SetRule`](@ref) that only writes to its neighborhood, and does not need to bounds-check.
[`positions`](@ref) and [`offsets`](@ref) are useful iterators for modifying
neighborhood values.
`SetNeighborhoodRule` rules must return a [`Neighborhood`](@ref) object from the function
`neighborhood(rule)`. By default this is `rule.neighborhood`. If this property exists,
no interface methods are required.
"""
abstract type SetNeighborhoodRule{R,W} <: SetRule{R,W} end
ruletype(::SetNeighborhoodRule) = SetNeighborhoodRule
neighborhood(rule::SetNeighborhoodRule) = rule.neighborhood
offsets(rule::SetNeighborhoodRule) = offsets(neighborhood(rule))
kernel(rule::SetNeighborhoodRule) = kernel(neighborhood(rule))
positions(rule::SetNeighborhoodRule, args...) = positions(neighborhood(rule), args...)
radius(rule::SetNeighborhoodRule, args...) = radius(neighborhood(rule))
neighborhoodkey(rule::SetNeighborhoodRule{R,W}) where {R,W} = R
neighborhoodkey(rule::SetNeighborhoodRule{<:Tuple{R1,Vararg},W}) where {R1,W} = R1
"""
SetNeighbors <: SetNeighborhoodRule
SetNeighbors(f, neighborhood=Moor(1))
SetNeighbors{R,W}(f, neighborhood=Moor(1))
A [`SetCellRule`](@ref) to manually write to the array with the specified
neighborhood. Indexing outside the neighborhood is undefined behaviour.
Function `f` is passed four arguments: a [`SimData`](@ref) object, the specified
[`Neighborhood`](@ref) object, the grid state or `Tuple` of grid states for the cell,
and the `Tuple{Int,Int}` index of the current cell.
To update the grid, you can use: [`add!`](@ref), [`sub!`](@ref) for `Number`,
and [`and!`](@ref), [`or!`](@ref) for `Bool`. These methods can be safely combined
writes from all grid cells.
Directly using `setindex!` is possible, but may cause bugs as multiple cells
may write to the same location in an unpredicatble order. As a rule, directly
setting a neighborhood index should only be done if it always sets the samevalue -
then it can be guaranteed that any writes from othe grid cells reach the same result.
[`neighbors`](@ref), [`offsets`](@ref) and [`positions`](@ref) are useful methods for
`SetNeighbors` rules.
## Example
This example adds a value to all neighbors:
```jldoctest
using DynamicGrids
rule = SetNeighbors{:a}() do data, neighborhood, a, I
add_to_neighbors = your_func(a)
for pos in positions(neighborhood)
add!(data[:b], add_to_neighbors, pos...)
end
end
# output
SetNeighbors{:a,:a}(
f = var"#1#2"
neighborhood = Moore{1, 2, 8, Nothing}
)
```
"""
struct SetNeighbors{R,W,F,N} <: SetNeighborhoodRule{R,W}
"Function to apply to the data, index and R grid values"
f::F
"The neighborhood of cells around the central cell"
neighborhood::N
end
SetNeighbors{R,W}(; kw...) where {R,W} = _nofunctionerror(SetNeighbors)
SetNeighbors{R,W}(f; neighborhood=Moore(1)) where {R,W} = SetNeighbors{R,W}(f, neighborhood)
@inline function applyrule!(data, rule::SetNeighbors, read, I)
let data=data, hood=neighborhood(rule), rule=rule, read=read, I=I
rule.f(data, hood, read, I)
end
end
"""
SetGridRule <: Rule
A `Rule` applies to whole grids. This is used for operations that don't benefit from
having neighborhood buffering or looping over the grid handled for them, or any specific
optimisations. Best suited to simple functions like `rand!(grid)` or using convolutions
from other packages like DSP.jl. They may also be useful for doing other custom things that
don't fit into the DynamicGrids.jl framework during the simulation.
Grid rules specify the grids they want and are sequenced just like any other grid.
```julia
struct MySetGridRule{R,W} <: SetGridRule{R,W} end
```
And applied as:
```julia
function applyrule!(data::AbstractSimData, rule::MySetGridRule{R,W}) where {R,W}
rand!(data[W])
end
```
"""
abstract type SetGridRule{R,W} <: Rule{R,W} end
ruletype(::SetGridRule) = SetGridRule
"""
SetGrid{R,W}(f)
Apply a function `f` to fill whole grid/s.
Broadcasting is a good way to update values.
## Example
This example simply sets grid `a` to equal grid `b`:
```jldoctest
using DynamicGrids
rule = SetGrid{:a,:b}() do a, b
b .= a
end
# output
SetGrid{:a,:b}(
f = var"#1#2"
)
```
"""
struct SetGrid{R,W,F} <: SetGridRule{R,W}
"Function to apply to the read values"
f::F
end
SetGrid{R,W}(; kw...) where {R,W} = _nofunctionerror(SetGrid)
@inline function applyrule!(data, rule::SetGrid{R,W}) where {R,W}
let data = data, rule=rule
read = map(r -> source(getindex(data, r)), _asiterable(R))
write = map(w -> source(getindex(data, w)), _asiterable(W))
rule.f(read..., write...)
end
end
# Utils
@noinline _nofunctionerror(t) =
throw(ArgumentError("No function passed to $t. Did you mean to use a do block?"))
# Check number of args passed in as we don't get a normal method
# error because of the splatted args in the default constructor.
# @generated function _checkfields(::Type{T}, args::A) where {T,A<:Tuple}
# length(fieldnames(T)) == length(fieldnames(A)) ? :(nothing) : :(_fielderror(T, args))
# end
# @noinline function _fielderror(T, args)
# throw(ArgumentError("$T has $(length(fieldnames(T))) fields: $(fieldnames(T)), you have used $(length(args))"))
# end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 2894 | """
AbstractRuleset <: ModelParameters.AbstractModel
Abstract supertype for [`Ruleset`](@ref) objects and variants.
"""
abstract type AbstractRuleset <: AbstractModel end
# Getters
ruleset(rs::AbstractRuleset) = rs
rules(rs::AbstractRuleset) = rs.rules
settings(rs::AbstractRuleset) = rs.settings
boundary(rs::AbstractRuleset) = boundary(settings(rs))
proc(rs::AbstractRuleset) = proc(settings(rs))
opt(rs::AbstractRuleset) = opt(settings(rs))
cellsize(rs::AbstractRuleset) = cellsize(settings(rs))
timestep(rs::AbstractRuleset) = timestep(settings(rs))
radius(set::AbstractRuleset) = radius(rules(set))
Base.step(rs::AbstractRuleset) = timestep(rs)
# ModelParameters interface
Base.parent(rs::AbstractRuleset) = rules(rs)
ModelParameters.setparent!(rs::AbstractRuleset, rules) = rs.rules = rules
ModelParameters.setparent(rs::AbstractRuleset, rules) = @set rs.rules = rules
"""
Rulseset <: AbstractRuleset
Ruleset(rules...; kw...)
Ruleset(rules, settings)
A container for holding a sequence of `Rule`s and simulation
details like boundary handing and optimisation.
Rules will be run in the order they are passed, ie. `Ruleset(rule1, rule2, rule3)`.
# Keywords
- `proc`: a [`Processor`](@ref) to specificy the hardware to run simulations on,
like [`SingleCPU`](@ref), [`ThreadedCPU`](@ref) or [`CuGPU`](@ref) when
KernelAbstractions.jl and a CUDA gpu is available.
- `opt`: a [`PerformanceOpt`](@ref) to specificy optimisations like
[`SparseOpt`](@ref). Defaults to [`NoOpt`](@ref).
- `boundary`: what to do with boundary of grid edges.
Options are `Remove()` or `Wrap()`, defaulting to [`Remove`](@ref).
- `cellsize`: size of cells.
- `timestep`: fixed timestep where this is required for some rules.
eg. `Month(1)` or `1u"s"`.
"""
mutable struct Ruleset{S} <: AbstractRuleset
# Rules in Ruleset are intentionally not type-stable.
# But they are when rebuilt in a StaticRuleset later
rules::Tuple{Vararg{<:Rule}}
settings::S
end
Ruleset(rule1, rules::Rule...; kw...) = Ruleset((rule1, rules...); kw...)
Ruleset(rules::Tuple; kw...) = Ruleset(rules, SimSettings(; kw...))
Ruleset(rs::AbstractRuleset) = Ruleset(rules(rs), settings(rs))
function Ruleset(; rules=(), settings=nothing, kw...)
settings1 = settings isa Nothing ? SimSettings(; kw...) : settings
Ruleset(rules, settings1)
end
struct StaticRuleset{R<:Tuple,S} <: AbstractRuleset
rules::R
settings::S
end
StaticRuleset(rule1, rules::Rule...; kw...) = StaticRuleset((rule1, rules...); kw...)
StaticRuleset(rules::Tuple; kw...) = StaticRuleset(rules, SimSettings(; kw...))
StaticRuleset(rs::AbstractRuleset) = StaticRuleset(rules(rs), settings(rs))
function StaticRuleset(; rules=(), settings=nothing, kw...)
settings1 = settings isa Nothing ? SimSettings(; kw...) : settings
StaticRuleset(rules, settings1)
end
const SRuleset = StaticRuleset
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 796 |
# Sequence rules over the [`SimData`](@ref) object,
# calling [`maprule!`](@ref) for each individual `Rule`.
function sequencerules!(simdata::AbstractSimData)
newsimdata = sequencerules!(simdata, rules(simdata))
# We run masking here to mask out cells that are `false` in the
# `mask` array, if it exists. Not all rules run masking, so it is
# applied here so that the final grid is always masked.
_maybemask!(grids(newsimdata))
newsimdata
end
function sequencerules!(simdata::AbstractSimData, rules::Tuple)
rule = rules[1]
rest = tail(rules)
# Run the first rules
newsimdata = maprule!(simdata, rule)
# Run the rest of the rules recursively
sequencerules!(newsimdata, rest)
end
sequencerules!(simdata::AbstractSimData, rules::Tuple{}) = simdata
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 663 | """
AbstractSimSettings
Abstract supertype for [`SimSettings`](@ref) object and variants.
"""
abstract type AbstractSimSettings end
"""
SimSettings <: AbstractSimSettings
Holds settings for the simulation, inside a `Ruleset` or `SimData` object.
"""
Base.@kwdef struct SimSettings{B,P,O,C,T} <: AbstractSimSettings
boundary::B = Remove()
proc::P = SingleCPU()
opt::O = NoOpt()
cellsize::C = 1
timestep::T = nothing
end
boundary(s::AbstractSimSettings) = s.boundary
proc(s::AbstractSimSettings) = s.proc
opt(s::AbstractSimSettings) = s.opt
cellsize(s::AbstractSimSettings) = s.cellsize
timestep(s::AbstractSimSettings) = s.timestep
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 2434 |
function Base.show(io::IO, mime::MIME"text/plain", ruleset::Ruleset)
indent = " "
ctx = IOContext(io, :compact => true, :indent => indent)
printstyled(io, Base.nameof(typeof(ruleset)), "(\n"; color=:blue)
println(io, indent * "rules = (")
rulectx = IOContext(ctx, :indent => indent * indent)
for rule in rules(ruleset)
show(rulectx, mime, rule)
print(io, ",\n")
end
print(io, indent * "),\n")
_showsettings(ctx, mime, settings(ruleset))
print(io, ")\n\n")
ModelParameters.printparams(io, ruleset)
end
function Base.show(io::IO, ::MIME"text/plain", rule::T) where T<:Rule{R,W} where {R,W}
indent = get(io, :indent, "")
if R === :_default_ && W === :_default_
printstyled(io, indent, Base.nameof(typeof(rule)); color=:red)
else
printstyled(io, indent, Base.nameof(typeof(rule)),
"{", sprint(show, R), ",", sprint(show, W), "}"; color=:red)
end
print(io, "(")
if !get(io, :compact, false)
if nfields(rule) > 0
println(io)
for fn in fieldnames(T)
if fieldtype(T, fn) <: Union{Number,Symbol,String}
println(io, indent, " ", fn, " = ", repr(getfield(rule, fn)))
else
# Avoid prining arrays etc. Just show the type.
println(io, indent, " ", fn, " = ", fieldtype(T, fn))
end
end
end
end
print(io, ")")
end
function Base.show(io::IO, mime::MIME"text/plain", s::SimSettings)
string =
"""
SimSettings(;
$(_showsettings(io, mime, s)))
"""
print(io, string)
end
function _showsettings(io::IO, ::MIME"text/plain", s::SimSettings)
indent = get(io, :indent, "")
settings = """
$(indent)boundary = $(s.boundary),
$(indent)proc = $(s.proc),
$(indent)opt = $(s.opt),
$(indent)cellsize = $(s.cellsize),
$(indent)timestep = $(s.timestep),
"""
print(io, settings)
end
function Base.show(io::IO, mime::MIME"text/plain", chain::Chain{R,W}) where {R,W}
indent = get(io, :indent, "")
ctx = IOContext(io, :compact => true, :indent => indent * " ")
printstyled(io, indent, string("Chain{", sprint(show, R), ",", sprint(show, W), "}"); color=:green)
print(io, "(")
for rule in rules(chain)
println(io)
show(ctx, mime, rule)
print(io, ",")
end
print(io, "\n)")
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 8999 |
"""
AbstractSimData
Supertype for simulation data objects. Thes hold [`GridData`](@ref),
[`SimSettings`](@ref) and other objects needed to run the simulation,
and potentially required from within rules.
