license: other
license_name: seallms
inference: false
language:
- en
- vi
- id
- th
- zh

SeaLLMs - Large Language Models for Southeast Asia
We introduce SeaLLMs - a family of language models optimized for Southeast Asian (SEA) languages. The SeaLLM-base models (to be released) were pre-trained from Llama-2, on a tailored publicly-available dataset, which comprises mainly Vietnamese 🇻🇳, Indonesian 🇮🇩 and Thai 🇹🇭 texts, along with those in English 🇬🇧 and Chinese 🇨🇳. The pre-training stage involves multiple stages with dynamic data control to preserve the original knowledge base of Llama-2 while gaining new abilities in SEA languages.
The SeaLLM-chat model underwent supervised finetuning (SFT) on a mix of public instruction data (e.g. OpenORCA) and a small number of queries used by SEA language native speakers in natural settings, which adapt to the local cultural norms, customs, styles and laws in these areas, as well as other SFT enhancement techniques (to be revealed later).
Our customized SFT process helps enhance our models' ability to understand, respond, and serve communities whose languages are often neglected by previous English-dominant LLMs, while outperforming existing polyglot LLMs, like BLOOM or PolyLM.
Our first released SeaLLM supports Vietnamese 🇻🇳, Indonesian 🇮🇩, and Thai 🇹🇭. Future versions endeavor to cover all languages spoken in Southeast Asia.
- DEMO: SeaLLMs/SeaLLM-Chat-13b
- Model weights: To be released.
- Technical report: To be released.
Terms of Use: By using our released weights, codes, and demos, you agree to and comply with the following terms and conditions:
- Follow LLama-2 License and Terms of Use.
- Strictly comply with the local regulations from where you operate, and do not attempt to generate or elicit content that is locally or internationally illegal and inappropriate from our models.
Disclaimer: We must note that even though the weights, codes, and demos are released in an open manner, similar to other pre-trained language models, and despite our best efforts in red teaming and safety finetuning and enforcement, our models come with potential risks. These risks are influenced by various complex factors, including but not limited to over-diversified, inaccurate, misleading or potentially harmful generation. Developers and stakeholders should perform their own red teaming and provide related security measures before deployment, and they must abide by and comply with local governance and regulations. In no event shall the authors be held liable for any claim, damages, or other liability arising from the use of the released weights, codes, or demos.
The logo was generated by DALL-E 3.
The following sections summarize the Pre-training, Supervised-Finetuning (SFT) and performance evaluations.
Pre-training
Vocabulary Expansion
Like many English/Latin-dominant LLMs, Llama-2's BPE tokenizer breaks non-European and non-Latin linguistic texts into unsustainably long byte-level sequences that cover much shorter semantic meanings, leading to degraded performance. For instance, it takes 4.3x more tokens to encode the same sentence in Thai compared to that in English. This leads to the models failing to perform summarization and comprehension tasks without exceeding the context length.
Our goal for vocabulary expansion is threefold: (1) the number of newly-added tokens must be minimal and only cover the new languages, (2) the tokens should bring the compression ratios of new languages close to that of English, and (3) minimize the disruption of existing European tokens to preserve Llama-2 knowledge. In the end, we obtain ~11K new tokens for Vi, Id, Th, and Zh to augment the original 32000-token vocabulary. Details of our expansion technique will be revealed in our upcoming technical report.
As seen in the table below, our new vocabulary reduces the compression ratio from 4.29 to 1.57 for Thai - meaning it can now encode 2.7x longer Thai text given the same context length. Meanwhile, English is only compressed by 0.3%, thus preserving its integrity.
| Language | ChatGPT's ratio | Llama's ratio | Our ratio | # New tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vi | 4.41 | 2.91 | 1.2488 | 2304 |
| Zh | 2.80 | 1.99 | 1.1806 | 3456 |
| Th | 9.09 | 4.29 | 1.5739 | 1536 |
| Id | 2.00 | 1.76 | 1.1408 | 3840 |
| En | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.9976 |
Pre-training Data
The pre-training dataset of SeaLLMs is formed by the documents from diverse public sources, including web texts (e.g., Common Crawl), news documents (e.g., CC-News), academic articles and the texts with expert knowledge (e.g., wikipedia). We firstly employ FastText language indentifier to filter out the documents that do not belong to Thai, Vietnamese or Indonesian. To further remove harmful or undesirable content, we develop a pipeline with various data cleaning and filtering modules to preprocess the collected data. Meanwhile, to maintain the English performance of SeaLLMs, we also introduce a set of high-quality English texts sampled from RedPajama-Data into pre-training.
