Introducing BERTopic Integration with the Hugging Face Hub
We are thrilled to announce a significant update to the BERTopic Python library, expanding its capabilities and further streamlining the workflow for topic modelling enthusiasts and practitioners. BERTopic now supports pushing and pulling trained topic models directly to and from the Hugging Face Hub. This new integration opens up exciting possibilities for leveraging the power of BERTopic in production use cases with ease.
What is Topic Modelling?
Topic modelling is a method that can help uncover hidden themes or "topics" within a group of documents. By analyzing the words in the documents, we can find patterns and connections that reveal these underlying topics. For example, a document about machine learning is more likely to use words like "gradient" and "embedding" compared to a document about baking bread.
Each document usually covers multiple topics in different proportions. By examining the word statistics, we can identify clusters of related words that represent these topics. This allows us to analyze a set of documents and determine the topics they discuss, as well as the balance of topics within each document. More recently, new approaches to topic modelling have moved beyond using words to using more rich representations such as those offered through Transformer based models.
What is BERTopic?
BERTopic is a state-of-the-art Python library that simplifies the topic modelling process using various embedding techniques and c-TF-IDF to create dense clusters allowing for easily interpretable topics whilst keeping important words in the topic descriptions.
An overview of the BERTopic library
Whilst BERTopic is easy to get started with, it supports a range of advanced approaches to topic modelling including guided, supervised, semi-supervised and manual topic modelling. More recently BERTopic has added support for multi-modal topic models. BERTopic also have a rich set of tools for producing visualizations.
BERTopic provides a powerful tool for users to uncover significant topics within text collections, thereby gaining valuable insights. With BERTopic, users can analyze customer reviews, explore research papers, or categorize news articles with ease, making it an essential tool for anyone looking to extract meaningful information from their text data.
BERTopic Model Management with the Hugging Face Hub
With the latest integration, BERTopic users can seamlessly push and pull their trained topic models to and from the Hugging Face Hub. This integration marks a significant milestone in simplifying the deployment and management of BERTopic models across different environments.
The process of training and pushing a BERTopic model to the Hub can be done in a few lines
from bertopic import BERTopic
topic_model = BERTopic("english")
topics, probs = topic_model.fit_transform(docs)
topic_model.push_to_hf_hub('davanstrien/transformers_issues_topics')
You can then load this model in two lines and use it to predict against new data.
from bertopic import BERTopic
topic_model = BERTopic.load("davanstrien/transformers_issues_topics")
By leveraging the power of the Hugging Face Hub, BERTopic users can effortlessly share, version, and collaborate on their topic models. The Hub acts as a central repository, allowing users to store and organize their models, making it easier to deploy models in production, share them with colleagues, or even showcase them to the broader NLP community.
You can use the libraries filter on the hub to find BERTopic models.
Once you have found a BERTopic model you are interested in you can use the Hub inference widget to try out the model and see if it might be a good fit for your use case.
Once you have a trained topic model, you can push it to the Hugging Face Hub in one line. Pushing your model to the Hub will automatically create an initial model card for your model, including an overview of the topics created. Below you can see an example of the topics resulting from a model trained on ArXiv data.
Click here for an overview of all topics.