An `AbstractSimData` object is accessable in [`applyrule`](@ref) as the first parameter.
Multiple grids can be indexed into using their key if you need to read
from arbitrary locations:
```julia
funciton applyrule(data::AbstractSimData, rule::SomeRule{Tuple{A,B}},W}, (a, b), I) where {A,B,W}
grid_a = data[A]
grid_b = data[B]
...
end
```
In single-grid simulations `AbstractSimData` objects can be indexed directly as
if they are a `Matrix`.
## Methods
- `currentframe(data)`: get the current frame number, an `Int`
- `currenttime(data)`: the current frame time, which `isa eltype(tspan)`
- `aux(data, args...)`: get the `aux` data `NamedTuple`, or `Nothing`.
adding a `Symbol` or `Val{:symbol}` argument will get a field of aux.
- `tspan(data)`: get the simulation time span, an `AbstractRange`.
- `timestep(data)`: get the simulaiton time step.
- `boundary(data)` : returns the [`BoundaryCondition`](@ref) - `Remove` or `Wrap`.
- `padval(data)` : returns the value to use as grid border padding.
These are also available, but you probably shouldn't use them and their behaviour
is not guaranteed in furture versions. Using them will also mean a rule is useful
only in specific contexts, which is discouraged.
- `settings(data)`: get the simulaitons [`SimSettings`](@ref) object.
- `extent(data)` : get the simulation [`AbstractExtent`](@ref) object.
- `init(data)` : get the simulation init `AbstractArray`/`NamedTuple`
- `mask(data)` : get the simulation mask `AbstractArray`
- `source(data)` : get the `source` grid that is being read from.
- `dest(data)` : get the `dest` grid that is being written to.
- `radius(data)` : returns the `Int` radius used on the grid,
which is also the amount of border padding.
"""
abstract type AbstractSimData{S,N} end
# Getters
extent(d::AbstractSimData) = d.extent
frames(d::AbstractSimData) = d.frames
grids(d::AbstractSimData) = d.grids
auxframe(d::AbstractSimData) = d.auxframe
currentframe(d::AbstractSimData) = d.currentframe
# Forwarded to the Extent object
gridsize(d::AbstractSimData) = gridsize(extent(d))
padval(d::AbstractSimData) = padval(extent(d))
init(d::AbstractSimData) = init(extent(d))
mask(d::AbstractSimData) = mask(extent(d))
aux(d::AbstractSimData, args...) = aux(extent(d), args...)
auxframe(d::AbstractSimData, key) = auxframe(d)[_unwrap(key)]
tspan(d::AbstractSimData) = tspan(extent(d))
timestep(d::AbstractSimData) = step(tspan(d))
# Calculated:
# Get the current time for this frame
currenttime(d::AbstractSimData) = tspan(d)[currentframe(d)]
# Get the actual current timestep, e.g. in seconds instead of variable periods like Month
currenttimestep(d::AbstractSimData) = currenttime(d) + timestep(d) - currenttime(d)
# Base methods forwarded to grids NamedTuple
Base.keys(d::AbstractSimData) = keys(grids(d))
Base.values(d::AbstractSimData) = values(grids(d))
Base.first(d::AbstractSimData) = first(grids(d))
Base.last(d::AbstractSimData) = last(grids(d))
Base.getindex(d::AbstractSimData, key::Symbol) = getindex(grids(d), key)
Base.ndims(d::AbstractSimData{<:Any,N}) where N = N
Base.size(d::AbstractSimData{S}) where S = Tuple(StaticArrays.Size(S))
# Indexing forwarded to the first grid
@propagate_inbounds Base.setindex!(d::AbstractSimData, x, I...) =
setindex!(first(grids(d)), x, I...)
@propagate_inbounds Base.getindex(d::AbstractSimData, I...) = getindex(first(grids(d)), I...)
# Uptate timestamp
function _updatetime(simdata::AbstractSimData, f::Integer)
@set! simdata.currentframe = f
@set simdata.auxframe = _calc_auxframe(simdata)
end
"""
SimData <: AbstractSimData
SimData(extent::AbstractExtent, ruleset::AbstractRuleset)
Simulation dataset to hold all intermediate arrays, timesteps
and frame numbers for the current frame of the simulation.
Additional methods not found in [`AbstractSimData`](@ref):
- `rules(d::SimData)` : get the simulation rules.
- `ruleset(d::SimData)` : get the simulation [`AbstractRuleset`](@ref).
"""
struct SimData{S<:Tuple,N,G<:NamedTuple,E,RS,F,CF,AF} <: AbstractSimData{S,N}
grids::G
extent::E
ruleset::RS
frames::F
currentframe::CF
auxframe::AF
end
function SimData{S,N}(
grids::G, extent::E, ruleset::RS, frames::F, currentframe::CF, auxframe::AF
) where {S,N,G,E,RS,F,CF,AF}
SimData{S,N,G,E,RS,F,CF,AF}(grids, extent, ruleset, frames, currentframe, auxframe)
end
SimData(o, ruleset::AbstractRuleset) = SimData(o, extent(o), ruleset)
SimData(o, r1::Rule, rs::Rule...) = SimData(o, extent(o), Ruleset(r1, rs...))
function SimData(o, extent::AbstractExtent, ruleset::AbstractRuleset)
frames_ = if hasdelay(rules(ruleset))
isstored(o) || _notstorederror()
frames(o)
else
nothing
end
SimData(extent, ruleset, frames_)
end
# Convenience constructors
SimData(extent::AbstractExtent, r1::Rule, rs::Rule...) = SimData(extent, (r1, rs...))
SimData(extent::AbstractExtent, rs::Tuple{<:Rule,Vararg}) = SimData(extent, Ruleset(rs))
# Convert grids in extent to NamedTuple
function SimData(extent::AbstractExtent, ruleset::AbstractRuleset, frames=nothing)
SimData(_asnamedtuple(extent), ruleset)
end
function SimData(
extent::AbstractExtent{<:NamedTuple{Keys}}, ruleset::AbstractRuleset, frames=nothing
) where Keys
# Calculate the neighborhood radus (and grid padding) for each grid
S = Val{Tuple{gridsize(extent)...}}()
radii = map(k-> Val{get(radius(ruleset), k, 0)}(), Keys)
radii = NamedTuple{Keys}(radii)
grids = _buildgrids(extent, ruleset, S, radii)
# Construct the SimData for each grid
SimData(grids, extent, ruleset, frames)
end
function SimData(
grids::G, extent::AbstractExtent, ruleset::AbstractRuleset, frames
) where {G<:Union{<:NamedTuple{<:Any,<:Tuple{<:GridData,Vararg}},<:GridData}}
currentframe = 1; auxframe = nothing
S = Tuple{size(extent)...}
N = ndims(extent)
# SimData is isbits-only, so use Static versions
s_extent = StaticExtent(extent)
s_ruleset = StaticRuleset(ruleset)
SimData{S,N}(grids, s_extent, s_ruleset, frames, currentframe, auxframe)
end
# Build the grids for the simulation from the exebnt, ruleset, init and padval
function _buildgrids(extent, ruleset, s, radii::NamedTuple)
map(radii, init(extent), padval(extent)) do r, in, pv
_buildgrids(extent, ruleset, s, r, in, pv)
end
end
function _buildgrids(extent, ruleset, ::Val{S}, ::Val{R}, init, padval) where {S,R}
ReadableGridData{S,R}(
init, mask(extent), proc(ruleset), opt(ruleset), boundary(ruleset), padval
)
end
ConstructionBase.constructorof(::Type{<:SimData{S,N}}) where {S,N} = SimData{S,N}
# Getters
ruleset(d::SimData) = d.ruleset
rules(d::SimData) = rules(ruleset(d))
boundary(d::SimData) = boundary(ruleset(d))
proc(d::SimData) = proc(ruleset(d))
opt(d::SimData) = opt(ruleset(d))
settings(d::SimData) = settings(ruleset(d))
# When no simdata is passed in, create new AbstractSimData
function initdata!(::Nothing, output, extent::AbstractExtent, ruleset::AbstractRuleset)
SimData(output, extent, ruleset)
end
# Initialise a AbstractSimData object with a new `Extent` and `Ruleset`.
function initdata!(
simdata::SimData, output, extent::AbstractExtent, ruleset::AbstractRuleset
)
# TODO: make sure this works with delays and new outputs?
map(copy!, values(simdata), values(init(extent)))
@set! simdata.extent = StaticExtent(extent)
@set! simdata.ruleset = StaticRuleset(ruleset)
if hasdelay(rules(ruleset))
isstored(o) || _not_stored_delay_error()
@set! simdata.frames = frames(o)
end
simdata
end
"""
RuleData <: AbstractSimData
RuleData(extent::AbstractExtent, settings::SimSettings)
[`AbstractSimData`](@ref) object that is passed to rules.
Basically a trimmed-down version of [`SimData`](@ref).
The simplified object actually passed to rules with the current design.
Passing a smaller object than `SimData` to rules leads to faster GPU compilation.
"""
struct RuleData{S<:Tuple,N,G<:NamedTuple,E,Se,F,CF,AF} <: AbstractSimData{S,N}
grids::G
extent::E
settings::Se
frames::F
currentframe::CF
auxframe::AF
end
function RuleData{S,N}(
grids::G, extent::E, settings::Se, frames::F, currentframe::CF, auxframe::AF
) where {S,N,G,E,Se,F,CF,AF}
RuleData{S,N,G,E,Se,F,CF,AF}(grids, extent, settings, frames, currentframe, auxframe)
end
function RuleData(d::AbstractSimData{S,N}) where {S,N}
RuleData{S,N}(grids(d), extent(d), settings(d), frames(d), currentframe(d), auxframe(d))
end
ConstructionBase.constructorof(::Type{<:RuleData{S,N}}) where {S,N} = RuleData{S,N}
# Getters
settings(d::RuleData) = d.settings
boundary(d::RuleData) = boundary(settings(d))
proc(d::RuleData) = proc(settings(d))
opt(d::RuleData) = opt(settings(d))
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 11219 |
"""
SparseOpt <: PerformanceOpt
SparseOpt()
An optimisation flag that ignores all padding valuesin the grid,
by default zeros.
For low-density simulations performance may improve by
orders of magnitude, as only used cells are run.
Specifiy with:
```julia
ruleset = Ruleset(rule; opt=SparseOpt())
# or
output = sim!(output, rule; opt=SparseOpt())
```
`SparseOpt` is best demonstrated with this simulation, where the grey areas do not
run except where the neighborhood partially hangs over an area that is not grey:
"""
struct SparseOpt{F<:Function} <: PerformanceOpt
f::F
end
SparseOpt() = SparseOpt(==(0))
@inline _isactive(val, opt::SparseOpt{<:Function}) = !opt.f(val)
sourcestatus(d::GridData) = optdata(d).sourcestatus
deststatus(d::GridData) = optdata(d).deststatus
# Run kernels with SparseOpt, block by block:
function optmap(
f, simdata::AbstractSimData{S}, proc, ::SparseOpt, ruletype::Val{<:Rule}, rkeys
) where {S<:Tuple{Y,X}} where {Y,X}
# Only use SparseOpt for single-grid rules with grid radii > 0
grid = _firstgrid(simdata, rkeys)
R = radius(grid)
if R == 0
optmap(f, simdata, proc, NoOpt(), ruletype, rkeys)
return nothing
end
B = 2R
status = sourcestatus(grid)
let f=f, proc=proc, status=status
procmap(proc, 1:_indtoblock(X+R, B)) do bj
for bi in 1:_indtoblock(Y+R, B)
status[bi, bj] || continue
# Convert from padded block to init dimensions
istart, jstart = _blocktoind(bi, B) - R, _blocktoind(bj, B) - R
# Stop at the init row/column size, not the padding or block multiple
istop, jstop = min(istart + B - 1, Y), min(jstart + B - 1, X)
# Skip the padding
istart, jstart = max(istart, 1), max(jstart, 1)
for j in jstart:jstop
@simd for i in istart:istop
f((i, j))
end
end
end
end
end
return nothing
end
function row_kernel!(
simdata::AbstractSimData, grid::GridData{<:Tuple{Y,X},R}, proc, opt::SparseOpt,
ruletype::Val, rule::Rule, rkeys, wkeys, bi
) where {Y,X,R}
# No SparseOpt for radius 0
if R === 0
return row_kernel!(simdata, grid, proc, NoOpt(), ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys, bi)
end
B = 2R
S = 2R + 1
nblockcols = _indtoblock(X+R, B)
src = parent(source(grid))
srcstatus, dststatus = sourcestatus(grid), deststatus(grid)
# Blocks ignore padding! the first block contains padding.
i = _blocktoind(bi, B)