Pre-training Strategies
We conduct pre-training in 4 different stages. Each stage serves a different specific objective and involves dynamic control of (unsupervised and supervised) data mixture, as well as data specification and categorization. We also employ novel sequence construction and masking techniques during these stages. More details are to be provided in the technical report.
As our goal is for Llama-2 to learn new languages with the least number of tokens and computing resources, we control an appropriate data mix of new (Vi, Id & Th) and old (En, Zh) languages so that the new vocabulary and knowledge are trained quickly, while relatively maintaining the performance of the original Llama-2 model and establishing a knowledge bridge between new and existing languages.
We pre-train our SeaLLM-base in ~4 weeks on 32gpus, clocking ~150B tokens. We use Flash-attention-V2 as well as fusing many operations to achieve greater training throughput.
Supervised Finetuning (SFT)
SFT Data
Our supervised finetuning (SFT) data consists of many categories. The largest of them are public and open-source, such as OpenORCA and Platypus. As the aforementioned are monolingual, we employ several established or novel automatic techniques to gather more instruction data for SEA languages.
Even more noteworthy is that we engaged native speakers to collect a small number of queries used by SEA-language native speakers in natural settings, which helps in adaptation to the local cultural customs, norms, and laws. We also collect country-relevant safety data that cover many culturally and legally sensitive topics in each of these SEA countries - such data tend to be ignored, or may even appear in conflict with Western safety data. Therefore, we believe that our models are more local-friendly and abide by local rules to a higher degree.
SFT Strategies
We conduct SFT with a relatively balanced mix of SFT data from different categories. We make use of the system prompt during training, as we found it helps induce a prior which conditions the model to a behavioral distribution that focuses on safety and usefulness. More details will be provided in the technical report.
Evaluation
Peer Comparison
One of the most reliable ways to compare chatbot models is peer comparison. With the help of native speakers, we built an instruction test set that focuses on various aspects expected in a user-facing chatbot, namely: (1) NLP tasks (e.g. translation & comprehension), (2) Reasoning, (3) Instruction-following and (4) Natural and Informal questions. The test set also covers all languages that we are concerned with.
We use GPT-4 as an evaluator to rate the comparison between our models versus ChatGPT-3.5 and other baselines.