| Topic ID | Topic Keywords | Topic Frequency | Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | language - models - model - data - based | 20 | -1_language_models_model_data |
| 0 | dialogue - dialog - response - responses - intent | 14247 | 0_dialogue_dialog_response_responses |
| 1 | speech - asr - speech recognition - recognition - end | 1833 | 1_speech_asr_speech recognition_recognition |
| 2 | tuning - tasks - prompt - models - language | 1369 | 2_tuning_tasks_prompt_models |
| 3 | summarization - summaries - summary - abstractive - document | 1109 | 3_summarization_summaries_summary_abstractive |
| 4 | question - answer - qa - answering - question answering | 893 | 4_question_answer_qa_answering |
| 5 | sentiment - sentiment analysis - aspect - analysis - opinion | 837 | 5_sentiment_sentiment analysis_aspect_analysis |
| 6 | clinical - medical - biomedical - notes - patient | 691 | 6_clinical_medical_biomedical_notes |
| 7 | translation - nmt - machine translation - neural machine - neural machine translation | 586 | 7_translation_nmt_machine translation_neural machine |
| 8 | generation - text generation - text - language generation - nlg | 558 | 8_generation_text generation_text_language generation |
| 9 | hate - hate speech - offensive - speech - detection | 484 | 9_hate_hate speech_offensive_speech |
| 10 | news - fake - fake news - stance - fact | 455 | 10_news_fake_fake news_stance |
| 11 | relation - relation extraction - extraction - relations - entity | 450 | 11_relation_relation extraction_extraction_relations |
| 12 | ner - named - named entity - entity - named entity recognition | 376 | 12_ner_named_named entity_entity |
| 13 | parsing - parser - dependency - treebank - parsers | 370 | 13_parsing_parser_dependency_treebank |
| 14 | event - temporal - events - event extraction - extraction | 314 | 14_event_temporal_events_event extraction |
| 15 | emotion - emotions - multimodal - emotion recognition - emotional | 300 | 15_emotion_emotions_multimodal_emotion recognition |
| 16 | word - embeddings - word embeddings - embedding - words | 292 | 16_word_embeddings_word embeddings_embedding |
| 17 | explanations - explanation - rationales - rationale - interpretability | 212 | 17_explanations_explanation_rationales_rationale |
| 18 | morphological - arabic - morphology - languages - inflection | 204 | 18_morphological_arabic_morphology_languages |
| 19 | topic - topics - topic models - lda - topic modeling | 200 | 19_topic_topics_topic models_lda |
| 20 | bias - gender - biases - gender bias - debiasing | 195 | 20_bias_gender_biases_gender bias |
| 21 | law - frequency - zipf - words - length | 185 | 21_law_frequency_zipf_words |
| 22 | legal - court - law - legal domain - case | 182 | 22_legal_court_law_legal domain |
| 23 | adversarial - attacks - attack - adversarial examples - robustness | 181 | 23_adversarial_attacks_attack_adversarial examples |
| 24 | commonsense - commonsense knowledge - reasoning - knowledge - commonsense reasoning | 180 | 24_commonsense_commonsense knowledge_reasoning_knowledge |
| 25 | quantum - semantics - calculus - compositional - meaning | 171 | 25_quantum_semantics_calculus_compositional |