i > Y && return nothing
# Get current bloc
skippedlastblock = true
# Initialise block status for the start of the row
# The first column always runs, it's buggy otherwise.
@inbounds bs11, bs12 = true, true
@inbounds bs21, bs22 = true, true
# New block status
newbs12 = false
newbs22 = false
windows = _initialise_windows(src, Val{R}(), i, 1)
for bj = 1:nblockcols
# Shuffle current window status
bs11, bs21 = bs12, bs22
@inbounds bs12, bs22 = srcstatus[bi, bj + 1], srcstatus[bi + 1, bj + 1]
# Skip this block if it and the neighboring blocks are inactive
if !(bs11 | bs12 | bs21 | bs22)
skippedlastblock = true
# Run the rest of the chain if it exists and more than 1 grid is used
if rule isa Chain && length(rule) > 1 && length(rkeys) > 1
# Loop over the grid COLUMNS inside the block
jstart = _blocktoind(bj, B)
jstop = min(jstart + B - 1, X)
for j in jstart:jstop
# Loop over the grid ROWS inside the block
blocklen = min(Y, i + B - 1) - i + 1
for b in 1:blocklen
cell_kernel!(simdata, ruletype, rule, rkeys, wkeys, i + b - 1, j)
end
end
end
continue
end
# Define area to loop over with the block.
# It's variable because the last block may be partial
jstart = _blocktoind(bj, B)
jstop = min(jstart + B - 1, X)
# Reinitialise neighborhood windows if we have skipped a section of the array
if skippedlastblock
windows = _initialise_windows(src, Val{R}(), i, jstart)
skippedlastblock = false
end
# Shuffle new window status
newbs11 = newbs12
newbs21 = newbs22
newbs12 = newbs22 = false
# Loop over the grid COLUMNS inside the block
for j in jstart:jstop
# Update windows unless feshly populated
windows = _slide_windows(windows, src, Val{R}(), i, j)
# Which block column are we in, 1 or 2
curblockj = (j - jstart) ÷ R + 1
# Loop over the COLUMN of windows covering the block
blocklen = min(Y, i + B - 1) - i + 1
for b in 1:blocklen
# Set rule window
rule1 = setwindow(rule, windows[b])
# Run the rule kernel for the cell
writeval = cell_kernel!(simdata, ruletype, rule1, rkeys, wkeys, i + b - 1, j)
# Update the status for the current block
cs = _cellstatus(opt, wkeys, writeval)
curblocki = R == 1 ? b : (b - 1) ÷ R + 1
if curblocki == 1
curblockj == 1 ? (newbs11 |= cs) : (newbs12 |= cs)
else
curblockj == 1 ? (newbs21 |= cs) : (newbs22 |= cs)
end
end
# Combine new block status with deststatus array
@inbounds dststatus[bi, bj] |= newbs11
@inbounds dststatus[bi+1, bj] |= newbs21
@inbounds dststatus[bi, bj+1] |= newbs12
@inbounds dststatus[bi+1, bj+1] |= newbs22
end
end
return nothing
end
@inline _cellstatus(opt::SparseOpt, wkeys::Tuple, writeval) = _isactive(writeval[1], opt)
@inline _cellstatus(opt::SparseOpt, wkeys, writeval) = _isactive(writeval, opt)
# SparseOpt methods
# _build_status => (Matrix{Bool}, Matrix{Bool})
# Build block-status arrays
# We add an additional block that is never used so we can
# index into it in the block loop without checking
function _build_optdata(opt::SparseOpt, source, r::Int)
r > 0 || return nothing
hoodsize = 2r + 1
blocksize = 2r
nblocs = _indtoblock.(size(source), blocksize) .+ 1
sourcestatus = zeros(Bool, nblocs)
deststatus = zeros(Bool, nblocs)
return (; sourcestatus, deststatus)
end
function _swapoptdata(opt::SparseOpt, grid::GridData)
isnothing(optdata(grid)) && return grid
od = optdata(grid)
srcstatus = od.sourcestatus
dststatus = od.deststatus
@set! od.deststatus = srcstatus
@set! od.sourcestatus = dststatus
return @set grid.optdata = od
end
# Initialise the block status array.
# This tracks whether anything has to be done in an area of the main array.
function _update_optdata!(grid, opt::SparseOpt)
isnothing(optdata(grid)) && return grid
blocksize = 2 * radius(grid)
src = parent(source(grid))
for I in CartesianIndices(src)
# Mark the status block (by default a non-zero value)
if _isactive(src[I], opt)
bi = _indtoblock.(Tuple(I), blocksize)
@inbounds sourcestatus(grid)[bi...] = true
@inbounds deststatus(grid)[bi...] = true
end
end
return grid
end
# Clear the destination grid and its status for SparseOpt.
# NoOpt writes to every cell, so this is not required
function _cleardest!(grid, opt::SparseOpt)
dest(grid) .= source(grid)
if !isnothing(optdata(grid))
deststatus(grid) .= false
end
end
# Sets the status of the destination block that the current index is in.
# It can't turn of block status as the block is larger than the cell
# But should be used inside a LOCK
function _setoptindex!(grid::WritableGridData{<:Any,R}, opt::SparseOpt, x, I...) where R
isnothing(optdata(grid)) && return grid
blockindex = _indtoblock.(I .+ R, 2R)
@inbounds deststatus(grid)[blockindex...] |= !(opt.f(x))
return nothing
end
# _wrapopt!
# Copies status from opposite sides/corners in Wrap boundary mode
function _wrapopt!(grid, ::SparseOpt)
isnothing(optdata(grid)) && return grid
status = sourcestatus(grid)
# !!! The end row/column is always empty !!!
# Its padding for block opt. So we work with end-1 and end-2
# We should probably re-write this using the known grid sizes,
# instead of `end`
# This could be further optimised by not copying the end-2
# block column/row when the blocks are aligned at both ends.
# Sides
status[1, :] .|= status[end-1, :] .| status[end-2, :]
status[:, 1] .|= status[:, end-1] .| status[:, end-2]
status[end-1, :] .|= status[1, :]
status[:, end-1] .|= status[:, 1]
status[end-2, :] .|= status[1, :]
status[:, end-2] .|= status[:, 1]
# Corners
status[1, 1] |= status[end-1, end-1] | status[end-2, end-1] |
status[end-1, end-2] | status[end-2, end-2]
status[end-1, 1] |= status[1, end-1] | status[1, end-2]
status[end-2, 1] |= status[1, end-1] | status[1, end-2]
status[1, end-1] |= status[end-1, 1] | status[end-2, 1]
status[1, end-2] |= status[end-1, 1] | status[end-2, 1]
status[end-1, end-1] |= status[1, 1]
status[end-2, end-2] |= status[1, 1]
return grid
end
"""
SparseOptInspector()
A [`Renderer`](@ref) that checks [`SparseOpt`](@ref) visually.
Cells that do not run show in gray. Errors show in red, but if they do there's a bug.
"""
struct SparseOptInspector{A} <: SingleGridRenderer
accessor::A
end
SparseOptInspector() = SparseOptInspector(identity)
accessor(p::SparseOptInspector) = p.accessor
function cell_to_pixel(p::SparseOptInspector, mask, minval, maxval, data::AbstractSimData, val, I::Tuple)
opt(data) isa SparseOpt || error("Can only use SparseOptInspector with SparseOpt grids")
r = radius(first(grids(data)))
blocksize = 2r
blockindex = _indtoblock.((I[1] + r, I[2] + r), blocksize)
normedval = normalise(val, minval, maxval)
# This is done at the start of the next frame, so wont show up in
# the image properly. So do it preemtively?
_wrapopt!(first(data))
status = sourcestatus(first(data))
if status[blockindex...]
if normedval > 0
to_rgb(normedval)
else
to_rgb((0.0, 0.0, 0.0))
end
elseif normedval > 0
to_rgb((1.0, 0.0, 0.0)) # This (a red cell) would mean there is a bug in SparseOpt
else
to_rgb((0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
end
end
# Custom SimSettings constructor: SparseOpt does not work on GPU
function SimSettings(
boundary::B, proc::P, opt::SparseOpt, cellsize::C, timestep::T
) where {B,P<:GPU,C,T}
@info "SparseOpt does not work on GPU. Using NoOpt instead."
SimSettings{B,P,NoOpt,C,T}(boundary, proc, NoOpt(), cellsize, timestep)
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 4627 |
"""
ismasked(data, I...)
Check if a cell is masked, using the `mask` array.
Used used internally during simulations to skip masked cells.
If `mask` was not passed to the `Output` constructor or `sim!`
it defaults to `nothing` and `false` is always returned.
"""
ismasked(data::AbstractSimData, I...) = ismasked(mask(data), I...)
ismasked(data::GridData, I...) = ismasked(mask(data), I...)
ismasked(mask::Nothing, I...) = false
ismasked(mask::AbstractArray, I...) = @inbounds !(mask[I...])
"""
isinferred(output::Output, ruleset::Ruleset)
isinferred(output::Output, rules::Rule...)
Test if a custom rule is inferred and the return type is correct when
`applyrule` or `applyrule!` is run.
Type-stability can give orders of magnitude improvements in performance.
"""
isinferred(output::Output, rules::Rule...) = isinferred(output, rules)
isinferred(output::Output, rules::Tuple) = isinferred(output, Ruleset(rules...))
function isinferred(output::Output, ruleset::Ruleset)
simdata = _updaterules(rules(ruleset), SimData(output, ruleset))
map(rules(simdata)) do rule
isinferred(simdata, rule)
end
return true
end
isinferred(simdata::AbstractSimData, rule::Rule) = _isinferred(simdata, rule)
function isinferred(simdata::AbstractSimData,
rule::Union{NeighborhoodRule,Chain{<:Any,<:Any,<:Tuple{<:NeighborhoodRule,Vararg}}}
)
grid = simdata[neighborhoodkey(rule)]
r = max(1, radius(rule))
T = eltype(grid)
S = 2r + 1
window = SArray{Tuple{S,S},T,2,S^2}(Tuple(zero(T) for i in 1:S^2))
rule = setwindow(rule, window)
return _isinferred(simdata, rule)
end
function isinferred(simdata::AbstractSimData, rule::SetCellRule)
rkeys, rgrids = _getreadgrids(rule, simdata)
wkeys, wgrids = _getwritegrids(rule, simdata)
simdata = @set simdata.grids = _combinegrids(rkeys, rgrids, wkeys, wgrids)
readval = _readcell(simdata, rkeys, 1, 1)
@inferred applyrule!(simdata, rule, readval, (1, 1))
return true
end
function _isinferred(simdata, rule)
rkeys, rgrids = _getreadgrids(rule, simdata)
wkeys, wgrids = _getwritegrids(rule, simdata)
simdata = @set simdata.grids = _combinegrids(rkeys, rgrids, wkeys, wgrids)
readval = _readcell(simdata, rkeys, 1, 1)
_example_writeval(grids::Tuple) = map(_example_writeval, grids)
_example_writeval(grid::WritableGridData) = grid[1, 1]
ex_writeval = Tuple(_example_writeval(wgrids))
writeval = @inferred applyrule(simdata, rule, readval, (1, 1))
typeof(Tuple(writeval)) == typeof(ex_writeval) ||
error("return type `$(typeof(Tuple(writeval)))` doesn't match grids `$(typeof(ex_writeval))`")
return true
end
# _zerogrids
# Generate a Vector of zero valued grids
_zerogrids(initgrid::AbstractArray, length) = [zero(initgrid) for f in 1:length]
_zerogrids(initgrids::NamedTuple, length) =
[map(grid -> zero(grid), initgrids) for f in 1:length]
# _asiterable
# Return some iterable value from a
# Symbol, Tuple or tuple type
@inline _asiterable(x) = (x,)
@inline _asiterable(x::Symbol) = (x,)
@inline _asiterable(x::Type{<:Tuple}) = x.parameters
@inline _asiterable(x::Tuple) = x
@inline _asiterable(x::AbstractArray) = x
# _astuple
# Wrap a value in a tuple if the matching keys are not a tuple
# we cant just dispatch on state, as it may be meant to be a tuple.
@inline _astuple(rule::Rule, state) = _astuple(_readkeys(rule), state)
@inline _astuple(keys::Tuple, state) = state
@inline _astuple(key, state) = (state,)
# _asnamedtuple => NamedTuple
# Returns a NamedTuple given a NamedTuple or an Array.
# the Array will be called _default_.
@inline _asnamedtuple(x::NamedTuple) = x
@inline _asnamedtuple(x::AbstractArray) = (_default_=x,)
@inline function _asnamedtuple(e::Extent)
@set! e.init = _asnamedtuple(init(e))
@set e.padval = _samenamedtuple(init(e), padval(e))
end
# _samenamedtuple => NamedTuple
# Returns a NamedTuple with length and keys matching the `init`
# NamedTuple, for another NamedTuple, a Tuple, or a scalar.
@inline _samenamedtuple(init::NamedTuple{K}, x::NamedTuple{K}) where K = x
@noinline _samenamedtuple(init::NamedTuple{K}, x::NamedTuple{J}) where {K,J} =
error("Keys $K and $J do not match")
@inline _samenamedtuple(init::NamedTuple{K}, x::Tuple) where K = NamedTuple{K}(x)
@inline _samenamedtuple(init::NamedTuple, x) = map(_ -> x, init)
# Unwrap a Val or Val type to its internal value
_unwrap(x) = x
_unwrap(::Val{X}) where X = X
_unwrap(::Type{<:Val{X}}) where X = X
@inline _firstgrid(simdata, ::Val{K}) where K = simdata[K]
@inline _firstgrid(simdata, ::Tuple{Val{K},Vararg}) where K = simdata[K]
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 22722 | module Neighborhoods
using ConstructionBase, StaticArrays
export Neighborhood, Window, AbstractKernelNeighborhood, Kernel,
Moore, VonNeumann, AbstractPositionalNeighborhood, Positional, LayeredPositional
export neighbors, neighborhood, kernel, kernelproduct, offsets, positions, radius, distances
export setwindow, updatewindow, unsafe_updatewindow
export pad_axes, unpad_axes
export broadcast_neighborhood, broadcast_neighborhood!