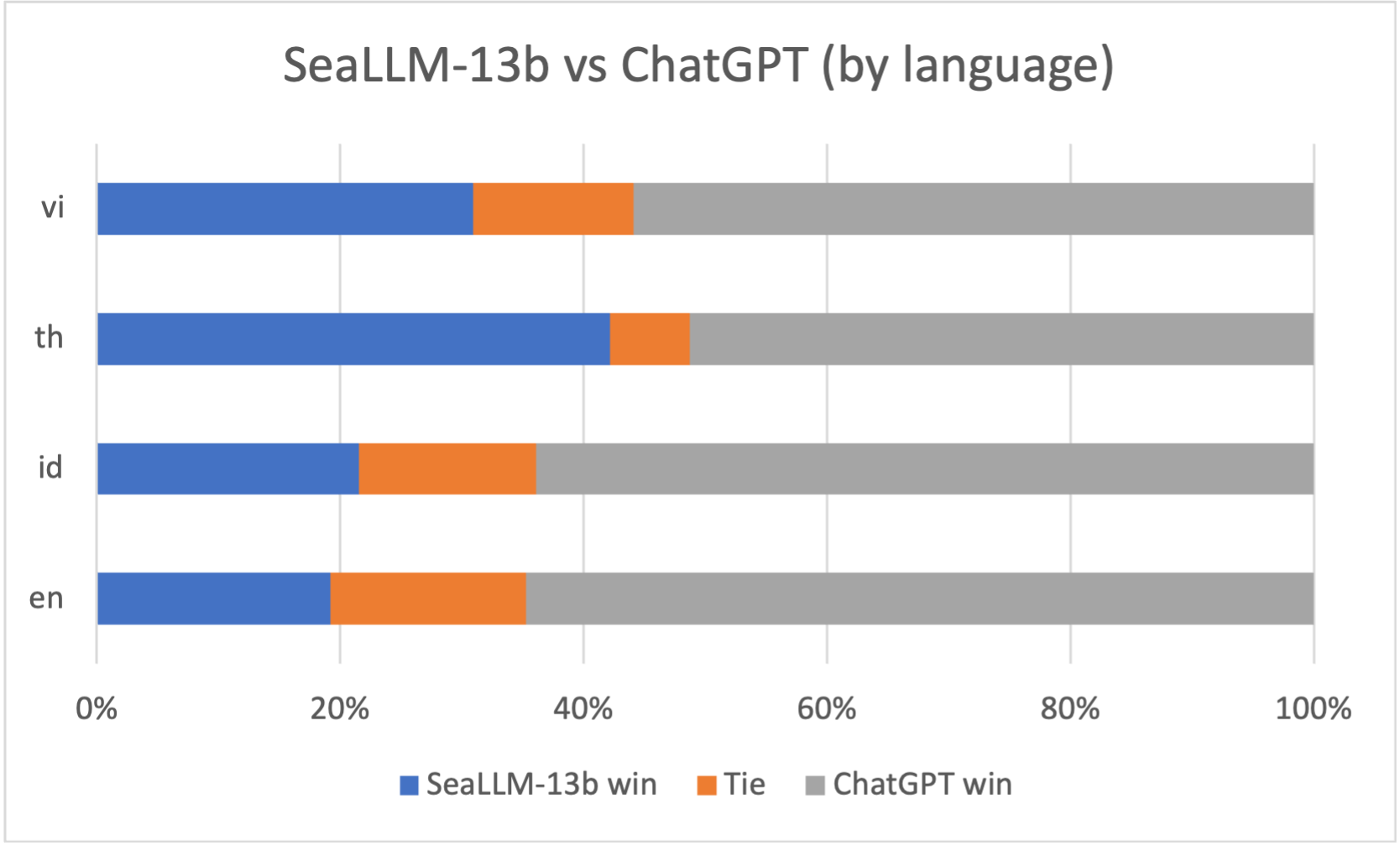
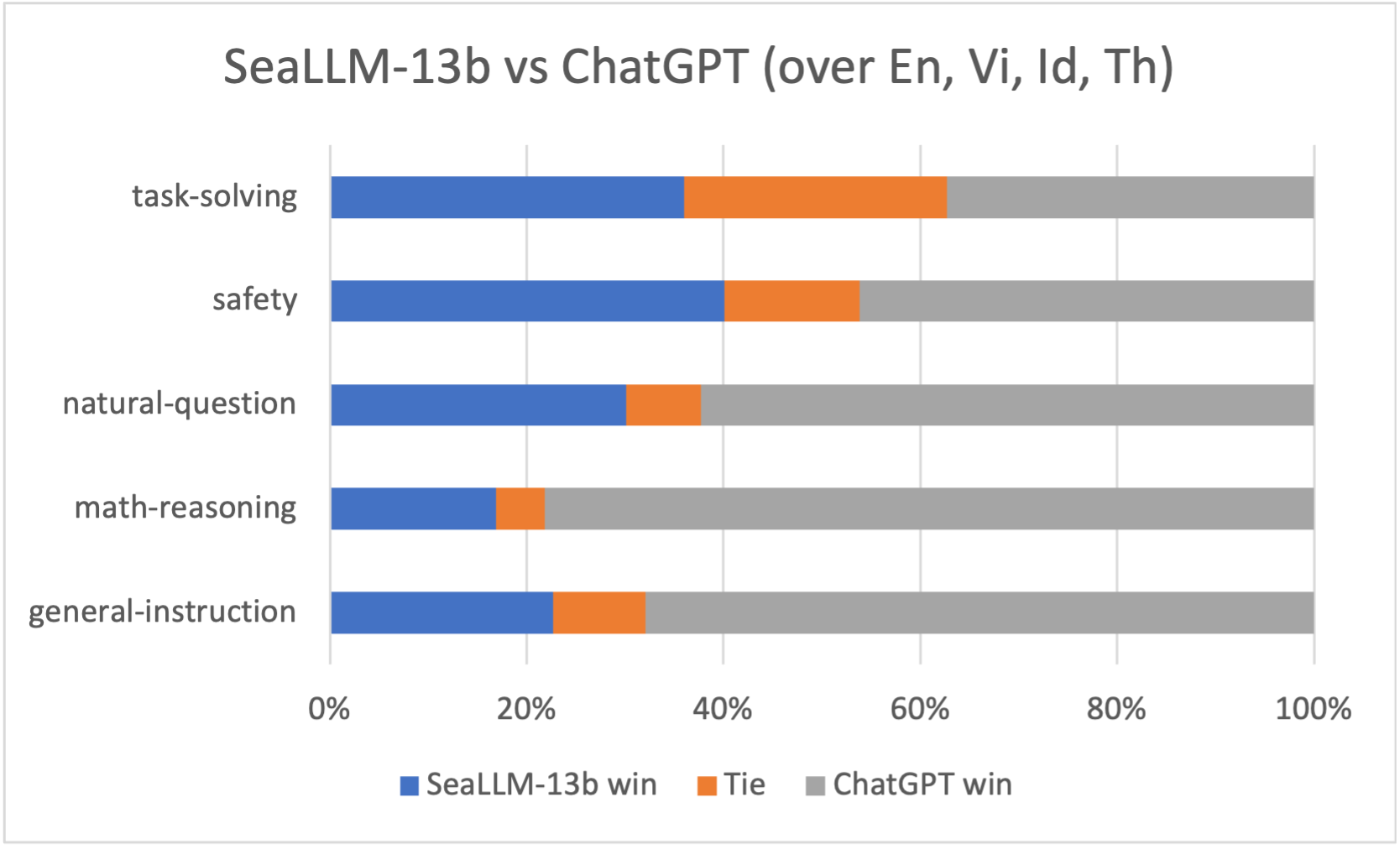
M3Exam - World Knowledge in Regional Languages
M3Exam is a collection of real-life and native official human exam question benchmarks. This benchmark covers questions from multiple countries in the SEA region, which require strong multilingual proficiency and cultural knowledge across various critical educational periods, from primary- to high-school levels of difficulty.
As shown in the table, our SeaLLM model outperforms most 13B baselines and reaches closer to ChatGPT's performance. Notably, for Thai - a seemingly low-resource language, our model is just 1% behind ChatGPT despite the large size difference.
| M3Exam / 3-shot (Acc) | En | Zh | Vi | Id | Th |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random | 25.00 | 25.00 | 25.00 | 23.00 | 23.00 |
| ChatGPT | 75.46 | 60.20 | 58.64 | 49.27 | 37.41 |
| Llama-2-13b | 59.88 | 43.40 | 41.70 | 34.80 | 23.18 |
| Llama-2-13b-chat | 61.17 | 43.29 | 39.97 | 35.50 | 23.74 |
| Polylm-13b-chat | 32.23 | 29.26 | 29.01 | 25.36 | 18.08 |
| Qwen-PolyLM-7b-chat | 53.65 | 61.58 | 39.26 | 33.69 | 29.02 |
| SeaLLM-13b-chat | 63.53 | 46.31 | 49.25 | 40.61 | 36.30 |
MMLU - Preserving English-based knowledge
On the 5-shot MMLU, our SeaLLM models not only preserve but also slightly outperform 13B LLama-2 and Llama-2-chat, despite the fact that optimizing for this English and Chinese dominant test set is not part of our goal.