| 26 | correction - error - error correction - grammatical - grammatical error | 161 | 26_correction_error_error correction_grammatical |
| 27 | argument - arguments - argumentation - argumentative - mining | 160 | 27_argument_arguments_argumentation_argumentative |
| 28 | sarcasm - humor - sarcastic - detection - humorous | 157 | 28_sarcasm_humor_sarcastic_detection |
| 29 | coreference - resolution - coreference resolution - mentions - mention | 156 | 29_coreference_resolution_coreference resolution_mentions |
| 30 | sense - word sense - wsd - word - disambiguation | 153 | 30_sense_word sense_wsd_word |
| 31 | knowledge - knowledge graph - graph - link prediction - entities | 149 | 31_knowledge_knowledge graph_graph_link prediction |
| 32 | parsing - semantic parsing - amr - semantic - parser | 146 | 32_parsing_semantic parsing_amr_semantic |
| 33 | cross lingual - lingual - cross - transfer - languages | 146 | 33_cross lingual_lingual_cross_transfer |
| 34 | mt - translation - qe - quality - machine translation | 139 | 34_mt_translation_qe_quality |
| 35 | sql - text sql - queries - spider - schema | 138 | 35_sql_text sql_queries_spider |
| 36 | classification - text classification - label - text - labels | 136 | 36_classification_text classification_label_text |
| 37 | style - style transfer - transfer - text style - text style transfer | 136 | 37_style_style transfer_transfer_text style |
| 38 | question - question generation - questions - answer - generation | 129 | 38_question_question generation_questions_answer |
| 39 | authorship - authorship attribution - attribution - author - authors | 127 | 39_authorship_authorship attribution_attribution_author |
| 40 | sentence - sentence embeddings - similarity - sts - sentence embedding | 123 | 40_sentence_sentence embeddings_similarity_sts |
| 41 | code - identification - switching - cs - code switching | 121 | 41_code_identification_switching_cs |
| 42 | story - stories - story generation - generation - storytelling | 118 | 42_story_stories_story generation_generation |
| 43 | discourse - discourse relation - discourse relations - rst - discourse parsing | 117 | 43_discourse_discourse relation_discourse relations_rst |
| 44 | code - programming - source code - code generation - programming languages | 117 | 44_code_programming_source code_code generation |
| 45 | paraphrase - paraphrases - paraphrase generation - paraphrasing - generation | 114 | 45_paraphrase_paraphrases_paraphrase generation_paraphrasing |
| 46 | agent - games - environment - instructions - agents | 111 | 46_agent_games_environment_instructions |
| 47 | covid - covid 19 - 19 - tweets - pandemic | 108 | 47_covid_covid 19_19_tweets |
| 48 | linking - entity linking - entity - el - entities | 107 | 48_linking_entity linking_entity_el |
| 49 | poetry - poems - lyrics - poem - music | 103 | 49_poetry_poems_lyrics_poem |
| 50 | image - captioning - captions - visual - caption | 100 | 50_image_captioning_captions_visual |
| 51 | nli - entailment - inference - natural language inference - language inference | 96 | 51_nli_entailment_inference_natural language inference |