"""
Neighborhood
Neighborhoods define the pattern of surrounding cells in the "neighborhood"
of the current cell. The `neighbors` function returns the surrounding
cells as an iterable.
The main kinds of neighborhood are demonstrated below:
Neighborhoods can be used in `NeighborhoodRule` and `SetNeighborhoodRule` -
the same shapes with different purposes. In a `NeighborhoodRule` the neighborhood specifies
which cells around the current cell are returned as an iterable from the `neighbors` function.
These can be counted, summed, compared, or multiplied with a kernel in an
`AbstractKernelNeighborhood`, using [`kernelproduct`](@ref).
In `SetNeighborhoodRule` neighborhoods give the locations of cells around the central cell,
as [`offsets`] and absolute [`positions`](@ref) around the index of each neighbor. These
can then be written to manually.
"""
abstract type Neighborhood{R,N,L} end
ConstructionBase.constructorof(::Type{<:T}) where T <: Neighborhood{R,N,L} where {R,N,L} =
T.name.wrapper{R,N,L}
"""
kernelproduct(rule::NeighborhoodRule})
kernelproduct(hood::AbstractKernelNeighborhood)
kernelproduct(hood::Neighborhood, kernel)
Returns the vector dot product of the neighborhood and the kernel,
although differing from `dot` in that the dot product is not take for
vector members of the neighborhood - they are treated as scalars.
"""
function kernelproduct end
"""
radius(rule, [key]) -> Int
Return the radius of a rule or ruleset if it has one, otherwise zero.
"""
function radius end
radius(hood::Neighborhood{R}) where R = R
"""
neighbors(x::Union{Neighborhood,NeighborhoodRule}}) -> iterable
Returns an indexable iterator for all cells in the neighborhood,
either a `Tuple` of values or a range.
Custom `Neighborhood`s must define this method.
"""
function neighbors end
neighbors(hood::Neighborhood) = begin
map(i -> _window(hood)[i], window_indices(hood))
end
"""
offsets(x) -> iterable
Returns an indexable iterable over all cells, containing `Tuple`s of
the index offset from the central cell.
Custom `Neighborhood`s must define this method.
"""
function offsets end
offsets(hood::Neighborhood) = offsets(typeof(hood))
_window(hood::Neighborhood) = hood._window
"""
positions(x::Union{Neighborhood,NeighborhoodRule}}, cellindex::Tuple) -> iterable
Returns an indexable iterable, over all cells as `Tuple`s of each
index in the main array. Useful in `SetNeighborhoodRule` for
setting neighborhood values, or for getting values in an Aux array.
"""
function positions end
@inline positions(hood::Neighborhood, I::CartesianIndex) = positions(hood, Tuple(I))
@inline positions(hood::Neighborhood, I::Int...) = positions(hood, I)
@inline positions(hood::Neighborhood, I::Tuple) = map(o -> o .+ I, offsets(hood))
"""
distances(hood::Neighborhood)
Get the center-to-center distance of each neighborhood position from the central cell,
so that horizontally or vertically adjacent cells have a distance of `1.0`, and a
diagonally adjacent cell has a distance of `sqrt(2.0)`.
Vales are calculated at compile time, so `distances` can be used inside rules with little
overhead.
"""
@generated function distances(hood::Neighborhood{N,R,L}) where {N,R,L}
expr = Expr(:tuple, ntuple(i -> :(bd[bi[$i]]), L)...)
return quote
bd = window_distances(hood)
bi = window_indices(hood)
$expr
end
end
@generated function window_indices(H::Neighborhood{R,N}) where {R,N}
# Offsets can be anywhere in the window, specified with
# all dimensions. Here we transform them to a linear index.
bi = map(offsets(H)) do o
# Calculate strides
S = 2R + 1
strides = ntuple(i -> S^(i-1), N)
# Offset indices are centered, we want them as regular array indices
# Return the linear index in the square window
sum(map((i, s) -> (i + R) * s, o, strides)) + 1
end
return Expr(:tuple, bi...)
end
@generated function window_distances(hood::Neighborhood{R,N}) where {R,N}
values = map(CartesianIndices(ntuple(_ -> SOneTo{2R+1}(), N))) do I
sqrt(sum((Tuple(I) .- (R + 1)) .^ 2))
end
x = SArray(values)
quote
return $x
end
end
Base.eltype(hood::Neighborhood) = eltype(_window(hood))
Base.length(hood::Neighborhood{<:Any,<:Any,L}) where L = L
Base.ndims(hood::Neighborhood{<:Any,N}) where N = N
# Note: size is radial, and may not relate to `length` in the same way
# as in an array. A neighborhood does not have to include all cells includeding
# in the area covered by `size` and `axes`.
Base.size(hood::Neighborhood{R,N}) where {R,N} = ntuple(_ -> 2R+1, N)
Base.axes(hood::Neighborhood{R,N}) where {R,N} = ntuple(_ -> SOneTo{2R+1}(), N)
Base.iterate(hood::Neighborhood, args...) = iterate(neighbors(hood), args...)
Base.getindex(hood::Neighborhood, i) = begin
# @show _window(hood) window_indices(hood)
getindex(_window(hood), window_indices(hood)[i])
end
"""
Moore <: Neighborhood
Moore(radius::Int=1; ndims=2)
Moore(; radius=1, ndims=2)
Moore{R}(; ndims=2)
Moore{R,N}()
Moore neighborhoods define the neighborhood as all cells within a horizontal or
vertical distance of the central cell. The central cell is omitted.
Radius `R = 1`:
```
N = 1 N = 2
▄ ▄ █▀█
▀▀▀
```
Radius `R = 2`:
```
N = 1 N = 2
█████
▀▀ ▀▀ ██▄██
▀▀▀▀▀
```
Using `R` and `N` type parameters removes runtime cost of generating the neighborhood,
compated to passing arguments/keywords.
"""
struct Moore{R,N,L,W} <: Neighborhood{R,N,L}
_window::W
end
Moore(radius::Int=1; ndims=2) = Moore{radius,ndims}()
Moore(args...; radius=1, ndims=2) = Moore{radius,ndims}(args...)
Moore{R}(_window=nothing; ndims=2) where R = Moore{R,ndims,}(_window)
Moore{R,N}(_window=nothing) where {R,N} = Moore{R,N,(2R+1)^N-1}(_window)
Moore{R,N,L}(_window::W=nothing) where {R,N,L,W} = Moore{R,N,L,W}(_window)
@generated function offsets(::Type{<:Moore{R,N}}) where {R,N}
exp = Expr(:tuple)
for I in CartesianIndices(ntuple(_-> -R:R, N))
if !all(map(iszero, Tuple(I)))
push!(exp.args, :($(Tuple(I))))
end
end
return exp
end
@inline setwindow(n::Moore{R,N,L}, win::W2) where {R,N,L,W2} = Moore{R,N,L,W2}(win)
"""
VonNeumann(radius=1; ndims=2) -> Positional
VonNeumann(; radius=1, ndims=2) -> Positional
VonNeumann{R,N}() -> Positional
A Von Neuman neighborhood is a damond-shaped, omitting the central cell:
Radius `R = 1`:
```
N = 1 N = 2
▄ ▄ ▄▀▄
▀
```
Radius `R = 2`:
```
N = 1 N = 2
▄█▄
▀▀ ▀▀ ▀█▄█▀
▀
```
In 1 dimension it is identical to [`Moore`](@ref).
Using `R` and `N` type parameters removes runtime cost of generating the neighborhood,
compated to passing arguments/keywords.
"""
struct VonNeumann{R,N,L,W} <: Neighborhood{R,N,L}
_window::W
end
VonNeumann(; radius=1, ndims=2) = VonNeumann(radius; ndims)
VonNeumann(radius, _window=nothing; ndims=2) = VonNeumann{radius,ndims}(_window)
VonNeumann{R}(_window=nothing; ndims=2) where R = VonNeumann{R,ndims}(_window)
function VonNeumann{R,N}(_window=nothing) where {R,N}
L = 2sum(1:R) + 2R
VonNeumann{R,N,L}(_window)
end
VonNeumann{R,N,L}(_window::W=nothing) where {R,N,L,W} = VonNeumann{R,N,L,W}(_window)
@inline setwindow(n::VonNeumann{R,N,L}, win::W2) where {R,N,L,W2} = VonNeumann{R,N,L,W2}(win)
@generated function offsets(::Type{T}) where {T<:VonNeumann{R,N}} where {R,N}
offsets_expr = Expr(:tuple)
rngs = ntuple(_ -> -R:R, N)
for I in CartesianIndices(rngs)
manhatten_distance = sum(map(abs, Tuple(I)))
if manhatten_distance in 1:R
push!(offsets_expr.args, Tuple(I))
end
end
return offsets_expr
end
"""
Window <: Neighborhood
Window(; radius=1, ndims=2)
Window{R}(; ndims=2)
Window{R,N}()
A neighboorhood of radius R that includes the central cell.
Radius `R = 1`:
```
N = 1 N = 2
▄▄▄ ███
▀▀▀
```
Radius `R = 2`:
```
N = 1 N = 2
█████
▀▀▀▀▀ █████
▀▀▀▀▀
```
"""
struct Window{R,N,L,W} <: Neighborhood{R,N,L}
_window::W
end
Window(; radius=1, ndims=2) = Window{radius,ndims}(args...)
Window(R::Int, args...; ndims=2) = Window{R,ndims}(args...)
Window{R}(_window=nothing; ndims=2) where {R} = Window{R,ndims}(_window)
Window{R,N}(_window=nothing) where {R,N} = Window{R,N,(2R+1)^N}(_window)
Window{R,N,L}(_window::W=nothing) where {R,N,L,W} = Window{R,N,L,W}(_window)
Window(A::AbstractArray) = Window{(size(A, 1) - 1) ÷ 2,ndims(A)}()
# The central cell is included
@inline function offsets(::Type{<:Window{R,N}}) where {R,N}
D = 2R + 1
ntuple(i -> (rem(i - 1, D) - R, (i - 1) ÷ D - R), D^N)
end
distances(hood::Window) = Tuple(window_distances(hood))
@inline setwindow(::Window{R,N,L}, win::W2) where {R,N,L,W2} = Window{R,N,L,W2}(win)
window_indices(hood::Window{R,N}) where {R,N} = SOneTo{(2R + 1)^N}()
neighbors(hood::Window) = _window(hood)
"""
AbstractKernelNeighborhood <: Neighborhood
Abstract supertype for kernel neighborhoods.
These can wrap any other neighborhood object, and include a kernel of
the same length and positions as the neighborhood.
"""
abstract type AbstractKernelNeighborhood{R,N,L,H} <: Neighborhood{R,N,L} end
neighbors(hood::AbstractKernelNeighborhood) = neighbors(neighborhood(hood))
offsets(::Type{<:AbstractKernelNeighborhood{<:Any,<:Any,<:Any,H}}) where H = offsets(H)
positions(hood::AbstractKernelNeighborhood, I::Tuple) = positions(neighborhood(hood), I)
"""
kernel(hood::AbstractKernelNeighborhood) => iterable
Returns the kernel object, an array or iterable matching the length
of the neighborhood.
"""
function kernel end
kernel(hood::AbstractKernelNeighborhood) = hood.kernel
"""
neighborhood(x) -> Neighborhood
Returns a neighborhood object.
"""
function neighborhood end
neighborhood(hood::AbstractKernelNeighborhood) = hood.neighborhood
"""
kernelproduct(hood::AbstractKernelNeighborhood)
kernelproduct(hood::Neighborhood, kernel)
Take the vector dot produce of the neighborhood and the kernel,
without recursion into the values of either. Essentially `Base.dot`
without recursive calls on the contents, as these are rarely what is
intended.
"""
function kernelproduct(hood::AbstractKernelNeighborhood)
kernelproduct(neighborhood(hood), kernel(hood))
end
function kernelproduct(hood::Neighborhood{<:Any,<:Any,L}, kernel) where L
sum = zero(first(hood))
@simd for i in 1:L
@inbounds sum += hood[i] * kernel[i]
end
return sum
end
function kernelproduct(hood::Window{<:Any,<:Any,L}, kernel) where L
sum = zero(first(hood))
@simd for i in 1:L
@inbounds sum += _window(hood)[i] * kernel[i]
end
return sum
end
"""
Kernel <: AbstractKernelNeighborhood
Kernel(neighborhood, kernel)
Wrap any other neighborhood object, and includes a kernel of
the same length and positions as the neighborhood.
"""
struct Kernel{R,N,L,H,K} <: AbstractKernelNeighborhood{R,N,L,H}
neighborhood::H
kernel::K
end
Kernel(A::AbstractMatrix) = Kernel(Window(A), A)
function Kernel(hood::H, kernel::K) where {H<:Neighborhood{R,N,L},K} where {R,N,L}
length(hood) == length(kernel) || _kernel_length_error(hood, kernel)
Kernel{R,N,L,H,K}(hood, kernel)
end
function Kernel{R,N,L}(hood::H, kernel::K) where {R,N,L,H<:Neighborhood{R,N,L},K}
Kernel{R,N,L,H,K}(hood, kernel)
end
function _kernel_length_error(hood, kernel)
throw(ArgumentError("Neighborhood length $(length(hood)) does not match kernel length $(length(kernel))"))
end
function setwindow(n::Kernel{R,N,L,<:Any,K}, win) where {R,N,L,K}
hood = setwindow(neighborhood(n), win)
return Kernel{R,N,L,typeof(hood),K}(hood, kernel(n))
end
"""
AbstractPositionalNeighborhood <: Neighborhood
Positional neighborhoods are tuples of coordinates that are specified in relation
to the central point of the current cell. They can be any arbitrary shape or size,
but should be listed in column-major order for performance.