| MMLU (Acc) | STEM | Humanities | Social | Others | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-2-13b | 44.1 | 52.8 | 62.6 | 61.1 | 54.8 |
| Llama-2-13b-chat | 43.7 | 49.3 | 62.6 | 60.1 | 53.5 |
| SeaLLM-13b-chat | 43.4 | 53.0 | 63.3 | 61.4 | 55.1 |
NLP tasks
We also test our models on many different NLP tasks.
Reading Comprehension (XQUAD & IndoQA)
XQUAD is a popular multilingual variant of SQUAD benchmark, which evaluates models on reading comprehension ability. As XQUAD does not support Indonesian, we substitute it with IndoQA, which was created for the same purpose.
As shown in the table below, the 1-shot reading comprehension performance is significantly better than Llama-2 for the SEA languages, while preserving the high performance in existing languages (En & Zh).
| XQUAD/IndoQA (F1) | En | Zh | Vi | Id | Th | ALL | SEA-lang |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-2-13b | 83.22 | 78.02 | 71.03 | 59.31 | 30.73 | 64.46 | 59.77 |
| Llama-2-13b-chat | 80.46 | 70.54 | 62.87 | 63.05 | 25.73 | 60.93 | 51.21 |
| SeaLLM-13b-chat | 75.23 | 75.65 | 72.86 | 64.37 | 61.37 | 69.90 | 66.20 |
Translation
For translation tasks, we evaluate our models with the FloRes-200 using chrF++ scores in 4-shot settings.
Similarly observed, our SeaLLM models outperform Llama-2 significantly in the new languages.
| FloRes-200 (chrF++) | En-Zh | En-Vi | En-Id | En-Th | En->X | Zh-En | Vi-En | Id-En | Th-En | X->En |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-2-13b | 24.36 | 53.20 | 60.41 | 22.16 | 45.26 | 53.20 | 59.10 | 63.42 | 38.48 | 53.55 |
| Llama-2-13b-chat | 19.58 | 51.70 | 57.14 | 21.18 | 37.40 | 52.27 | 54.32 | 60.55 | 30.18 | 49.33 |
| SeaLLM-13b-chat | 23.12 | 59.00 | 66.16 | 43.33 | 47.91 | 53.67 | 60.93 | 65.66 | 57.39 | 59.42 |
Our models are also performing competitively with ChatGPT for translation between SEA languages without English pivoting.
| FloRes-200 (chrF++) | Vi-Id | Id-Vi | Vi-Th | Th-Vi | Id-Th | Th-Id |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | 56.75 | 54.17 | 40.48 | 46.54 | 40.59 | 51.87 |
| SeaLLM-13b-chat | 53.77 | 53.60 | 30.74 | 49.09 | 36.96 | 48.73 |
Summarization
Lastly, in 2-shot XL-sum summarization tasks, our models also achieve a better performance, with substantial gains in Thai.
| XL-Sum (rouge-L) | En | Zh | Vi | Id | Th |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama-2-13b | 32.57 | 34.37 | 18.61 | 25.14 | 16.91 |
| Llama-2-13b-chat | 25.11 | 31.13 | 18.29 | 22.45 | 17.51 |
| SeaLLM-13b-chat | 26.88 | 33.39 | 19.39 | 25.96 | 21.37 |
Acknowledge our linguists
Citation
If you find our project useful, hope you can star our repo and cite our work as follows:
@article{damonlpsg2023seallm,
author = {Xuan-Phi Nguyen*, Wenxuan Zhang*, Xin Li*, Mahani Aljunied*, Qingyu Tan, Liying Cheng, Guanzheng Chen, Yue Deng, Sen Yang, Chaoqun Liu, Hang Zhang, Lidong Bing},
title = {SeaLLMs - Large Language Models for Southeast Asia},
year = 2023,
}