| 52 | keyphrase - keyphrases - extraction - document - phrases | 95 | 52_keyphrase_keyphrases_extraction_document |
| 53 | simplification - text simplification - ts - sentence - simplified | 95 | 53_simplification_text simplification_ts_sentence |
| 54 | empathetic - emotion - emotional - empathy - emotions | 95 | 54_empathetic_emotion_emotional_empathy |
| 55 | depression - mental - health - mental health - social media | 93 | 55_depression_mental_health_mental health |
| 56 | segmentation - word segmentation - chinese - chinese word segmentation - chinese word | 93 | 56_segmentation_word segmentation_chinese_chinese word segmentation |
| 57 | citation - scientific - papers - citations - scholarly | 85 | 57_citation_scientific_papers_citations |
| 58 | agreement - syntactic - verb - grammatical - subject verb | 85 | 58_agreement_syntactic_verb_grammatical |
| 59 | metaphor - literal - figurative - metaphors - idiomatic | 83 | 59_metaphor_literal_figurative_metaphors |
| 60 | srl - semantic role - role labeling - semantic role labeling - role | 82 | 60_srl_semantic role_role labeling_semantic role labeling |
| 61 | privacy - private - federated - privacy preserving - federated learning | 82 | 61_privacy_private_federated_privacy preserving |
| 62 | change - semantic change - time - semantic - lexical semantic | 82 | 62_change_semantic change_time_semantic |
| 63 | bilingual - lingual - cross lingual - cross - embeddings | 80 | 63_bilingual_lingual_cross lingual_cross |
| 64 | political - media - news - bias - articles | 77 | 64_political_media_news_bias |
| 65 | medical - qa - question - questions - clinical | 75 | 65_medical_qa_question_questions |
| 66 | math - mathematical - math word - word problems - problems | 73 | 66_math_mathematical_math word_word problems |
| 67 | financial - stock - market - price - news | 69 | 67_financial_stock_market_price |
| 68 | table - tables - tabular - reasoning - qa | 69 | 68_table_tables_tabular_reasoning |
| 69 | readability - complexity - assessment - features - reading | 65 | 69_readability_complexity_assessment_features |
| 70 | layout - document - documents - document understanding - extraction | 64 | 70_layout_document_documents_document understanding |
| 71 | brain - cognitive - reading - syntactic - language | 62 | 71_brain_cognitive_reading_syntactic |
| 72 | sign - gloss - language - signed - language translation | 61 | 72_sign_gloss_language_signed |
| 73 | vqa - visual - visual question - visual question answering - question | 59 | 73_vqa_visual_visual question_visual question answering |
| 74 | biased - biases - spurious - nlp - debiasing | 57 | 74_biased_biases_spurious_nlp |
| 75 | visual - dialogue - multimodal - image - dialog | 55 | 75_visual_dialogue_multimodal_image |
| 76 | translation - machine translation - machine - smt - statistical | 54 | 76_translation_machine translation_machine_smt |
| 77 | multimodal - visual - image - translation - machine translation | 52 | 77_multimodal_visual_image_translation |
| 78 | geographic - location - geolocation - geo - locations | 51 | 78_geographic_location_geolocation_geo |
| 79 | reasoning - prompting - llms - chain thought - chain | 48 | 79_reasoning_prompting_llms_chain thought |