"""
abstract type AbstractPositionalNeighborhood{R,N,L} <: Neighborhood{R,N,L} end
const CustomOffset = Tuple{Vararg{Int}}
const CustomOffsets = Union{AbstractArray{<:CustomOffset},Tuple{Vararg{<:CustomOffset}}}
"""
Positional <: AbstractPositionalNeighborhood
Positional(coord::Tuple{Vararg{Int}}...)
Positional(offsets::Tuple{Tuple{Vararg{Int}}})
Positional{O}()
Neighborhoods that can take arbitrary shapes by specifying each coordinate,
as `Tuple{Int,Int}` of the row/column distance (positive and negative)
from the central point.
The neighborhood radius is calculated from the most distant coordinate.
For simplicity the window read from the main grid is a square with sides
`2r + 1` around the central point.
The dimensionality `N` of the neighborhood is taken from the length of
the first coordinate, e.g. `1`, `2` or `3`.
Example radius `R = 1`:
```
N = 1 N = 2
▄▄ ▀▄
▀
```
Example radius `R = 2`:
```
N = 1 N = 2
▄▄
▀ ▀▀ ▀███
▀
```
Using the `O` parameter e.g. `Positional{((1, 2), (1, 1))}()` removes any
runtime cost of generating the neighborhood.
"""
struct Positional{O,R,N,L,W} <: AbstractPositionalNeighborhood{R,N,L}
"A tuple of tuples of Int, containing 2-D coordinates relative to the central point"
_window::W
end
Positional(args::CustomOffset...) = Positional(args)
function Positional(offsets::CustomOffsets, _window=nothing)
Positional{offsets}(_window)
end
function Positional(offsets::O, _window=nothing) where O
Positional{offsets}(_window)
end
function Positional{O}(_window=nothing) where O
R = _absmaxcoord(O)
N = length(first(O))
L = length(O)
Positional{O,R,N,L}(_window)
end
function Positional{O,R,N,L}(_window::W=nothing) where {O,R,N,L,W}
Positional{O,R,N,L,W}(_window)
end
# Calculate the maximum absolute value in the offsets to use as the radius
function _absmaxcoord(offsets::Union{AbstractArray,Tuple})
maximum(map(x -> maximum(map(abs, x)), offsets))
end
function ConstructionBase.constructorof(::Type{Positional{O,R,N,L,W}}) where {O,R,N,L,W}
Positional{O,R,N,L}
end
offsets(::Type{<:Positional{O}}) where O = O
@inline function setwindow(n::Positional{O,R,N,L}, win::W2) where {O,R,N,L,W2}
Positional{O,R,N,L,W2}(win)
end
"""
LayeredPositional <: AbstractPositional
LayeredPositional(layers::Positional...)
Sets of [`Positional`](@ref) neighborhoods that can have separate rules for each set.
`neighbors` for `LayeredPositional` returns a tuple of iterators
for each neighborhood layer.
"""
struct LayeredPositional{R,N,L,La,W} <: AbstractPositionalNeighborhood{R,N,L}
"A tuple of custom neighborhoods"
layers::La
_window::W
end
LayeredPositional(layers::Positional...) = LayeredPositional(layers)
function LayeredPositional(layers::Tuple{Vararg{<:Positional}}, _window=nothing)
R = maximum(map(radius, layers))
N = ndims(first(layers))
L = map(length, layers)
LayeredPositional{R,N,L}(layers, _window)
end
function LayeredPositional{R,N,L}(layers, _window::W) where {R,N,L,W}
# Child layers must have the same _window, and the
# same R and L parameters. So we rebuild them all here.
layers = map(l -> Positional{offsets(l),R,N,L}(_window), layers)
LayeredPositional{R,N,L,typeof(layers),W}(layers, _window)
end
@inline neighbors(hood::LayeredPositional) = map(l -> neighbors(l), hood.layers)
@inline offsets(::Type{<:LayeredPositional{R,N,L,La}}) where {R,N,L,La} =
map(p -> offsets(p), tuple_contents(La))
@inline positions(hood::LayeredPositional, args::Tuple) = map(l -> positions(l, args...), hood.layers)
@inline function setwindow(n::LayeredPositional{R,N,L}, win) where {R,N,L}
LayeredPositional{R,N,L}(n.layers, win)
end
@inline Base.sum(hood::LayeredPositional) = map(sum, neighbors(hood))
function _subwindow(l::Neighborhood{R,N}, window) where {R,N}
window_inds = ntuple(_-> R + 1, R + 1, N)
vals = map(ps) do p
window[p...]
end
L = (2R + 1) ^ N
S = Tuple{ntuple(_ -> 2R + 1, N)...}
return SArray{S,eltype(window),N,L}(vals)
end
# Utils
# Get the size of a neighborhood dimension from its radius,
# which is always 2r + 1.
@inline hoodsize(hood::Neighborhood{R}) where R = hoodsize(R)
@inline hoodsize(radius::Integer) = 2radius + 1
# Copied from StaticArrays. If they can do it...
Base.@pure function tuple_contents(::Type{X}) where {X<:Tuple}
return tuple(X.parameters...)
end
tuple_contents(xs::Tuple) = xs
"""
unsafe_readwindow(hood::Neighborhood, A::AbstractArray, I) => SArray
Get a single window square from an array, as an `SArray`, checking bounds.
"""
readwindow(hood::Neighborhood, A::AbstractArray, I::Int...) = readwindow(hood, A, I)
@inline function readwindow(hood::Neighborhood{R,N}, A::AbstractArray, I) where {R,N}
for O in ntuple(_ -> (-R, R), N)
edges = Tuple(I) .+ O
map(I -> checkbounds(A, I...), edges)
end
return unsafe_readwindow(hood, A, I...)
end
"""
unsafe_readwindow(hood::Neighborhood, A::AbstractArray, I) => SArray
Get a single window square from an array, as an `SArray`, without checking bounds.
"""
@inline unsafe_readwindow(hood::Neighborhood, A::AbstractArray, I::CartesianIndex) =
unsafe_readwindow(hood, A, Tuple(I))
@inline unsafe_readwindow(hood::Neighborhood, A::AbstractArray, I::Int...) =
unsafe_readwindow(hood, A, I)
@generated function unsafe_readwindow(
::Neighborhood{R,N}, A::AbstractArray{T,N}, I::NTuple{N,Int}
) where {T,R,N}
R = 1
S = 2R+1
L = S^N
sze = ntuple(_ -> S, N)
vals = Expr(:tuple)
nh = CartesianIndices(ntuple(_ -> -R:R, N))
for i in 1:L
Iargs = map(Tuple(nh[i]), 1:N) do nhi, n
:(I[$n] + $nhi)
end
Iexp = Expr(:tuple, Iargs...)
exp = :(@inbounds A[$Iexp...])
push!(vals.args, exp)
end
sze_exp = Expr(:curly, :Tuple, sze...)
return :(SArray{$sze_exp,$T,$N,$L}($vals))
end
@generated function unsafe_readwindow(
::Neighborhood{R,N1}, A::AbstractArray{T,N2}, I::NTuple{N3,Int}
) where {T,R,N1,N2,N3}
throw(DimensionMismatch("neighborhood has $N1 dimensions while array has $N2 and index has $N3"))
end
# Reading windows without padding
# struct Padded{S,V}
# padval::V
# end
# Padded{S}(padval::V) where {S,V} = Padded{S,V}(padval)
# @generated function unsafe_readwindow(
# ::Neighborhood{R,N}, bounds::Padded{V}, ::AbstractArray{T,N}, I::NTuple{N,Int}
# ) where {T,R,N,V}
# R = 1
# S = 2R+1
# L = S^N
# sze = ntuple(_ -> S, N)
# vals = Expr(:tuple)
# for X in CartesianIndices(ntuple(_ -> -R:R, N))
# if X in CartesianIndices(V)
# # Generate indices for this position
# Iargs = map(Tuple(X), 1:N) do x, n
# :(I[$n] + $x)
# end
# Iexp = Expr(:tuple, Iargs...)
# push!(vals.args, :(@inbounds A[$Iexp...]))
# else
# push!(vals.args, :(bounds.padval))
# end
# end
# sze_exp = Expr(:curly, :Tuple, sze...)
# return :(SArray{$sze_exp,$T,$N,$L}($vals))
# end
"""
updatewindow(x, A::AbstractArray, I...) => Neighborhood
Set the window of a neighborhood to values from the array A around index `I`.
Bounds checks will reduce performance, aim to use `unsafe_setwindow` directly.
"""
@inline function updatewindow(x, A::AbstractArray, i, I...)
setwindow(x, readwindow(x, A, i, I...))
end
"""
unsafe_setwindow(x, A::AbstractArray, I...) => Neighborhood
Set the window of a neighborhood to values from the array A around index `I`.
No bounds checks occur, ensure that A has padding of at least the neighborhood radius.
"""
@inline function unsafe_updatewindow(h::Neighborhood, A::AbstractArray, i, I...)
setwindow(h, unsafe_readwindow(h, A, i, I...))
end
"""
broadcast_neighborhood(f, hood::Neighborhood, As...)
Simple neighborhood application, where `f` is passed
each neighborhood in `A`, returning a new array.
The result is smaller than `A` on all sides, by the neighborhood radius.
"""
function broadcast_neighborhood(f, hood::Neighborhood, sources...)
checksizes(sources...)
ax = unpad_axes(first(sources), hood)
sourceview = view(first(sources), ax...)
broadcast(sourceview, CartesianIndices(ax)) do _, I
applyneighborhood(f, sources, I)
end
end
"""
broadcast_neighborhood!(f, hood::Neighborhood{R}, dest, sources...)
Simple neighborhood broadcast where `f` is passed each neighborhood
of `src` (except padding), writing the result of `f` to `dest`.
`dest` must either be smaller than `src` by the neighborhood radius on all
sides, or be the same size, in which case it is assumed to also be padded.
"""
function broadcast_neighborhood!(f, hood::Neighborhood, dest, sources)
checksizes(sources...)
if axes(dest) === axes(src)
ax = unpad_axes(src, hood)
destview = view(dest, ax...)
broadcast!(destview, CartesianIndices(ax)) do I
applyneighborhood(f, sources, I)
end
else
broadcast!(dest, CartesianIndices(unpad_axes(src, hood))) do I
applyneighborhood(f, sources, I)
end
end
end
function checksizes(sources...)
map(sources) do s
size(s) === size(first(sources)) || throw(ArgumentError("Source array sizes must match"))
end
end
function applyneighborhood(f, sources, I)
hoods = map(sources) do s
unsafe_updatewindow(hood, s, I)
end
f(hoods...)
end
"""
pad_axes(A, hood::Neighborhood{R})
pad_axes(A, radius::Int)
Add padding to axes.
"""
pad_axes(A, hood::Neighborhood{R}) where R = pad_axes(A, R)
function pad_axes(A, radius::Int)
map(axes(A)) do axis
firstindex(axis) - radius:lastindex(axis) + radius
end
end
"""
unpad_axes(A, hood::Neighborhood{R})
unpad_axes(A, radius::Int)
Remove padding from axes.
"""
unpad_axes(A, hood::Neighborhood{R}) where R = unpad_axes(A, R)
function unpad_axes(A, radius::Int)
map(axes(A)) do axis
firstindex(axis) + radius:lastindex(axis) - radius
end
end
end # Module Neighborhoods
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 1575 | """
ArrayOutput <: Output
ArrayOutput(init; tspan::AbstractRange, [aux, mask, padval])
A simple output that stores each step of the simulation in a vector of arrays.
# Arguments
- `init`: initialisation `AbstractArrayArray` or `NamedTuple` of `AbstractArrayArray`.
# Keywords (passed to [`Extent`](@ref))
$EXTENT_KEYWORDS
An `Extent` object can be also passed to the `extent` keyword, and other keywords will be ignored.
"""
mutable struct ArrayOutput{T,F<:AbstractVector{T},E} <: Output{T,F}
frames::F
running::Bool
extent::E
end
function ArrayOutput(; frames, running, extent, kw...)
append!(frames, _zerogrids(init(extent), length(tspan(extent))-1))
ArrayOutput(frames, running, extent)
end
"""
ResultOutput <: Output
ResultOutput(init; tspan::AbstractRange, kw...)
A simple output that only stores the final result, not intermediate frames.
# Arguments
- `init`: initialisation `Array` or `NamedTuple` of `Array`
# Keywords (passed to [`Extent`](@ref))
$EXTENT_KEYWORDS
An `Extent` object can be also passed to the `extent` keyword, and other keywords will be ignored.
"""
mutable struct ResultOutput{T,F<:AbstractVector{T},E} <: Output{T,F}
frames::F
running::Bool
extent::E
end
ResultOutput(; frames, running, extent, kw...) = ResultOutput(frames, running, extent)
isstored(o::ResultOutput) = false
storeframe!(o::ResultOutput, data::AbstractSimData) = nothing
function finalise!(o::ResultOutput, data::AbstractSimData)
# Only store after the last frame
_storeframe!(o, eltype(o), data)
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 3108 | """
savegif(filename::String, o::Output; kw...)