| 80 | essay - scoring - aes - essay scoring - essays | 45 | 80_essay_scoring_aes_essay scoring |
| 81 | crisis - disaster - traffic - tweets - disasters | 45 | 81_crisis_disaster_traffic_tweets |
| 82 | graph - text classification - text - gcn - classification | 44 | 82_graph_text classification_text_gcn |
| 83 | annotation - tools - linguistic - resources - xml | 43 | 83_annotation_tools_linguistic_resources |
| 84 | entity alignment - alignment - kgs - entity - ea | 43 | 84_entity alignment_alignment_kgs_entity |
| 85 | personality - traits - personality traits - evaluative - text | 42 | 85_personality_traits_personality traits_evaluative |
| 86 | ad - alzheimer - alzheimer disease - disease - speech | 40 | 86_ad_alzheimer_alzheimer disease_disease |
| 87 | taxonomy - hypernymy - taxonomies - hypernym - hypernyms | 39 | 87_taxonomy_hypernymy_taxonomies_hypernym |
| 88 | active learning - active - al - learning - uncertainty | 37 | 88_active learning_active_al_learning |
| 89 | reviews - summaries - summarization - review - opinion | 36 | 89_reviews_summaries_summarization_review |
| 90 | emoji - emojis - sentiment - message - anonymous | 35 | 90_emoji_emojis_sentiment_message |
| 91 | table - table text - tables - table text generation - text generation | 35 | 91_table_table text_tables_table text generation |
| 92 | domain - domain adaptation - adaptation - domains - source | 35 | 92_domain_domain adaptation_adaptation_domains |
| 93 | alignment - word alignment - parallel - pairs - alignments | 34 | 93_alignment_word alignment_parallel_pairs |
| 94 | indo - languages - indo european - names - family | 34 | 94_indo_languages_indo european_names |
| 95 | patent - claim - claim generation - chemical - technical | 32 | 95_patent_claim_claim generation_chemical |
| 96 | agents - emergent - communication - referential - games | 32 | 96_agents_emergent_communication_referential |
| 97 | graph - amr - graph text - graphs - text generation | 31 | 97_graph_amr_graph text_graphs |
| 98 | moral - ethical - norms - values - social | 29 | 98_moral_ethical_norms_values |
| 99 | acronym - acronyms - abbreviations - abbreviation - disambiguation | 27 | 99_acronym_acronyms_abbreviations_abbreviation |
| 100 | typing - entity typing - entity - type - types | 27 | 100_typing_entity typing_entity_type |
| 101 | coherence - discourse - discourse coherence - coherence modeling - text | 26 | 101_coherence_discourse_discourse coherence_coherence modeling |
| 102 | pos - taggers - tagging - tagger - pos tagging | 25 | 102_pos_taggers_tagging_tagger |
| 103 | drug - social - social media - media - health | 25 | 103_drug_social_social media_media |
| 104 | gender - translation - bias - gender bias - mt | 24 | 104_gender_translation_bias_gender bias |
| 105 | job - resume - skills - skill - soft | 21 | 105_job_resume_skills_skill |
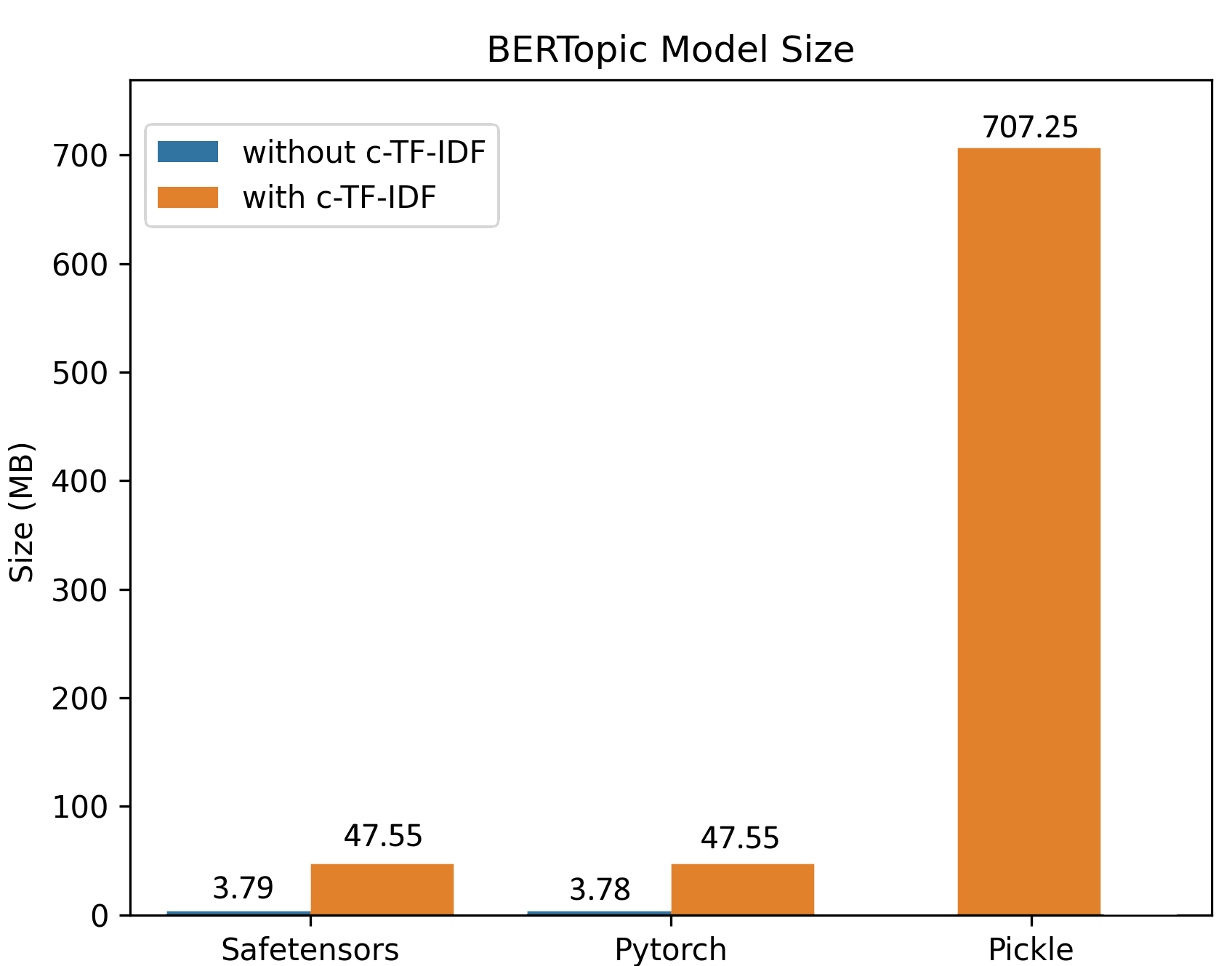
Due to the improved saving procedure, training on large datasets generates small model sizes. In the example below, a BERTopic model was trained on 100,000 documents, resulting in a ~50MB model keeping all of the original’s model functionality. For inference, the model can be further reduced to only ~3MB!