Write the output array to a gif.
# Arguments
- `filename`: File path to save the gif file to.
- `output`: An [`Output`](@ref) object. Note that to make a gif, the output should stores
frames, and run with `store=true`, and `@assert DynamicGrids.istored(o)` should pass.
# Keywords
[`ImageConfig`](@ref) keywords:
$IMAGECONFIG_KEYWORDS
"""
function savegif(filename::String, o::Output, ruleset=Ruleset();
minval=minval(o), maxval=maxval(o),
scheme=ObjectScheme(), zerocolor=ZEROCOL, maskcolor=MASKCOL,
renderer=autorenderer(init(o); scheme, zerocolor, maskcolor),
font=autofont(), text=TextConfig(font=font), textconfig=text, kw...
)
im_o = NoDisplayImageOutput(o;
imageconfig=ImageConfig(init(o);
minval=minval, maxval=maxval, renderer=renderer, textconfig=textconfig
)
)
savegif(filename, im_o, ruleset; kw...)
end
function savegif(filename::String, o::ImageOutput, ruleset=Ruleset(); fps=fps(o), kw...)
length(o) == 1 && @warn "The output has length 1: the saved gif will be a single image"
data = SimData(o, ruleset)
imsize = size(first(grids(data)))
gif = Array{ARGB32}(undef, imsize..., length(o))
foreach(firstindex(o):lastindex(o)) do f
@set! data.currentframe = f
render!(view(gif, :, :, f), renderer(o), o, data, o[f])
end
FileIO.save(File{format"GIF"}(filename), gif; fps=fps, kw...)
return filename
end
"""
GifOutput <: ImageOutput
GifOutput(init; filename, tspan, kw...)
Output that stores the simulation as images and saves a Gif file on completion.
# Arguments:
- `init`: initialisation `AbstractArrayArray` or `NamedTuple` of `AbstractArrayArray`.
# Keywords
Storing the gif:
- `filename`: File path to save the gif file to.
$IMAGEOUTPUT_KEYWORDS
"""
mutable struct GifOutput{T,F<:AbstractVector{T},E,GC,IC,G,N} <: ImageOutput{T,F}
frames::F
running::Bool
extent::E
graphicconfig::GC
imageconfig::IC
gif::G
filename::N
end
function GifOutput(; frames, running, extent, graphicconfig, imageconfig, filename, kw...)
gif = _allocgif(imageconfig, extent)
GifOutput(frames, running, extent, graphicconfig, imageconfig, gif, filename)
end
# Getters
filename(o::GifOutput) = o.filename
gif(o::GifOutput) = o.gif
# Output/ImageOutput interface methods
maybesleep(output::GifOutput, f) = nothing
function showimage(image, o::GifOutput, data::AbstractSimData)
gif(o)[:, :, currentframe(data)] .= image
end
finalisegraphics(o::GifOutput, data::AbstractSimData) = savegif(o)
# The gif is already generated, just save it again if neccessary
savegif(o::GifOutput) = savegif(filename(o), o)
function savegif(filename::String, o::GifOutput, fps=fps(o); kw...)
FileIO.save(File{format"GIF"}(filename), gif(o); fps=fps, kw...)
end
# Preallocate the 3 dimensional gif array
_allocgif(i::ImageConfig, e::Extent) = _allocgif(renderer(i), i::ImageConfig, e::Extent)
function _allocgif(r::Renderer, i::ImageConfig, e::Extent)
zeros(ARGB32, imagesize(r, e)..., length(tspan(e)))
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 5447 |
const GRAPHICCONFIG_KEYWORDS = """
- `fps::Real`: Frames per second.
- `store::Bool`: Whether to store frames like `ArrayOutput` or to disgard
them after visualising. Very long simulation runs may fill available
memory when `store=true`.
"""
"""
GraphicConfig
GraphicConfig(; fps=25.0, store=false)
Config and variables for graphic outputs.
# Keywords
$GRAPHICCONFIG_KEYWORDS
"""
mutable struct GraphicConfig{FPS,TS}
fps::FPS
store::Bool
timestamp::TS
stampframe::Int
stoppedframe::Int
end
GraphicConfig(; fps=25.0, store=false, kw...) = GraphicConfig(fps, store, 0.0, 1, 1)
fps(gc::GraphicConfig) = gc.fps
store(gc::GraphicConfig) = gc.store
timestamp(gc::GraphicConfig) = gc.timestamp
stampframe(gc::GraphicConfig) = gc.stampframe
stoppedframe(gc::GraphicConfig) = gc.stoppedframe
setfps!(gc::GraphicConfig, x) = gc.fps = x
function settimestamp!(o::GraphicConfig, frame::Int)
o.timestamp = time()
o.stampframe = frame
end
setstoppedframe!(gc::GraphicConfig, frame::Int) = gc.stoppedframe = frame
const GRAPHICOUTPUT_KEYWORDS = """
## [`Extent`](@ref) keywords:
$EXTENT_KEYWORDS
An `Extent` object can be also passed to the `extent` keyword, and other keywords will be ignored.
## [`GraphicConfig`](@ref) keywords:
$GRAPHICCONFIG_KEYWORDS
A `GraphicConfig` object can be also passed to the `graphicconfig` keyword, and other keywords will be ignored.
"""
"""
GraphicOutput <: Output
Abstract supertype for [`Output`](@ref)s that display the simulation frames.
All `GraphicOutputs` must have a [`GraphicConfig`](@ref) object
and define a [`showframe`](@ref) method.
See [`REPLOutput`](@ref) for an example.
# User Arguments for all `GraphicOutput`:
- `init`: initialisation `AbstractArray` or `NamedTuple` of `AbstractArray`
# Minimum user keywords for all `GraphicOutput`:
$GRAPHICOUTPUT_KEYWORDS
## Internal keywords for constructors of objects extending `GraphicOutput`:
The default constructor will generate these objects and pass them to the inheriting
object constructor, which must accept the following keywords:
- `frames`: a `Vector` of simulation frames (`NamedTuple` or `Array`).
- `running`: A `Bool`.
- `extent` an [`Extent`](@ref) object.
- `graphicconfig` a [`GraphicConfig`](@ref)object.
Users can also pass in these entire objects if required.
"""
abstract type GraphicOutput{T,F} <: Output{T,F} end
# Generic GraphicOutput constructor. Converts an init array to vector of arrays.
function (::Type{T})(
init::Union{NamedTuple,AbstractArray};
extent=nothing, graphicconfig=nothing, store=nothing, kw...
) where T <: GraphicOutput
extent = extent isa Nothing ? Extent(; init=init, kw...) : extent
store = check_stored(extent, store)
graphicconfig = graphicconfig isa Nothing ? GraphicConfig(; store, kw...) : graphicconfig
T(; frames=[deepcopy(init)], running=false, extent, graphicconfig, store, kw...)
end
function check_stored(extent, store)
if ndims(extent) == 1 && !(store === true)
if store === false
@warn "Setting `store=false` may cause errors when visualising a 1-dimensional simulation"
else
store = true
end
else
store = store isa Nothing ? false : store
end
return store
end
graphicconfig(o::Output) = GraphicConfig()
graphicconfig(o::GraphicOutput) = o.graphicconfig
# Forward getters and setters to GraphicConfig object ####################################
fps(o::GraphicOutput) = fps(graphicconfig(o))
timestamp(o::GraphicOutput) = timestamp(graphicconfig(o))
stampframe(o::GraphicOutput) = stampframe(graphicconfig(o))
stoppedframe(o::GraphicOutput) = stoppedframe(graphicconfig(o))
isstored(o::GraphicOutput) = store(o)
store(o::GraphicOutput) = store(graphicconfig(o))
setfps!(o::GraphicOutput, x) = setfps!(graphicconfig(o), x)
settimestamp!(o::GraphicOutput, f) = settimestamp!(graphicconfig(o), f)
setstoppedframe!(o::GraphicOutput, f) = setstoppedframe!(graphicconfig(o), f)
# Delay output to maintain the frame rate
maybesleep(o::GraphicOutput, f) =
sleep(max(0.0, timestamp(o) + (f - stampframe(o))/fps(o) - time()))
isshowable(o::GraphicOutput, f) = true
# Store frames, and show them graphically ################################################
function storeframe!(o::GraphicOutput, data)
f = frameindex(o, data)
if f > length(o)
_pushgrid!(eltype(o), o)
end
if isstored(o)
_storeframe!(o, eltype(o), data)
end
if isshowable(o, currentframe(data))
showframe(o, data)
end
return nothing
end
# Add additional grids if they were not pre-allocated
_pushgrid!(::Type{<:NamedTuple}, o) = push!(o, map(grid -> similar(grid), o[1]))
_pushgrid!(::Type{<:AbstractArray}, o) = push!(o, similar(o[1]))
function initialise!(o::GraphicOutput, data)
initalisegraphics(o, data)
end
function finalise!(o::GraphicOutput, data)
_storeframe!(o, eltype(o), data)
finalisegraphics(o, data)
end
# Additional interface for GraphicOutput
showframe(o::GraphicOutput, data) = showframe(o, proc(data), data)
showframe(o::GraphicOutput, ::Processor, data) = showframe(map(gridview, grids(data)), o, data)
# Handle NamedTuple for outputs that only accept AbstractArray
showframe(frame::NamedTuple, o::GraphicOutput, data) = showframe(first(frame), o, data)
initalisegraphics(o::GraphicOutput, data) = nothing
finalisegraphics(o::GraphicOutput, data) = showframe(o, data)
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 6222 |
const IMAGECONFIG_KEYWORDS = """
- `minval`: Minimum value in the grid(s) to normalise for conversion to an RGB pixel.
A `Vector/Matrix` for multiple grids, matching the `layout` array.
Note: The default is `0`, and will not be updated automatically for the simulation.
- `maxval`: Maximum value in the grid(s) to normalise for conversion to an RGB pixel.
A `Vector/Matrix` for multiple grids, matching the `layout` array.
Note: The default is `1`, and will not be updated automatically for the simulation.
- `font`: `String` name of font to search for. A default will be guessed.
- `text`: `TextConfig()` or `nothing` for no text. Default is `TextConfig(; font=font)`.
$IMAGE_RENDERER_KEYWORDS
- `renderer`: [`Renderer`](@ref) like [`Image`](@ref) or [`Layout`](@ref). Will be detected
automatically, and use `scheme`, `zerocolor` and `maskcolor` keywords if available.
Can be a `Vector/Matrix` for multiple grids, matching the `layout` array.
"""
"""
ImageConfig
ImageConfig(init; kw...)
Common configuration component for all [`ImageOutput`](@ref).
# Arguments
- `init` output init object, used to generate other arguments automatically.
# Keywords
$IMAGECONFIG_KEYWORDS
"""
struct ImageConfig{IB,Min,Max,Bu,TC}
renderer::IB
minval::Min
maxval::Max
imagebuffer::Bu
textconfig::TC
end
function ImageConfig(init;
font=autofont(), text=TextConfig(; font=font), textconfig=text,
renderer=nothing, minval=0, maxval=1, tspan=nothing, kw...
)
# Generate a renderer automatically if it is not passed in
renderer = renderer isa Nothing ? autorenderer(init; kw...) : renderer
# Allocate an image buffer based on the renderer and init grids
imagebuffer = _allocimage(renderer, init, tspan)
ImageConfig(renderer, minval, maxval, imagebuffer, textconfig)
end
renderer(ic::ImageConfig) = ic.renderer
minval(ic::ImageConfig) = ic.minval
maxval(ic::ImageConfig) = ic.maxval
imagebuffer(ic::ImageConfig) = ic.imagebuffer
textconfig(ic::ImageConfig) = ic.textconfig
const IMAGEOUTPUT_KEYWORDS = """
$GRAPHICOUTPUT_KEYWORDS
## [`ImageConfig`](@ref) keywords:
$IMAGECONFIG_KEYWORDS
An `ImageConfig` object can be also passed to the `imageconfig` keyword, and other keywords will be ignored.
"""
"""
ImageOutput <: GraphicOutput
Abstract supertype for Graphic outputs that display the simulation frames as RGB images.
`ImageOutput`s must have [`Extent`](@ref), [`GraphicConfig`](@ref)
and [`ImageConfig`](@ref) components, and define a [`showimage`](@ref) method.
See [`GifOutput`](@ref) for an example.
Although the majority of the code is maintained here to enable sharing
and reuse, most `ImageOutput`s are not provided in DynamicGrids.jl to avoid
heavy dependencies on graphics libraries. See
[DynamicGridsGtk.jl](https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGridsGtk.jl)
and [DynamicGridsInteract.jl](https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGridsInteract.jl)
for implementations.
# User Arguments for all `GraphicOutput`:
- `init`: initialisation `AbstractArray` or `NamedTuple` of `AbstractArray`
# Minimum user keywords for all `ImageOutput`:
$IMAGEOUTPUT_KEYWORDS
## Internal keywords for constructors of objects extending `GraphicOutput`:
The default constructor will generate these objects and pass them to the inheriting
object constructor, which must accept the following keywords:
- `frames`: a `Vector` of simulation frames (`NamedTuple` or `Array`).
- `running`: A `Bool`.
- `extent` an [`Extent`](@ref) object.
- `graphicconfig` a [`GraphicConfig`](@ref)object.
- `imageconfig` a [`ImageConfig`](@ref)object.
Users can also pass in these entire objects if required.
"""
abstract type ImageOutput{T,F} <: GraphicOutput{T,F} end
# Generic `ImageOutput` constructor that construct an `ImageOutput` from another `Output`.
function (::Type{F})(o::T;
frames=frames(o), extent=extent(o), graphicconfig=graphicconfig(o),
imageconfig=imageconfig(o), textconfig=textconfig(o), kw...
) where F <: ImageOutput where T <: Output
F(;
frames=frames, running=false, extent=extent, graphicconfig=graphicconfig,
imageconfig=imageconfig, textconfig=textconfig, kw...
)
end
# Generic `ImageOutput` constructor. Converts an init `AbstractArray` or `NamedTuple`
# to a vector of `AbstractArray`s, uses `kw` to constructs required
# [`Extent`](@ref), [`GraphicConfig`](@ref) and [`ImageConfig`](@ref) objects unless
# they are specifically passed in using `extent`, `graphicconfig`, `imageconfig`.
# All other keyword arguments are passed to these constructors.
# Unused or mis-spelled keyword arguments are ignored.
function (::Type{T})(init::Union{NamedTuple,AbstractArray};
extent=nothing, graphicconfig=nothing, imageconfig=nothing, store=nothing, kw...
) where T <: ImageOutput
extent = extent isa Nothing ? Extent(; init=init, kw...) : extent
store = check_stored(extent, store)
graphicconfig = graphicconfig isa Nothing ? GraphicConfig(; store, kw...) : extent
imageconfig = imageconfig isa Nothing ? ImageConfig(init; kw...) : imageconfig
T(;
frames=[deepcopy(init)], running=false,
extent, graphicconfig, imageconfig, store, kw...
)
end
# Getters
imageconfig(o::ImageOutput) = o.imageconfig
# Other outputs get a constructed ImageConfig
imageconfig(o::Output) = ImageConfig(init(o))
# Methods forwarded to ImageConfig
renderer(o::Output) = renderer(imageconfig(o))
minval(o::Output) = minval(imageconfig(o))
maxval(o::Output) = maxval(imageconfig(o))
imagebuffer(o::Output) = imagebuffer(imageconfig(o))
textconfig(o::Output) = textconfig(imageconfig(o))
# GraphicOutput interface methods
showframe(o::ImageOutput, data) = showimage(render!(o, data), o, data)
showimage(image, o, data) = showimage(image, o)
# Headless image output. Useful for gifs and testing.
mutable struct NoDisplayImageOutput{T,F<:AbstractVector{T},E,GC,IC} <: ImageOutput{T,F}
frames::F
running::Bool
extent::E
graphicconfig::GC
imageconfig::IC
end
function NoDisplayImageOutput(;
frames, running, extent, graphicconfig, imageconfig, kw...
)
NoDisplayImageOutput(frames, running, extent, graphicconfig, imageconfig)
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 4261 | # Interface for output methods
"""
extent(o::Output) => Extent
[`Output`](@ref) interface method. Return and [`Extent`](@ref) object.
"""
function extent end
"""
isrunning(o::Output) => Bool
[`Output`](@ref) interface method.
Check if the output is running. Prevents multiple versions of `sim!`
running on the same output for asynchronous outputs.
"""
function isrunning end
"""
isasync(o::Output) => Bool
[`Output`](@ref) interface method.
Check if the output should run asynchonously. Default is `false`.
"""
function isasync end
"""
isastored(o::Output) => Bool
[`Output`](@ref) interface method.
Check if the output is storing each frame, or just the the current one. Default is `true`.
"""
function isstored end
"""
isshowable(o::Output, f::Int) => Bool
[`Output`](@ref) interface method.
Check if the output can be shown visually, where f is the frame number. Default is `false`.
"""
function isshowable end
"""
initialise!(o::Output)
[`Output`](@ref) interface method.
Initialise the output at the start of the simulation.
"""
function initialise! end
"""
finalise!(o::Output, data::AbstractSimData)
[`Output`](@ref) interface method.
Finalise the output at the end of the simulation.
"""
function finalise! end
"""
frameindex(o::Output, data::AbstractSimData)
[`Output`](@ref) interface method.
Get the index of the current frame in the output.
Every frame has an index of 1 if the simulation isn't stored.
"""
function frameindex end
"""
showframe(o::Output, data::AbstractSimData)
showframe(frame::NamedTuple, o::Output, data::AbstractSimData)
showframe(frame::AbstractArray, o::Output, data::AbstractSimData)
[`GraphicOutput`](@ref) interface method.
Display the grid/s somehow in the output, if it can do that.
"""
function showframe end
"""
storeframe!(o::Output, data::AbstractSimData)
Store the current simulaiton frame in the output.
"""
function storeframe! end
"""
graphicconfig(output::GraphicOutput) => GraphicConfig
[`GraphicOutput`](@ref) interface method. Return an [`GraphicConfig`](@ref) object.
"""
function graphicconfig end
"""
fps(o::Output) => Real
[`GraphicOutput`](@ref) interface method.
Get the frames per second the output will run at. The default
is `nothing` - the simulation runs at full speed.
"""
function fps end
"""
setfps!(o::Output, x)
[`GraphicOutput`](@ref) interface method.
Set the frames per second the output will run at.
"""
function setfps! end
"""
initalisegraphics(o::Output, data::AbstractSimData)
[`GraphicOutput`](@ref) interface method.
Initialise the output graphics at the start of the simulation, if it has graphics.
"""
function initialisegraphics end
"""
finalisegraphics(o::Output, data::AbstractSimData)
[`GraphicOutput`](@ref) interface method.
Finalise the output graphics at the end of the simulation, if it has graphics.
"""
function finalisegraphics end
"""
imageconfig(output::ImageOutput) => ImageConfig
`ImageOutpu` interface method. Return an [`ImageConfig`](@ref) object.
"""
function imageconfig end
"""
showimage(image::AbstractArray, o::ImageOutput)
showimage(image::AbstractArray, o::ImageOutput, data::AbstractSimData)
[`ImageOutput`](@ref) interface method.
Display an image generated from the grid, a required method for all `ImageOutput`.
"""
function showimage end
"""
render!(o::ImageOutput, data::AbstractSimData)
render!(imbuf, renderer::Renderer, o::ImageOutput, data::AbstractSimData, grids)
Convert a grid or `NamedRuple` of grids to an `ARGB32` image, using an
[`Renderer`](@ref).
Rendered pixels are written to the image buffer matrix.
"""
function render! end
"""
to_rgb(val) => ARGB32
to_rgb(scheme, val) => ARGB32
`ImageOutput` interface method.
Display an image generated from the grid, a required method for all [`ImageOutput`](@ref).
Custom grid object will need to add methods for converting the object to a color,
```julia
to_rgb(::ObjectScheme, obj::CustomObj) = ...`
```
For use with other colorschemes, a method that calls `get` with a `Real` value
obtained from the object will be required:
```julia
to_rgb(scheme, obj::CustomObj) = ARGB32(get(scheme, real_from_obj(obj)))
```
"""
function to_rgb end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 4927 | """
Output
Abstract supertype for simulation outputs.
Outputs are store or display simulation results, usually
as a vector of grids, one for each timestep - but they may also
sum, combine or otherwise manipulate the simulation grids to improve
performance, reduce memory overheads or similar.
Simulation outputs are decoupled from simulation behaviour,
and in many cases can be used interchangeably.
"""
abstract type Output{T,A} <: AbstractDimArray{T,1,Tuple{Ti},A} end
# Generic ImageOutput constructor. Converts an init array to vector of arrays.
function (::Type{T})(
init::Union{NamedTuple,AbstractArray}; extent=nothing, kw...
) where T <: Output
extent = extent isa Nothing ? Extent(; init=init, kw...) : extent
T(; frames=[deepcopy(init)], running=false, extent=extent, kw...)
end
# Forward base methods to the frames array
Base.parent(o::Output) = frames(o)
Base.length(o::Output) = length(parent(o))
Base.size(o::Output) = size(parent(o))
Base.firstindex(o::Output) = firstindex(parent(o))
Base.lastindex(o::Output) = lastindex(parent(o))
Base.push!(o::Output, x) = push!(parent(o), x)
Base.step(o::Output) = step(tspan(o))
# DimensionalData interface ######################################################
# This allows indexing the output using values from tspan
function DimensionalData.dims(o::Output)
ts = tspan(o)
val = isstored(o) ? ts : ts[end]:step(ts):ts[end]
(Ti(Sampled(val; order=ForwardOrdered(), span=Regular(step(ts)), sampling=Intervals(Start()))),)
end
DimensionalData.refdims(o::Output) = ()
DimensionalData.name(o::Output) = Symbol("")
DimensionalData.metadata(o::Output) = NoMetadata()
# Output bebuild just returns a DimArray
DimensionalData.rebuild(o::Output, data, dims::Tuple, refdims, name, metadata) =
DimArray(data, dims, refdims, name, metadata)
# Required getters and setters for all outputs ###################################
frames(o::Output) = o.frames
isrunning(o::Output) = o.running
extent(o::Output) = o.extent
init(o::Output) = init(extent(o))
mask(o::Output) = mask(extent(o))
aux(o::Output, key...) = aux(extent(o), key...)
tspan(o::Output) = tspan(extent(o))
timestep(o::Output) = step(tspan(o))
setrunning!(o::Output, val) = o.running = val
settspan!(o::Output, tspan) = settspan!(extent(o), tspan)
# Default values for optional getters and setters ################################
ruleset(o::Output) =
throw(ArgumentError("No ruleset on the output. Pass one to `sim!` as the second argument"))
fps(o::Output) = nothing
stoppedframe(o::Output) = lastindex(o)
setfps!(o::Output, x) = nothing
settimestamp!(o::Output, f) = nothing
setstoppedframe!(o::Output, f) = nothing
isasync(o::Output) = false
isstored(o::Output) = true
isshowable(o::Output, frame) = false
initialise!(o::Output, data) = nothing
finalise!(o::Output, data) = nothing
initialisegraphics(o::Output, data) = nothing
finalisegraphics(o::Output, data) = nothing
maybesleep(o::Output, frame) = nothing
showframe(o::Output, data) = nothing
frameindex(o::Output, data::AbstractSimData) = frameindex(o, currentframe(data))
frameindex(o::Output, f::Int) = isstored(o) ? f : oneunit(f)
# Storing grid values to outputs during the simulation ###################################
function storeframe!(output::Output, data)
# Make sure the frame exists in the output
checkbounds(output, frameindex(output, data))
# copy to it
_storeframe!(output, eltype(output), data)
end
# copy one or multiple frames from grid/s to the Output
function _storeframe!(output::Output, ::Type{<:AbstractArray}, data)
grid = first(grids(data))
_copyto_output!(output[frameindex(output, data)], grid, proc(data))
end
function _storeframe!(output::Output, ::Type{<:NamedTuple}, data)
map(values(grids(data)), keys(data)) do grid, key
_copyto_output!(output[frameindex(output, data)][key], grid, proc(data))
end
end
# Copy cells from grid to output
function _copyto_output!(outgrid, grid::GridData, proc)
copyto!(outgrid, CartesianIndices(outgrid), source(grid), CartesianIndices(outgrid))
end
# Copy cells from grid to output using multiple threads
function _copyto_output!(outgrid, grid::GridData, proc::ThreadedCPU)
Threads.@threads for j in axes(outgrid, 2)
for i in axes(outgrid, 1)
@inbounds outgrid[i, j] = grid[i, j]
end
end
end
# Grid initialisation ###################################################################
# Grids are preallocated and reused.
init_output_grids!(o::Output, init) = init_output_grids!(o[1], o::Output, init)
# Array grids are copied
function init_output_grids!(grid::AbstractArray, o::Output, init::AbstractArray)
copyto!(grid, init)
return o
end
# All arrays are copied if both are named tuples
function init_output_grids!(grids::NamedTuple, o::Output, inits::NamedTuple)
map(grids, inits) do grid, init
copyto!(grid, init)
end
return o
end
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.21.3 | a99984c15928d6579f670c53077e0f937b378e8a | code | 13262 | const MASKCOL = ARGB32(0.5)
const ZEROCOL = ARGB32(0.3)
"""
Renderer
Abstract supertype for objects that convert a frame of the simulation into an `ARGB32`
image for display. Frames may be a single grid or a `NamedTuple` of multiple grids.
"""
abstract type Renderer end
imagesize(r::Renderer, e::Extent) = imagesize(r, init(e), tspan(e))
imagesize(r::Renderer, init::NamedTuple, tspan) = imagesize(r, first(init), tspan)
imagesize(::Renderer, init::AbstractArray{<:Any,1}, tspan) = (length(tspan), size(init)...)
imagesize(::Renderer, init::AbstractArray, tspan) = size(init)
# 1D : timespan y axis gets filled during the simulation
function _allocimage(r::Renderer, init, tspan)
fill(ARGB32(0), imagesize(r, init, tspan)...)
end
# render!
# Converts grid/s to an image for viewing.
function render!(o::Output, data::AbstractSimData)
render!(o, data, grids(data))
end
function render!(o::Output, data::AbstractSimData, grids)
render!(imagebuffer(o), renderer(o), o, data, grids)
end
# Single-grid renderers ###############################################################
"""
SingleGridRenderer <: Renderer
Abstract supertype for [`Renderer`](@ref)s that convert a single grid
into an image array.
The first grid will be displayed if a `SingleGridRenderer` is
used with a `NamedTuple` of grids.