 The benefits of this integration are particularly notable for production use cases. Users can now effortlessly deploy BERTopic models into their existing applications or systems, ensuring seamless integration within their data pipelines. This streamlined workflow enables faster iteration and efficient model updates and ensures consistency across different environments.
The benefits of this integration are particularly notable for production use cases. Users can now effortlessly deploy BERTopic models into their existing applications or systems, ensuring seamless integration within their data pipelines. This streamlined workflow enables faster iteration and efficient model updates and ensures consistency across different environments.
safetensors: Ensuring Secure Model Management
In addition to the Hugging Face Hub integration, BERTopic now supports serialization using the safetensors library. Safetensors is a new simple format for storing tensors safely (instead of pickle), which is still fast (zero-copy). We’re excited to see more and more libraries leveraging safetensors for safe serialization. You can read more about a recent audit of the library in this blog post.
An example of using BERTopic to explore RLHF datasets
To illustrate some of the power of BERTopic let's look at an example of how it can be used to monitor changes in topics in datasets used to train chat models.
The last year has seen several datasets for Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback released. One of these datasets is the OpenAssistant Conversations dataset. This dataset was produced via a worldwide crowd-sourcing effort involving over 13,500 volunteers. Whilst this dataset already has some scores for toxicity, quality, humour etc., we may want to get a better understanding of what types of conversations are represented in this dataset.
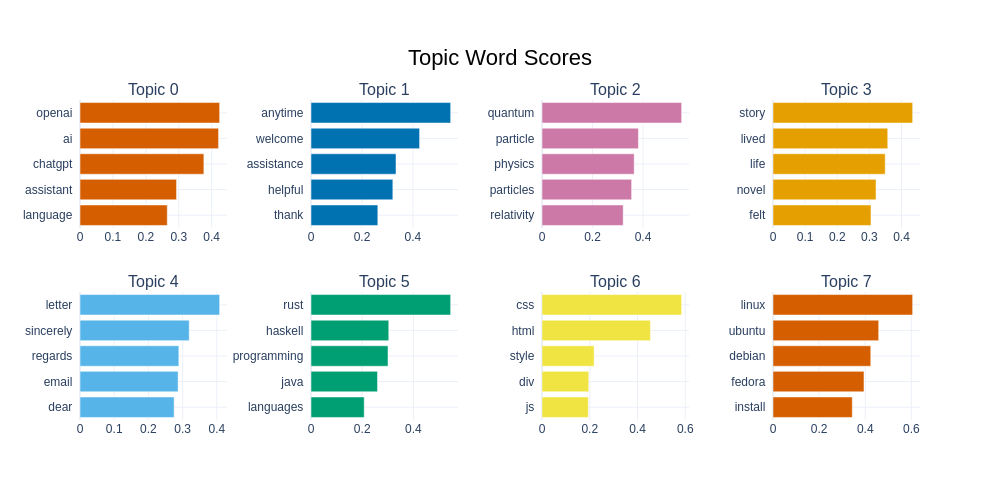
BERTopic offers one way of getting a better understanding of the topics in this dataset. In this case, we train a model on the English assistant responses part of the datasets. Resulting in a topic model with 75 topics.