"""
abstract type SingleGridRenderer <: Renderer end
function render!(
imagebuffer, ig::SingleGridRenderer, o::Output, data::AbstractSimData,
grids::NamedTuple;
name=string(first(keys(grids))), time=currenttime(data)
)
render!(imagebuffer, ig, o, data, first(grids); name=name, time=time)
end
function render!(
imagebuffer, ig::SingleGridRenderer, o::Output, data::AbstractSimData,
grids::NamedTuple{(DEFAULT_KEY,)};
name=nothing, time=currenttime(data)
)
render!(imagebuffer, ig, o, data, first(grids); name=name, time=time)
end
function render!(
imagebuffer, ig::SingleGridRenderer, o::Output,
data::AbstractSimData{S}, grid::AbstractArray{<:Any,2};
name=nothing, time=currenttime(data), accessor=nothing,
minval=minval(o), maxval=maxval(o),
) where S<:Tuple{Y,X} where {Y,X}
for j in 1:X, i in 1:Y
accessor = accessor isa Nothing ? DynamicGrids.accessor(ig) : accessor
@inbounds grid_obj = grid[i, j]
val = _access_grid_object(accessor, grid_obj)
pixel = to_rgb(cell_to_pixel(ig, mask(o), minval, maxval, data, val, (i, j)))
@inbounds imagebuffer[i, j] = pixel
end
_rendertext!(imagebuffer, textconfig(o), name, time)
return imagebuffer
end
function render!(
imagebuffer, ig::SingleGridRenderer, o::GraphicOutput,
data::AbstractSimData{S}, grid::AbstractArray{<:Any,1};
name=nothing, time=currenttime(data), accessor=nothing,
minval=minval(o), maxval=maxval(o),
) where S<:Tuple{L} where {L}
f = currentframe(data)
for i in 1:L
accessor = accessor isa Nothing ? DynamicGrids.accessor(ig) : accessor
@inbounds grid_obj = grid[i]
val = _access_grid_object(accessor, grid_obj)
pixel = to_rgb(cell_to_pixel(ig, mask(o), minval, maxval, data, val, (i,)))
# Image rows are simulation frames
@inbounds imagebuffer[f, i] = pixel
end
_rendertext!(imagebuffer, textconfig(o), name, time)
return imagebuffer
end
const IMAGE_RENDERER_KEYWORDS = """
- `scheme`: a ColorSchemes.jl colorscheme, [`ObjectScheme`](@ref) or object that defines
`Base.get(obj, val)` and returns a `Color` or a value that can be converted to `Color`
using `ARGB32(val)`.
- `zerocolor`: a `Col` to use when values are zero, or `nothing` to ignore.
- `maskcolor`: a `Color` to use when cells are masked, or `nothing` to ignore.
"""
"""
Image <: SingleGridRenderer
Image(f=identity; scheme=ObjectScheme(), zerocolor=nothing, maskcolor=nothing)
Converts output grids to a colorsheme.
# Arguments
- `f`: a function to convert value from the grid to `Real`
oran `RGB`. `Real` will be scaled by minval/maxval and be colored by the `scheme`.
`RGB` is used directly in the output. This is useful for grids of complex objects,
but not necessary for numbers. The default is `identity`.
# Keywords
$IMAGE_RENDERER_KEYWORDS
"""
struct Image{A,S,Z,M} <: SingleGridRenderer
accessor::A
scheme::S
zerocolor::Z
maskcolor::M
end
Image(accesor::Union{Function,Int}, scheme, zerocolor=ZEROCOL) = Image(scheme, zerocolor, MASKCOL)
Image(scheme, zerocolor=ZEROCOL, maskcolor=MASKCOL) = Image(identity, scheme, zerocolor, MASKCOL)
Image(accessor::Union{Function,Int}; kw...) = Image(; accessor, kw...)
Image(; accessor::Union{Function,Int}=identity, scheme=ObjectScheme(), zerocolor=ZEROCOL, maskcolor=MASKCOL, kw...) =
Image(accessor, scheme, zerocolor, maskcolor)
accessor(p::Image) = p.accessor
scheme(p::Image) = p.scheme
zerocolor(p::Image) = p.zerocolor
maskcolor(p::Image) = p.maskcolor
# Show colorscheme in Atom etc
Base.show(io::IO, m::MIME"image/svg+xml", p::Image) = show(io, m, scheme(p))
# cell_to_pixel!
# Convert a single sell to an ARGB pixel
@inline function cell_to_pixel(ig::Image, mask, minval, maxval, data::AbstractSimData, val, I)
if !(maskcolor(ig) isa Nothing) && ismasked(mask, I...)
to_rgb(maskcolor(ig))
else
normval = normalise(val, minval, maxval)
if !(zerocolor(ig) isa Nothing) && normval == zero(typeof(normval))
to_rgb(zerocolor(ig))
elseif normval isa Number && isnan(normval)
zerocolor(ig) isa Nothing ? to_rgb(scheme(ig), 0) : to_rgb(zerocolor(ig))
else
to_rgb(scheme(ig), normval)
end
end
end
# Multi-grid renderers ###############################################################
"""
MultiGridRenderer <: Renderer
Abstract type for `Renderer`s that convert a frame containing multiple
grids into a single image.
"""
abstract type MultiGridRenderer <: Renderer end
"""
Layout <: MultiGridRenderer
Layout(layout::Array, renderer::Matrix)
Layout allows displaying multiple grids in a block layout, by specifying a
layout matrix and a list of [`Image`](@ref)s to be run for each.
# Arguments
- `layout`: A `Vector` or `Matrix` containing the keys or numbers of grids in the
locations to display them. `nothing`, `missing` or `0` values will be skipped.
- `renderers`: `Vector/Matrix` of [`Image`](@ref), matching the `layout`.
Can be `nothing` or any other value for grids not in layout.
"""
Base.@kwdef struct Layout{L<:Union{AbstractVector,AbstractMatrix},R} <: MultiGridRenderer
layout::L
renderers::R
Layout(layouts::L, renderers::R) where {L,R} = begin
renderers1 = map(_asrenderer, renderers)
new{L,typeof(renderers1)}(layouts, renderers1)
end
end
layout(l::Layout) = l.layout
renderers(l::Layout) = l.renderers
imagesize(l::Layout, init::NamedTuple, tspan) = imagesize(l, first(init), tspan)
function imagesize(l::Layout, init::AbstractArray, tspan)
_imagesize(size(init), size(l.layout), tspan)
end
# 1D
_imagesize(gsize::NTuple{1}, lsize::NTuple{1}, tspan) = length(tspan), gsize .* lsize
# 2D
_imagesize(gsize::NTuple{2}, lsize::NTuple{2}, tspan) = gsize .* lsize
_imagesize(gsize::NTuple{2}, lsize::NTuple{1}, tspan) = gsize .* (first(lsize), 1)
_asrenderer(r::Renderer) = r
_asrenderer(x) = Image(x)
function render!(
imagebuffer, l::Layout, o::Output, data::AbstractSimData, grids::NamedTuple
)
npanes = length(layout(l))
minv, maxv = minval(o), maxval(o)
if !(minv isa Union{Number,Nothing})
length(minv) == npanes || _wronglengtherror(minval, npanes, length(minv))
end
if !(maxv isa Union{Number,Nothing})
length(maxv) == npanes || _wronglengtherror(maxval, npanes, length(maxv))
end
grid_ids = map(_grid_ids, layout(l))
grid_accessors = map(_grid_accessor, layout(l))
# Loop over the layout matrix
for I in CartesianIndices(grid_ids)
grid_id = grid_ids[I]
# Accept symbol keys and numbers, skip missing/nothing/0
(ismissing(grid_id) || grid_id === nothing || grid_id == 0) && continue
n = if grid_id isa Symbol
found = findfirst(k -> k === grid_id, keys(grids))
found === nothing && _grididnotinkeyserror(grid_id, grids)
found
else
grid_id
end
Itup = length(Tuple(I)) == 1 ? (Tuple(I)..., 1) : Tuple(I)
im_I = map(Itup, gridsize(data)) do l, gs
(l - 1) * gs + 1:l * gs
end
lin = LinearIndices(grid_ids)[I]
# Run image renderers for section
render!(
view(imagebuffer, im_I...), renderers(l)[lin], o, data, grids[n];
name=string(keys(grids)[n]), time=nothing,
minval=_get(minv, lin), maxval=_get(maxv, lin),
accessor=grid_accessors[I],
)
end
_rendertime!(imagebuffer, textconfig(o), currenttime(data))
return imagebuffer
end
_get(::Nothing, I) = nothing
_get(vals::Union{AbstractArray,Tuple}, I) = vals[I]
_get(x, I) = x
# Get the id of each grid in the layout
_grid_ids(id::Symbol) = id
_grid_ids(id::Integer) = id
_grid_ids(::Nothing) = nothing
_grid_ids(::Missing) = missing
_grid_ids(id::Pair{Symbol}) = first(id)
_grid_ids(id) = throw(ArgumentError("Layout id $id is not a valid grid name. Use an `Int`, `Symbol`, `Pair{Symbol,<:Any}` or `nothing`"))
# Get the grid accessor function/value if there is one
_grid_accessor(id::Pair) = last(id)
_grid_accessor(id) = nothing
# Access a grid object with a function or index, or use it as-is
_access_grid_object(::Nothing, obj) = obj
_access_grid_object(f::Function, obj) = f(obj)
_access_grid_object(i::Int, obj) = obj[i]
@noinline _grididnotinkeyserror(grid_id, grids) =
throw(ArgumentError("$grid_id is not in $(keys(grids))"))
@noinline _wronglengtherror(f, npanes, len) =
throw(ArgumentError("Number of layout panes ($npanes) and length of $f ($len) must be the same"))
# Automatically choose an image renderer ############################################################
autorenderer(init; scheme=ObjectScheme(), zerocolor=ZEROCOL, maskcolor=MASKCOL, kw...) =
_autorenderer(init, scheme, zerocolor, maskcolor; kw...)
# Single grid render
_autorenderer(init, scheme, zerocolor, maskcolor; kw...) = _asrenderer(scheme, zerocolor, maskcolor)
# Multi-grid renders
function _autorenderer(init::NamedTuple, scheme, zerocolor, maskcolor;
# If no layout argument was passed in, generate the layout from the init grids
layout=_autolayout(init),
# If no renders argument was passed in, generate them from the layout
renderers=_asrenderer.(layout, _iterable(scheme), _iterable(zerocolor), _iterable(maskcolor)),
kw...
)
Layout(layout, renderers)
end
# Maybe wrap in a tuple for broadcasting
_iterable(obj::AbstractArray) = obj
_iterable(obj::Tuple) = obj
_iterable(obj) = (obj,)
# _asrenderer
# Use a renderer as-is or convert a colorscheme to a renderer
_asrenderer(renderer::Renderer, zerocolor, maskcolor) = renderer
_asrenderer(scheme, zerocolor, maskcolor) = Image(scheme, zerocolor, maskcolor)
_asrenderer(layout, renderer, zerocolor, maskcolor) = _asrenderer(renderer, zerocolor, maskcolor)
# _autolayout
# Generate a layout from the provided grids and their contents
function _autolayout(init)
keys = _autokeys(init)
len = length(keys)
rows = len ÷ 4 + 1
cols = (len - 1) ÷ rows + 1
layout = Array{Any}(fill(nothing, rows, cols))
for i in eachindex(keys)
layout[i] = keys[i]
end
return layout
end
# _autokeys
# Generate a list of keys for layout grids.
# These may simply be the NamedTuple key or Pairs
# of the key name and index value, if the grid contains
# objects like FieldVector or StaticArray
function _autokeys(init)
foldl(pairs(init); init=()) do acc, (key, val)
keys = if eltype(val) <: AbstractArray
cellcontents = first(val)
map(i -> key => i, 1:length(cellcontents))
else
(key,)
end
(acc..., keys...)
end
end
# Colour conversion tools ############################################333
# Set a value to be between zero and one, before converting to Color.
# min and max of `nothing` are assumed to be 0 and 1.
normalise(x::X, minv, maxv) where X = max(min((x - minv) / (maxv - minv), oneunit(X)), zero(X))
normalise(x::X, minv, maxv::Nothing) where X = max((x - minv) / (oneunit(X) - minv), zero(X))
normalise(x::X, minv::Nothing, maxv) where X = min(x / maxv, oneunit(X), oneunit(X))
normalise(x, minv::Nothing, maxv::Nothing) = x
normalise(x; min=Nothing, max=Nothing) = normalise(x, min, max)
# Rescale a value between 0 and 1 to be between `min` and `max`.
# This can be used to shrink the range of a colorsheme that is displayed.
# min and max of `nothing` are assumed to be 0 and 1.
scale(x, min, max) = x * (max - min) + min
scale(x, ::Nothing, max) = x * max
scale(x, min, ::Nothing) = x * (oneunit(typeof(min)) - min) + min
scale(x, ::Nothing, ::Nothing) = x
to_rgb(vals::Tuple) = ARGB32(vals...)
to_rgb(val::Real) = ARGB32(RGB(val))
to_rgb(val::Color) = ARGB32(val)
to_rgb(val::ARGB32) = val
# Handle external colorshemes, such as from ColorSchemes.jl
to_rgb(scheme, val::Real) = to_rgb(get(scheme, val))
| DynamicGrids | https://github.com/cesaraustralia/DynamicGrids.jl.git |