BERTopic gives us various ways of visualizing a dataset. We can see the top 8 topics and their associated words below. We can see that the second most frequent topic consists mainly of ‘response words’, which we often see frequently from chat models, i.e. responses which aim to be ‘polite’ and ‘helpful’. We can also see a large number of topics related to programming or computing topics as well as physics, recipes and pets.
databricks/databricks-dolly-15k is another dataset that can be used to train an RLHF model. The approach taken to creating this dataset was quite different from the OpenAssistant Conversations dataset since it was created by employees of Databricks instead of being crowd sourced via volunteers. Perhaps we can use our trained BERTopic model to compare the topics across these two datasets?
The new BERTopic Hub integrations mean we can load this trained model and apply it to new examples.
topic_model = BERTopic.load("davanstrien/chat_topics")
We can predict on a single example text:
example = "Stalemate is a drawn position. It doesn't matter who has captured more pieces or is in a winning position"
topic, prob = topic_model.transform(example)
We can get more information about the predicted topic
topic_model.get_topic_info(topic)
| Count | Name | Representation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 240 | 22_chess_chessboard_practice_strategy | ['chess', 'chessboard', 'practice', 'strategy', 'learn', 'pawn', 'board', 'pawns', 'play', 'decks'] |
We can see here the topics predicted seem to make sense. We may want to extend this to compare the topics predicted for the whole dataset.
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("databricks/databricks-dolly-15k")
dolly_docs = dataset['train']['response']
dolly_topics, dolly_probs = topic_model.transform(dolly_docs)
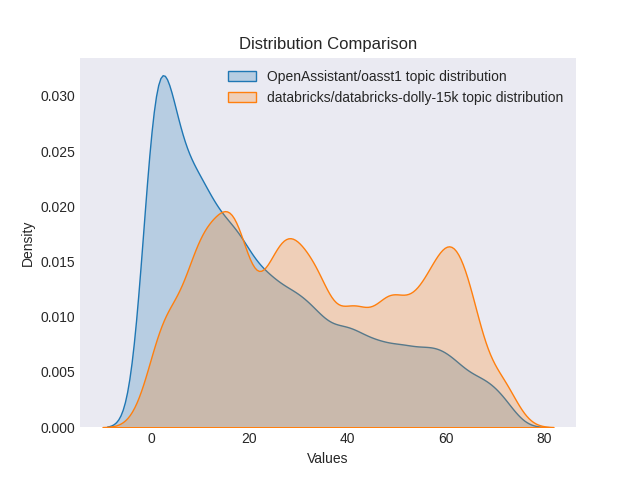
We can then compare the distribution of topics across both datasets. We can see here that there seems to be a broader distribution across topics in the dolly dataset according to our BERTopic model. This might be a result of the different approaches to creating both datasets (we likely want to retrain a BERTopic across both datasets to ensure we are not missing topics to confirm this).
Comparison of the distribution of topics between the two datasets
We can potentially use topic models in a production setting to monitor whether topics drift to far from an expected distribution. This can serve as a signal that there has been drift between your original training data and the types of conversations you are seeing in production. You may also decide to use a topic modelling as you are collecting training data to ensure you are getting examples for topics you may particularly care about.
Get Started with BERTopic and Hugging Face Hub
You can visit the official documentation for a quick start guide to get help using BERTopic.
You can find a starter Colab notebook here that shows how you can train a BERTopic model and push it to the Hub.
Some examples of BERTopic models already on the hub:
- MaartenGr/BERTopic_ArXiv: a model trained on ~30000 ArXiv Computation and Language articles (cs.CL) after 1991.
- MaartenGr/BERTopic_Wikipedia: a model trained on 1000000 English Wikipedia pages.
- davanstrien/imdb_bertopic: a model trained on the unsupervised split of the IMDB dataset
You can find a full overview of BERTopic models on the hub using the libraries filter
We invite you to explore the possibilities of this new integration and share your trained models on the hub!